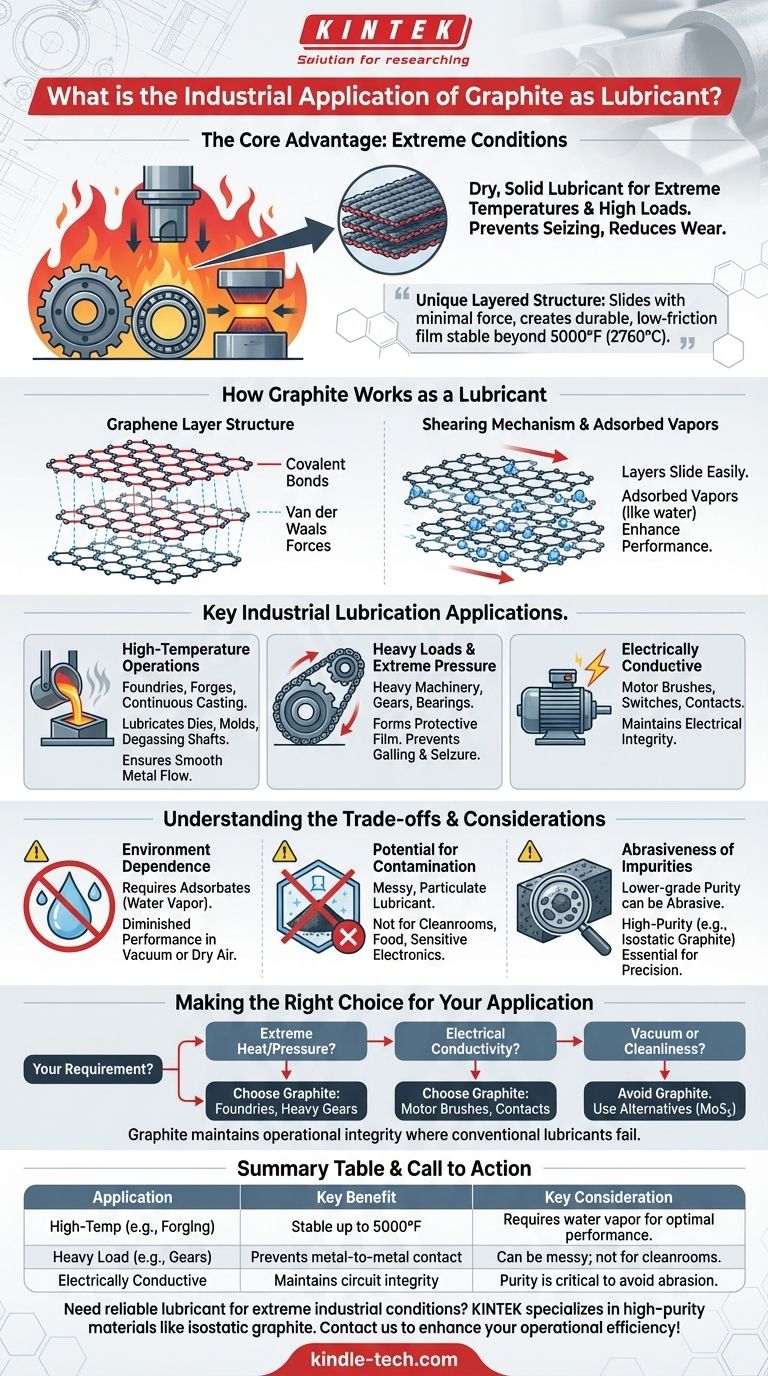
In industrial settings, graphite is used as a dry, solid lubricant in applications involving extreme temperatures and high loads where conventional oils and greases would decompose or fail. It is applied to heavy machinery components like gears, bearings, and die molds in industries such as metalworking, forging, and continuous casting to prevent seizing and reduce wear.
The core reason graphite excels as an industrial lubricant is its unique, layered crystal structure. These layers slide over one another with minimal force, creating a durable, low-friction film that remains stable even at temperatures exceeding 5000°F (2760°C).

