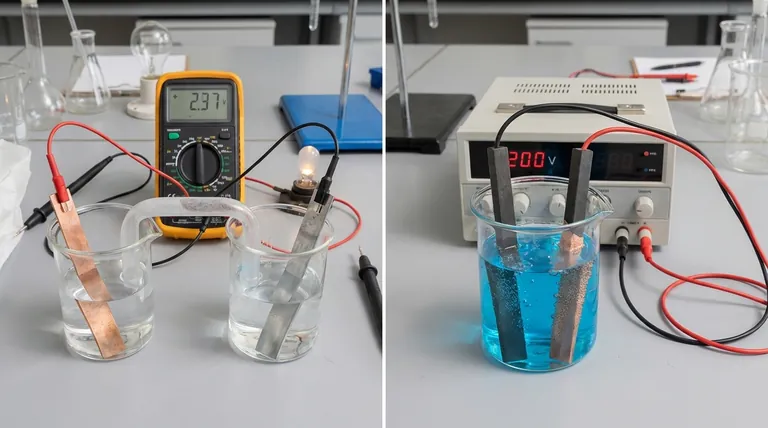
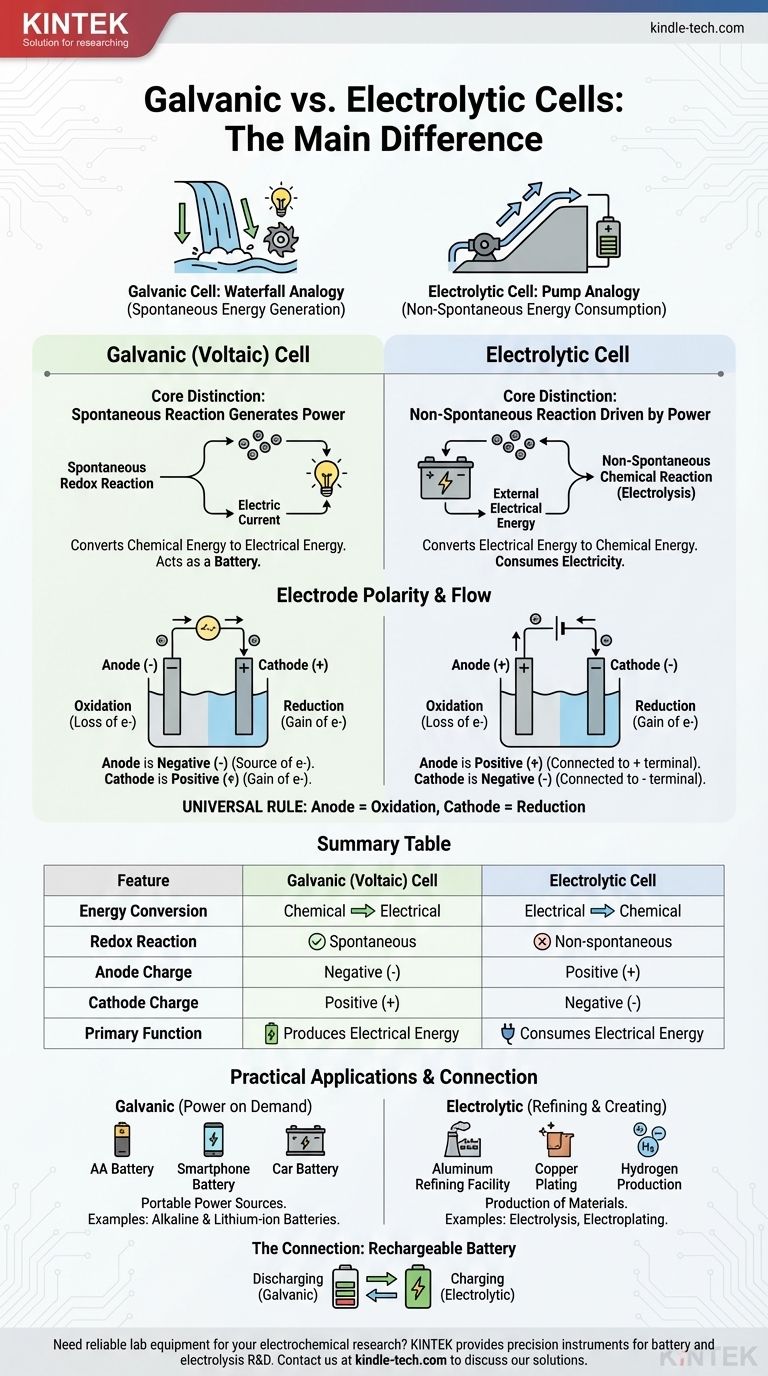
The fundamental difference lies in the direction of energy conversion and the nature of the chemical reaction. A galvanic cell spontaneously converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy, effectively acting as a battery. In contrast, an electrolytic cell uses an external source of electrical energy to force a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur.
Think of it as the difference between a waterfall generating power and a pump using power. A galvanic cell is like a waterfall, where a natural, spontaneous process (water flowing downhill) creates energy. An electrolytic cell is like a pump, using external energy to force a process that wouldn't happen on its own (pushing water uphill).
