In an industrial context, a sieve is a fundamental tool used for the mechanical separation and classification of materials based on particle size. While laboratory sieves are used for small-scale analysis, industrial sieves—often called screeners or separators—are engineered to process large volumes of material continuously for quality control, purification, and process optimization.
The core purpose of industrial sieving extends beyond simple sorting; it is a critical process for ensuring product consistency, guaranteeing safety and purity, and protecting downstream manufacturing equipment from damage.

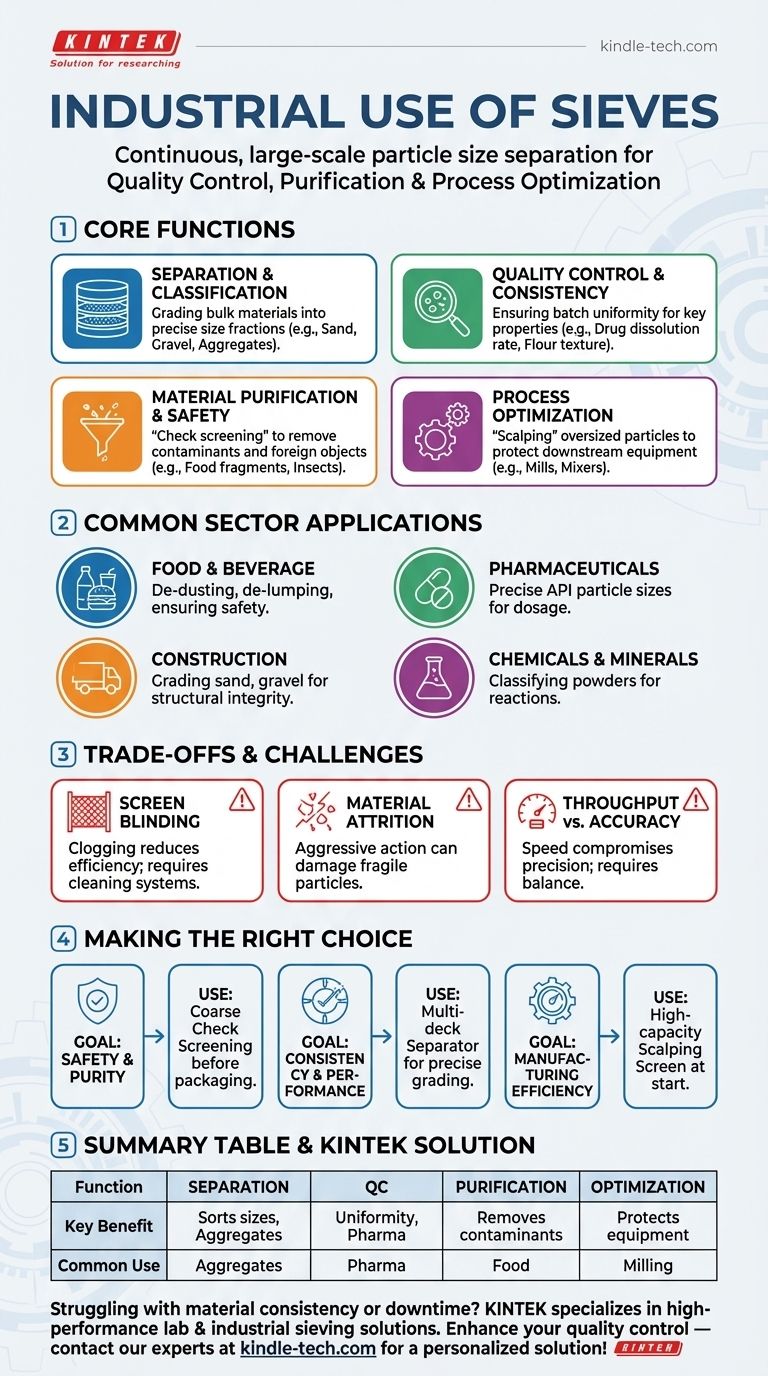
The Core Functions of Industrial Sieving
Industrial sieving accomplishes several essential tasks that are vital to manufacturing across numerous sectors. Each function addresses a specific need for material quality and process efficiency.
Separation and Classification
The most basic function is separating a bulk material into two or more grades based on particle size. This is also known as grading or sizing.
For example, a stream of crushed rock can be passed over a series of screens with progressively smaller mesh openings to efficiently separate it into distinct grades of sand, gravel, and larger aggregates.
