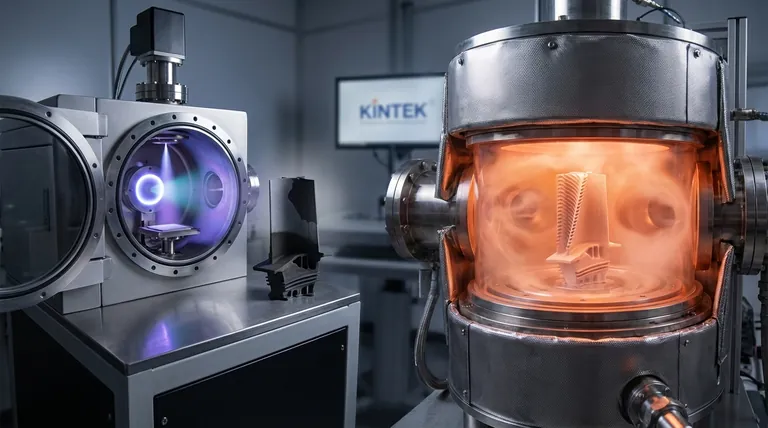
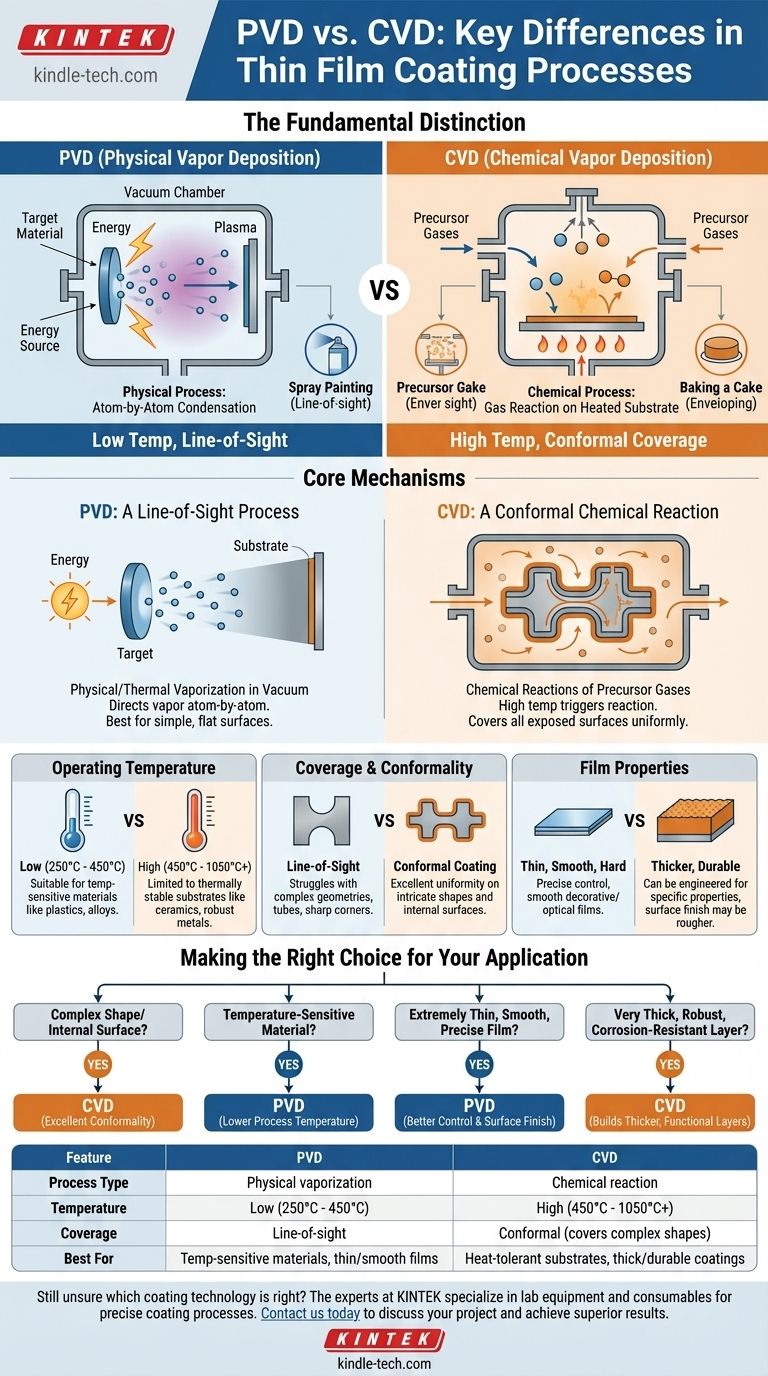
The fundamental distinction between PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) lies in the nature of the process used to create the thin film. PVD is a physical process where a solid material is vaporized in a vacuum and condenses onto a substrate, much like water vapor frosting a cold window. In contrast, CVD is a chemical process where precursor gases are introduced into a chamber and react on a heated substrate to form a solid layer.
Your choice between PVD and CVD is not just a process decision; it's a strategic one driven by your substrate's heat tolerance and the geometry of the part you need to coat. PVD is the go-to for lower-temperature, line-of-sight applications, while CVD excels at high-temperature, comprehensive coverage on complex shapes.

The Core Mechanisms: Physical vs. Chemical
To select the right technology, you must first understand how each one fundamentally operates. The "P" in PVD and "C" in CVD are the most important letters to consider.
How PVD Works: A Line-of-Sight Process
PVD is a mechanical or thermal vaporization process. A solid source material, known as a "target," is bombarded with energy inside a high-vacuum chamber.
This energy vaporizes the target material into a plasma of atoms or molecules. A voltage potential then directs this vapor toward the substrate, where it condenses atom-by-atom to form a thin, solid film.
Think of it like spray painting at an atomic level. The vapor travels in a straight line, meaning it only coats surfaces that are in its direct line of sight.
How CVD Works: A Conformal Chemical Reaction
CVD uses chemical reactions, not physical force. Volatile precursor gases are pumped into a reaction chamber containing the heated substrate.
The high temperature of the substrate provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction between the gases. This reaction causes a new, solid material to form and deposit onto the substrate's surface.
This process is more like baking a cake. The ingredients (gases) are mixed in the chamber, and the heat causes them to transform into a new solid (the coating) that covers every exposed surface, regardless of orientation.
Understanding the Key Differences
The divergence between a physical and chemical process creates significant practical differences in temperature, coating properties, and application suitability.
Operating Temperature
This is often the most critical deciding factor. PVD is a low-temperature process, typically operating between 250°C and 450°C. This makes it safe for materials that cannot withstand high heat, such as many steels, alloys, and plastics.
CVD is a high-temperature process, generally requiring temperatures from 450°C to over 1050°C. This intense heat limits its use to substrates that are thermally stable, like ceramics or certain robust metals.
Coverage and Conformality
PVD's line-of-sight nature means it struggles to coat complex geometries. The insides of tubes, shadowed areas, or sharp internal corners will receive little to no coating.
CVD excels at conformal coating. Because the gases envelop the entire substrate before reacting, the resulting film is highly uniform across even the most intricate surfaces and internal channels.
Film Properties
PVD typically produces thin, smooth, and extremely hard coatings. It offers precise control over film thickness and finish.
CVD can be used to create thicker coatings that are exceptionally durable and can be engineered for specific properties like corrosion resistance or electrical conductivity. However, the surface finish may be rougher than a PVD coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal technology is dictated by your project's specific constraints and goals. Base your decision on the material, the part's shape, and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex shape or internal surface: CVD is the superior choice due to its excellent conformality.
- If you must coat a temperature-sensitive material (like tempered steel, aluminum, or plastics): PVD is the necessary choice because of its lower process temperature.
- If your goal is an extremely thin, smooth, and precise decorative or optical film: PVD often provides better control and a smoother final surface.
- If you need a very thick, robust, or corrosion-resistant layer on a heat-tolerant substrate: CVD can build thicker, highly functional layers more effectively.
By understanding the trade-offs between a physical line-of-sight process and a high-temperature chemical reaction, you can confidently select the technology that aligns with your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical vaporization | Chemical reaction |
| Temperature | Low (250°C - 450°C) | High (450°C - 1050°C+) |
| Coverage | Line-of-sight | Conformal (covers complex shapes) |
| Best For | Temperature-sensitive materials, thin/smooth films | Heat-tolerant substrates, thick/durable coatings |
Still unsure which coating technology is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables for precise coating processes. We can help you select the ideal solution for your substrate and performance requirements. Contact us today to discuss your project and achieve superior results with the right technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology



