The Core Distinction: Spontaneity and Energy Flow
The behavior of these two cells is governed by one principle: whether the internal redox reaction happens on its own.
Galvanic Cells: Spontaneous Reactions that Generate Power
In a galvanic cell, also known as a voltaic cell, the chosen chemical reactants have a natural tendency to react with each other.
This spontaneous redox reaction releases energy. The cell is constructed to channel this energy not as heat, but as a directed flow of electrons—an electric current.
Essentially, a galvanic cell harnesses a naturally occurring chemical process to do electrical work. This is the principle behind all batteries.
Electrolytic Cells: Non-Spontaneous Reactions Driven by Power
In an electrolytic cell, the chemical reaction is non-spontaneous. The reactants will not interact on their own to produce the desired products.
To make the reaction happen, an external power source (like a battery or power supply) is connected to the cell. This external voltage provides the energy needed to force the electrons to move and drive the chemical change.
Electrolytic cells consume electricity to create a chemical product, a process known as electrolysis.
A Deeper Look at Electrode Polarity
While the terms "anode" and "cathode" are constant, their charge (polarity) is a common point of confusion because it is reversed between the two cell types. The key is to remember what drives the electron flow.
The Anode: Always the Site of Oxidation
In both cell types, the anode is defined as the electrode where oxidation (the loss of electrons) occurs. This definition is universal.
The Cathode: Always the Site of Reduction
Similarly, the cathode is always the electrode where reduction (the gain of electrons) takes place. This is the second universal rule.
The Critical Shift: Why Polarity Changes
The difference in polarity stems from whether the reaction is spontaneous or forced.
In a galvanic cell, the spontaneous oxidation at the anode releases electrons, creating a negative charge. The anode is the negative terminal because it is the source of electrons pushing out into the circuit.
In an electrolytic cell, an external power source is used. Its positive terminal pulls electrons away from the anode to force oxidation. Therefore, the anode is connected to the positive side and becomes the positive terminal.
| Feature | Galvanic (Voltaic) Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Chemical to Electrical | Electrical to Chemical |
| Redox Reaction | Spontaneous | Non-spontaneous |
| Anode Charge | Negative (-) | Positive (+) |
| Cathode Charge | Positive (+) | Negative (-) |
| Primary Function | Produces Electrical Energy | Consumes Electrical Energy |
Understanding the Practical Applications
This fundamental difference leads to distinct uses in technology and industry.
Galvanic Cells in Action: Power on Demand
Galvanic cells are designed to be portable sources of electrical power. Common examples include all types of batteries, from standard AA alkaline batteries to the lithium-ion battery in your phone.
Electrolytic Cells at Work: Refining and Creating
Electrolytic cells use power to produce materials. Key industrial processes rely on electrolysis, such as producing pure aluminum from its ore, refining copper, and splitting water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gas. Electroplating, where a thin layer of metal like silver or chromium is deposited onto another object, is another common application.
The Connection: How a Rechargeable Battery Works
A rechargeable battery is the perfect illustration of both cell types in one device.
When it is powering your device (discharging), it is operating as a galvanic cell. A spontaneous chemical reaction inside the battery produces an electric current.
When you plug it in to charge, the charger acts as an external power source. It applies a voltage that forces the non-spontaneous, reverse reaction to occur, replenishing the reactants. During charging, the battery is functioning as an electrolytic cell.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your goal determines which electrochemical framework you are using.
- If your primary focus is generating electricity from a chemical process: You are describing a galvanic (voltaic) cell.
- If your primary focus is using electricity to drive a specific chemical change: You are working with an electrolytic cell.
- If you are analyzing a rechargeable battery: Remember it operates as a galvanic cell during discharge and an electrolytic cell during recharge.
Ultimately, the spontaneity of the reaction and the resulting direction of energy flow are the defining characteristics that separate these two pillars of electrochemistry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Galvanic (Voltaic) Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Chemical to Electrical | Electrical to Chemical |
| Redox Reaction | Spontaneous | Non-spontaneous |
| Anode Charge | Negative (-) | Positive (+) |
| Cathode Charge | Positive (+) | Negative (-) |
| Primary Function | Produces Electrical Energy | Consumes Electrical Energy |
Need reliable lab equipment for your electrochemical research? Whether you're developing new battery technologies or optimizing electrolysis processes, KINTEK provides the precision instruments and consumables your laboratory requires. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can power your innovations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
People Also Ask
- What is the typical volume range of the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Choosing the Right Size for Your Lab
- What role does a three-electrode glass electrolytic cell play in IrSn/MMT catalysts? Optimize OER Screening Performance
- What are the requirements for SO2 Depolarized Electrolyzer membranes? Optimize Performance in Hybrid Sulfur Cycles
- What is an example of electrodeposition? From Gold Plating to Microchip Fabrication
- Why is a three-electrode electrochemical cell system necessary for Ni-Cr alloy corrosion kinetics? Expert Analysis
- Why must electrochemical cells have a condenser and water seal for Alloy 22 studies at 90°C? Ensure Data Integrity
- Why are flow cells and GDE used in CORR stability testing? Achieve Industrial-Grade Catalyst Performance
- What are the available volumes and dimensions for the all-quartz electrolytic cell? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab















