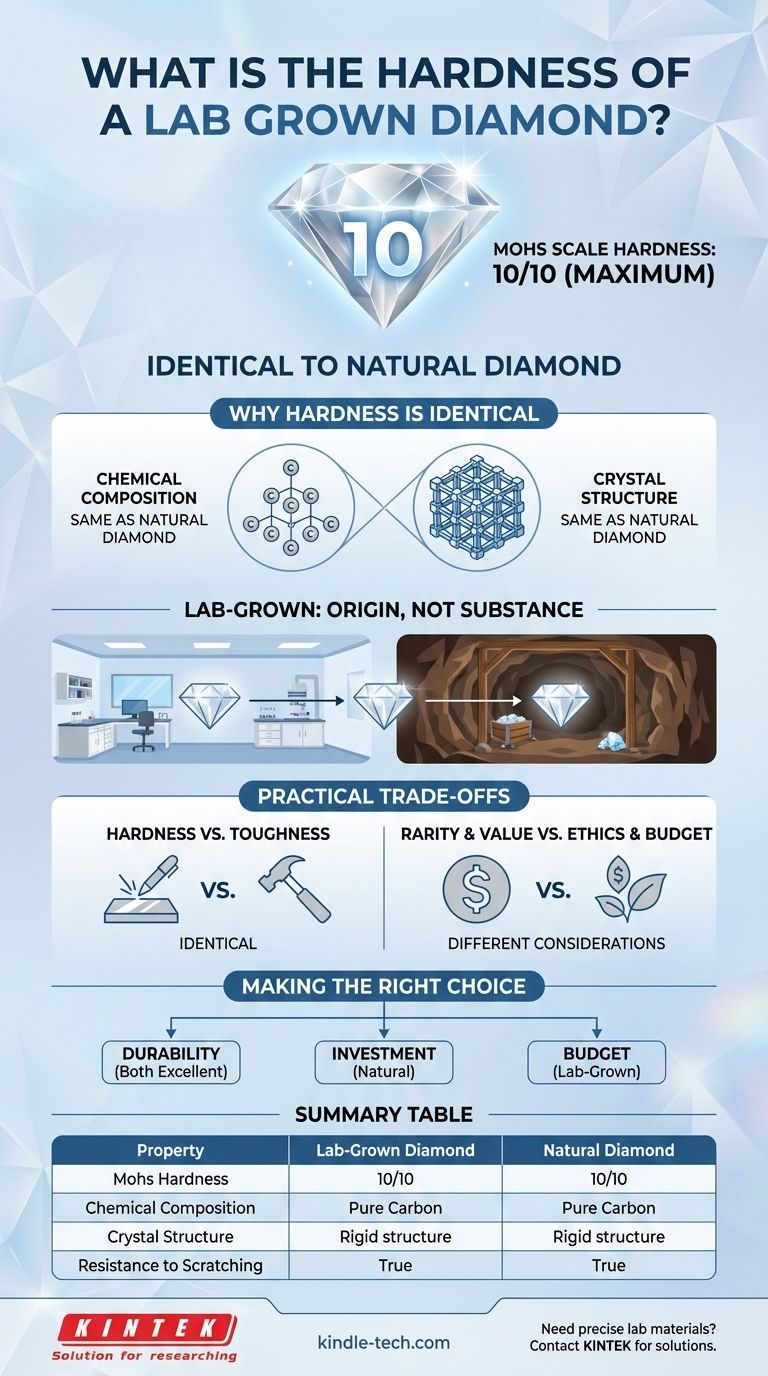
A lab-grown diamond is physically and chemically identical to a natural diamond, and therefore shares the exact same hardness. Both natural and lab-grown diamonds score a 10 on the Mohs scale of hardness, the highest possible rating for any mineral. This means a lab-grown diamond is just as durable and resistant to scratching as its earth-mined counterpart.
The core principle to understand is that "lab-grown" describes a diamond's origin, not its substance. Because lab-grown diamonds are composed of pure carbon in the same rigid crystal structure as natural diamonds, they possess all the same physical properties, including maximum hardness.

Why Hardness is Identical: A Matter of Structure
The hardness of any crystalline material is not a matter of opinion or quality, but a direct result of its atomic composition and structure. Lab-grown diamonds are identical to natural ones in these two fundamental areas.
The Same Chemical Composition
Both lab-grown and natural diamonds are made of the same single element: pure carbon. The manufacturing processes, such as High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), are specifically designed to crystallize carbon atoms, and nothing else.
The Same Crystal Structure
More importantly, the carbon atoms in a lab-grown diamond are bonded together in the exact same way as in a natural diamond. They form a rigid, interlocking crystal lattice known as an isometric system. This incredibly strong atomic bond is what gives a diamond its unparalleled hardness.
Because the material and the structure are identical, the physical property of hardness must also be identical.
"Lab-Grown" Refers to Origin, Not Substance
The primary confusion about lab-grown diamonds stems from the misconception that they are "fakes" or imitations like cubic zirconia. This is incorrect. Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds.
Replicating a Natural Process
The laboratory environment simply accelerates a natural process, recreating the intense heat and pressure that forms diamonds deep within the Earth. The result is a stone that is visibly and physically indistinguishable from a mined diamond.
Confirmation by Experts
Distinguishing a high-quality lab-grown diamond from a natural one is impossible for a consumer or even a trained jeweler without highly specialized equipment. This confirms that on a material level, they are the same.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
While the hardness is identical, the choice between a lab-grown and a natural diamond involves other important considerations. The differences are not in physical performance, but in value and ethics.
Hardness vs. Toughness
It's crucial to understand that hardness is not the same as toughness. Hardness refers to the resistance to scratching, which is where diamonds excel. Toughness is the resistance to chipping or breaking from impact.
While diamonds are the hardest mineral, they can still chip if struck at the right angle. This is true for both lab-grown and natural diamonds. Their toughness is identical.
The Real Difference: Rarity and Resale Value
The primary trade-off is economic. Natural diamonds are a finite resource mined from the earth, and their rarity is a major component of their long-term value. Lab-grown diamonds can be created on demand, which generally gives them a lower initial price but also less potential for long-term value appreciation.
Ethical and Environmental Factors
Many choose lab-grown diamonds to avoid the potential environmental and social concerns associated with diamond mining. This provides the same physical beauty and durability without the footprint of a mined stone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on your priorities, not on any perceived difference in quality or durability.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for daily wear: Both lab-grown and natural diamonds are equally excellent choices, as their hardness and toughness are identical.
- If your primary focus is long-term investment and resale value: Natural diamonds are generally considered the superior choice due to their inherent rarity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: Lab-grown diamonds offer the same physical properties as natural diamonds at a significantly lower price point.
Ultimately, the choice between a lab-grown and a natural diamond is a matter of personal values, not a compromise on hardness or quality.
Summary Table:
| Property | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 10 | 10 |
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Isometric System | Isometric System |
| Resistance to Scratching | Maximum | Maximum |
Need precise, durable materials for your laboratory? The science is clear: lab-grown diamonds offer the same supreme hardness as their natural counterparts. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your research and material testing. Whether your work involves advanced materials science or quality control, our solutions are designed for accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your lab for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- Are CVD diamonds synthetic? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- How plasma is used in diamond coating films? Unlock the Power of MPCVD for Superior Coatings
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- Can a jeweler distinguish a lab grown diamond? The Truth About Identifying Diamond Origin
- What are the advantages of diamond cutting tool material? Achieve Superior Precision and Productivity
- What advantages does a Multimode Cavity (MCC) reactor offer for large-area diamond films? Scale Beyond 4-Inch Wafers
- What is MPCVD? Unlock Atom-by-Atom Precision for High-Purity Materials
- What are the applications of microwave plasma? From Diamond Synthesis to Semiconductor Fabrication