How Graphite Works as a Lubricant
The Graphene Layer Structure
Graphite consists of stacked layers of carbon atoms, known as graphene sheets. Within each sheet, the carbon atoms are held together by extremely strong covalent bonds.
However, the forces holding these sheets together are very weak van der Waals forces.
The Shearing Mechanism
This structural arrangement is the key to its lubricating property. When a shear force is applied, such as between two moving machine parts, the weak bonds between the layers break easily.
This allows the graphene sheets to slide over one another with very little resistance, much like a deck of cards, creating a highly effective lubricating film.
The Critical Role of Adsorbed Vapors
For graphite to achieve its lowest friction, it relies on the presence of adsorbed vapors, most commonly water vapor from the air.
These molecules get between the graphite layers and further weaken the bonds, making it even easier for the layers to shear and slide. This is why its performance can degrade in a vacuum or in extremely dry environments.
Key Industrial Lubrication Applications
High-Temperature Operations
Graphite's most significant advantage is its thermal stability. It does not burn, melt, or decompose at the operating temperatures of many industrial processes.
It is used extensively in foundries and forges for lubricating dies, molds, and degassing shafts. In continuous casting, it ensures the smooth flow of molten metal without sticking.
Heavy Loads and Extreme Pressure
In machinery with large gears, chains, and bearings, graphite can be applied as a dry powder or as an additive in greases.
It forms a protective film that can withstand immense pressure, preventing direct metal-to-metal contact, galling, and seizure.
Electrically Conductive Lubrication
Unlike most lubricants, graphite is an excellent electrical conductor.
This unique property makes it the ideal lubricant for components that must maintain an electrical circuit, such as motor brushes, switches, and electrical contacts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Dependence on Environment
As noted, graphite's effectiveness is tied to the presence of adsorbates like water vapor. In high-altitude or vacuum applications, its lubricating ability diminishes significantly, and it can even become abrasive.
Potential for Contamination
As a solid, particulate lubricant, graphite can be messy. It is not suitable for cleanroom environments, food processing, or sensitive electronics where particulate contamination is a critical concern.
Abrasiveness of Impurities
The purity of the graphite is crucial. Lower-grade graphite can contain abrasive impurities like silica, which can cause wear and damage to precision components. High-purity grades, such as isostatic graphite, are required for advanced and critical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right lubricant is a critical engineering decision. The unique properties of graphite make it an exceptional problem-solver for specific, challenging environments.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat or pressure: Graphite is often the only viable option for lubricating components in forges, foundries, and heavy-load gear systems.
- If your application requires electrical conductivity: Graphite is the standard choice for lubricating moving electrical parts like commutators and contacts.
- If you operate in a vacuum or require extreme cleanliness: You should avoid graphite and explore alternatives like Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS₂) or other dry-film lubricants.
Ultimately, graphite's value lies in its ability to maintain operational integrity in environments where conventional lubricants simply cannot survive.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Operations (e.g., forging, casting) | Stable up to 5000°F (2760°C) | Requires water vapor for optimal performance |
| Heavy Load & Extreme Pressure (e.g., gears, bearings) | Prevents metal-to-metal contact, galling, and seizure | Can be messy; not suitable for cleanrooms |
| Electrically Conductive Lubrication (e.g., motor brushes) | Maintains circuit integrity while reducing friction | Purity is critical to avoid abrasive impurities |
Need a reliable lubricant for extreme industrial conditions? Graphite's ability to withstand intense heat and pressure makes it a go-to solution for demanding applications in metalworking, forging, and electrical systems. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including advanced graphite materials like isostatic graphite, tailored for critical industrial needs. Let our experts help you select the right lubricant for your machinery—contact us today to enhance your operational integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is the purpose of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Purity and Performance
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What environmental conditions does a vacuum tube furnace provide for copper sintering? Ensure High-Purity Results


















