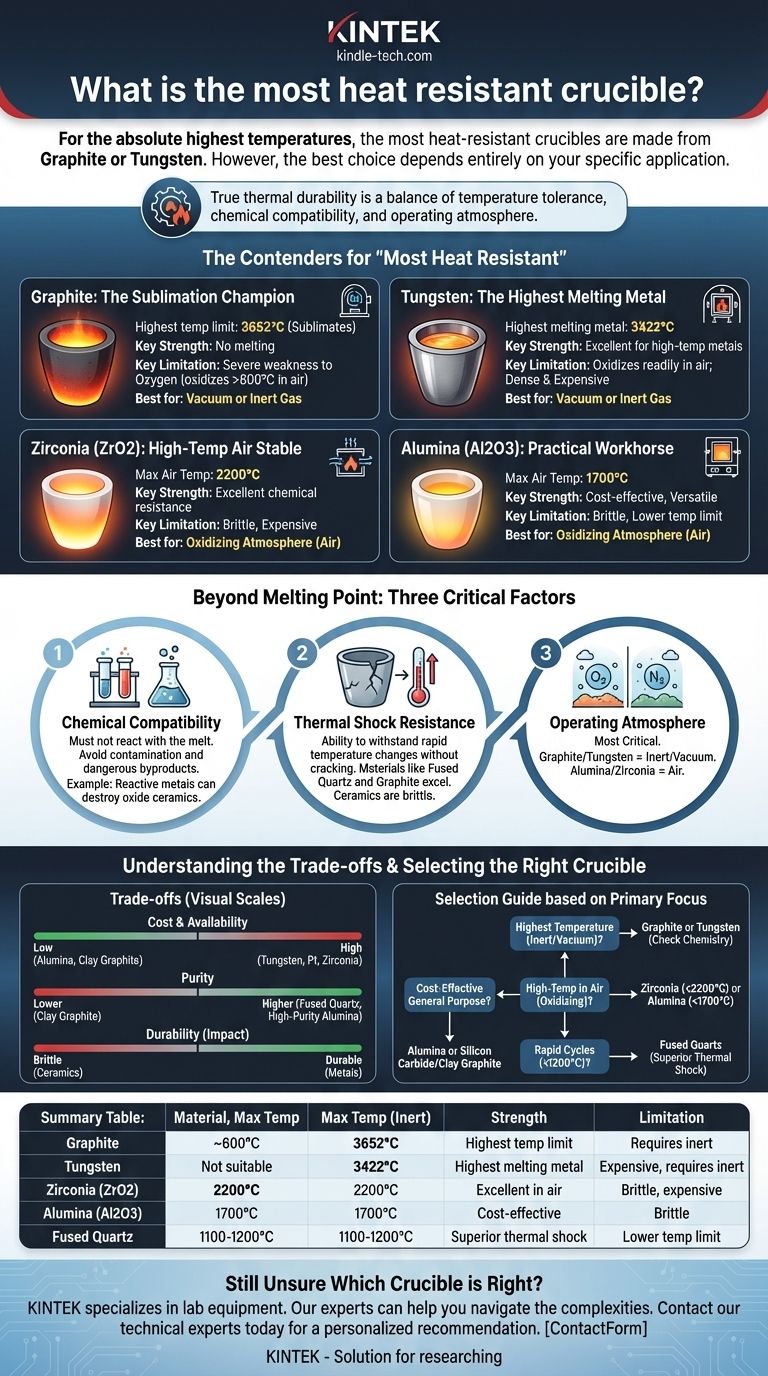
For the absolute highest temperatures, the most heat-resistant crucibles are made from Graphite or Tungsten. Graphite does not melt but sublimates at approximately 3652°C (6608°F), while Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal at 3422°C (6192°F). However, the best choice is rarely about a single number and depends entirely on your specific application.
The most "heat-resistant" crucible isn't just the one with the highest melting point. True thermal durability is a balance of temperature tolerance, chemical compatibility with the material being melted, and the ability to withstand the operating atmosphere without degrading.

The Contenders for "Most Heat Resistant"
The materials capable of handling extreme temperatures fall into a few distinct categories, each with unique strengths and critical weaknesses.
Graphite: The Sublimation Champion
Graphite has the highest temperature limit of any common crucible material. It does not melt at atmospheric pressure but turns directly into a gas (sublimation) at around 3652°C.
Its primary limitation is a severe weakness to oxygen. Graphite will rapidly oxidize (burn away) in an air atmosphere at temperatures above 600°C, making it suitable only for vacuum or inert gas environments.
Tungsten: The Highest Melting Metal
With a melting point of 3422°C, Tungsten is the premier choice for containing high-temperature molten metals when a non-metallic crucible is unsuitable.
Like graphite, tungsten must be used in a protective atmosphere. It oxidizes readily at high temperatures, so it is reserved for vacuum or inert gas furnaces. It is also extremely dense and expensive.
Advanced Ceramics: The Practical Workhorses
While they have lower melting points than graphite or tungsten, advanced ceramics are often the most practical choice because they are stable in air at very high temperatures.
Zirconia (ZrO2) crucibles, often stabilized with yttria, can be used in air up to 2200°C. They offer excellent chemical resistance and low thermal conductivity.
Alumina (Al2O3) is one of the most common and cost-effective crucible materials. High-purity alumina can be used in air up to 1700°C and is inert to a wide range of materials.
Beyond Melting Point: What "Heat Resistant" Truly Means
Choosing the right crucible requires you to look beyond a single temperature rating. Three factors are just as important as the melting point itself.
Chemical Compatibility
The crucible material must not react with the substance you are melting. A reaction can destroy the crucible, contaminate your material, and produce dangerous byproducts. For example, highly reactive metals like titanium can pull oxygen out of oxide ceramic crucibles, destroying them.
Thermal Shock Resistance
This is the material's ability to withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking. Materials like Fused Quartz and Graphite have excellent thermal shock resistance. Many ceramics, on the other hand, are brittle and must be heated and cooled slowly and carefully to prevent catastrophic failure.
Operating Atmosphere
This is the most critical and often overlooked factor. As noted, Graphite and Tungsten are useless in an oxidizing atmosphere (air). Conversely, Alumina and Zirconia excel in these conditions, providing a stable container for high-temperature work without the need for a vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every material choice involves balancing performance, limitations, and cost.
Cost and Availability
There is a massive cost disparity between materials. Alumina and Clay Graphite crucibles are relatively inexpensive and widely available. Tungsten, Platinum, and high-purity Zirconia are specialty items that are orders of magnitude more expensive.
Purity and Contamination
The crucible itself can be a source of contamination. For applications in electronics or material science that demand extreme purity, a high-purity Alumina or Fused Quartz crucible might be chosen, even if the temperature requirement is not extreme.
Brittleness vs. Durability
Ceramic crucibles are hard but brittle, making them susceptible to cracking from mechanical impact or thermal shock. Metallic crucibles like tungsten or platinum are much more durable and resistant to physical handling.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is reaching the absolute highest temperature in an inert/vacuum atmosphere: Your choice is between Graphite and Tungsten, depending on chemical compatibility with your melt.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature work in an open-air or oxidizing environment: Zirconia is your top choice for temperatures up to 2200°C, with Alumina being a cost-effective workhorse up to 1700°C.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling cycles below 1200°C: Fused Quartz is an exceptional choice due to its nearly unmatched thermal shock resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective general-purpose melting: An Alumina or a Silicon Carbide/Clay Graphite crucible will cover a vast range of common applications effectively.
Ultimately, matching the crucible material to the specific chemistry, atmosphere, and thermal cycle of your process is the key to success.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature (Air) | Max Temperature (Inert/Vacuum) | Key Strength | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | ~600°C (oxidizes) | 3652°C (sublimates) | Highest temp limit | Requires inert atmosphere |
| Tungsten | Not suitable | 3422°C (melts) | Highest melting metal | Expensive, requires inert atmosphere |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | 2200°C | 2200°C | Excellent in air, chemical resistance | Brittle, expensive |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | 1700°C | 1700°C | Cost-effective, versatile | Brittle, lower temp limit |
| Fused Quartz | 1100-1200°C | 1100-1200°C | Superior thermal shock resistance | Lower temperature limit |
Still Unsure Which Crucible is Right for Your Application?
Selecting the perfect crucible is critical for your lab's success, safety, and efficiency. The wrong choice can lead to failed experiments, contaminated samples, and damaged equipment.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of temperature, atmosphere, and chemical compatibility to identify the ideal crucible material for your specific process—whether you're working with extreme temperatures under vacuum or need a cost-effective solution for everyday melting.
Let us help you achieve precise and reliable results.
Contact our technical experts today for a personalized recommendation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why use an alumina crucible in a stainless steel autoclave? Ensure Purity in Liquid Lead and LBE Exposure Experiments
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What material is used for induction furnace crucibles? Match Your Metal & Frequency for Optimal Melting
- What can be used as a crucible for melting gold? A Guide to Graphite, Quartz, and More
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for molten FLiNaK? Ensure Peak Purity in Corrosive Salt Environments
- What is the efficiency of a crucible furnace? A Guide to Thermal Performance & Trade-offs
- Can crucibles withstand very high temperatures? Yes, if you choose the right material for your application.
- Why is an alumina crucible used for LATP glass? Ensure Pure, High-Temperature Synthesis Success



