Quality Control and Consistency
Many products derive their key properties from the size of their constituent particles. Sieving ensures that every batch meets a precise particle size distribution specification.
In pharmaceuticals, the dissolution rate of a pill is directly controlled by the particle size of its active ingredients. In food production, the texture of flour or sugar is determined by its particle size.
Material Purification and Safety
Sieving is a highly effective method for removing contaminants or foreign objects from a product stream. This is often referred to as "check screening" or "safety screening."
This process is critical for removing things like packaging fragments, insects, or oversized clumps from food ingredients like flour and spices, ensuring the final product is safe for consumption.
Process Optimization
Sieving is also used to prepare materials for subsequent manufacturing steps. Removing oversized particles can prevent blockages and damage to sensitive downstream equipment like mills, mixers, and extruders.
This "scalping" process protects capital equipment, reduces downtime, and ensures the entire production line runs smoothly and efficiently.
Common Industrial Applications by Sector
The principles of sieving are applied differently to solve unique challenges in various industries.
Food and Beverage Industry
Sieves are essential for de-dusting powders, de-lumping ingredients like flour and sugar, and removing foreign contaminants to ensure food safety and product consistency.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The industry relies on sieving to achieve precise particle size distributions for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), which is critical for ensuring proper dosage and drug efficacy.
Construction and Aggregates
Sieving is used on a massive scale to grade sand, gravel, and crushed stone. These materials must meet strict size specifications to produce concrete and asphalt with the required structural integrity.
Chemical and Mineral Processing
Chemical producers use sieves to classify powders and granules, ensuring materials have the correct surface area for chemical reactions and meet final product specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, industrial sieving is not without its operational challenges. Understanding these limitations is key to implementing an effective process.
Screen Blinding and Clogging
This is the most common issue, where particles become lodged in the mesh openings, reducing the screen's efficiency and throughput. This often requires specialized de-blinding systems, such as ultrasonic vibrators or mechanical balls, to keep the screen clear.
Material Attrition
The mechanical action of some sieving equipment can be aggressive, potentially breaking down or damaging fragile particles. This is undesirable when the goal is to preserve the material's original shape and size.
Throughput vs. Accuracy
There is a fundamental trade-off between the speed of the process and the precision of the separation. A finer mesh provides a more accurate size cut but will process material much more slowly than a coarse mesh. A plant must balance its quality requirements against its production targets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific sieving strategy you employ should be directly aligned with your primary industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is product safety and purity: Utilize check screening with a relatively coarse mesh just before packaging to remove any foreign contaminants.
- If your primary focus is product consistency and performance: Implement a multi-deck separator to accurately grade material into multiple, distinct size fractions.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing efficiency: Use a high-capacity scalping screen at the beginning of your process to remove oversized particles and protect downstream equipment.
Ultimately, industrial sieving is a foundational technology that transforms raw, variable materials into the safe, consistent, and high-quality products that consumers and industries rely on every day.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Common Industry Use |
|---|---|---|
| Separation & Classification | Sorts materials into precise size grades | Aggregates, Minerals |
| Quality Control & Consistency | Ensures batch-to-batch uniformity | Pharmaceuticals, Food |
| Material Purification & Safety | Removes contaminants and foreign objects | Food Ingredients, Chemicals |
| Process Optimization | Protects downstream equipment from damage | Manufacturing, Milling |
Struggling with material consistency, contamination, or equipment downtime? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including industrial sieving solutions tailored to your laboratory's unique challenges. Our expertise helps you achieve precise particle size distribution, ensure product purity, and optimize your entire manufacturing process. Let's enhance your quality control — contact our experts today for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is a 325-mesh standard sieve used for gold recovery? Enhance Adsorption Precision with 0.044mm Particle Control
- What is the primary function of fine-mesh test sieves? Master Natural Mordenite Purification
- What is the purpose of using a 40-mesh sieve for kaolin catalyst carriers? Optimizing Uniformity and Activity
- Why is sieving with specific mesh sizes necessary for biomass pretreatment? Optimize Precision and Reagent Penetration
- Why is sieve analysis important in geotechnical engineering? Unlock Soil Behavior for Safer Construction
- What are the different methods of sieving? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material
- What is the application of sieving method in pharmacy? Ensure Drug Quality, Safety, and Efficacy
- Why must standard test sieves be used to screen silicon nitride ceramic powder? Ensure Uniformity and Strength



















