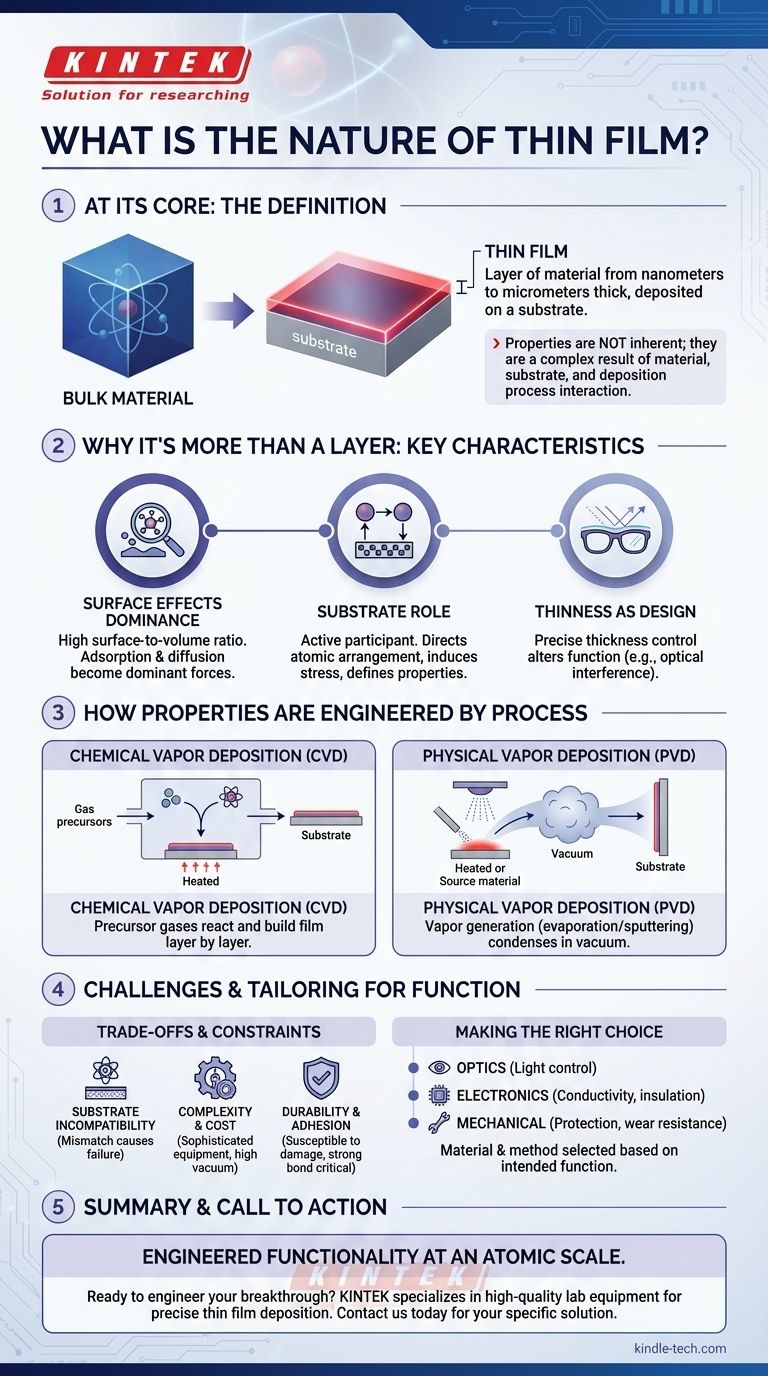
At its core, a thin film is a layer of material with a thickness ranging from just a few atoms (nanometers) to several micrometers, deposited onto a supporting surface known as a substrate. While defined by its minimal thickness, its true nature lies in how this dimension fundamentally alters its properties, making it behave very differently from the same material in its bulk form.
The defining characteristic of a thin film is not just its thinness. It is the fact that its properties are no longer inherent to the material alone, but are instead a complex result of the interaction between the material, the underlying substrate, and the precise method used for its deposition.

Why a Thin Film is More Than Just a Thin Layer
A block of gold and a thin film of gold are both made of gold atoms, but they do not behave the same way. The film's properties are dominated by its geometry and its environment, creating a unique material class.
The Dominance of Surface Effects
In a bulk material, most atoms are surrounded by other atoms. In a thin film, a huge proportion of atoms are at a surface or an interface.
This high surface-area-to-volume ratio means that surface phenomena—such as the adsorption of molecules from the environment or the diffusion (movement) of atoms across the surface—become dominant forces that dictate the film's behavior and stability.
The Critical Role of the Substrate
The substrate is not merely a passive holder for the film; it is an active participant in its structure.
The atomic arrangement, thermal expansion, and even the cleanliness of the substrate surface can direct how the film's atoms arrange themselves. This can induce stress, change the film's crystal structure, and ultimately define its electronic or optical properties.
Thickness as a Design Parameter
In the world of thin films, thickness is a powerful design tool. Changing the thickness by just a few nanometers can completely alter a film's function.
For example, this is how anti-reflection coatings on eyeglasses work. The thickness is precisely tuned to cause destructive interference for specific wavelengths of light, making the lens more transparent.
How Properties are Engineered by Process
A thin film's final characteristics are not an accident; they are a direct result of a highly controlled manufacturing process. The "how" it's made is just as important as the "what" it's made of.
The Blueprint: Deposition Methods
The process of creating a thin film is called deposition. The two most common families of techniques are Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- CVD uses precursor gases that react and decompose on the substrate surface to build the film layer by layer, almost like constructing it from atomic building blocks.
- PVD involves generating a vapor of the source material—either by heating it (evaporation) or bombarding it with ions (sputtering)—which then travels through a vacuum and condenses onto the substrate.
Other specialized techniques like ion implantation and plasma etching are used to further modify these layers.
Tailoring for Specific Functions
By precisely controlling deposition parameters—such as temperature, pressure, and deposition rate—engineers can fine-tune a film's properties.
This control allows for the creation of films that are transparent, scratch-resistant, electrically conductive, insulating, or that selectively transmit signals, all based on the needs of the application.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Constraints
The highly engineered nature of thin films also introduces specific challenges. Understanding these limitations is critical for their successful application.
Substrate Incompatibility
Not every material can be effectively deposited on every substrate. A mismatch in crystal structure or thermal properties can lead to high internal stress, causing the film to crack, peel, or fail to adhere properly (delamination).
Process Complexity and Cost
Creating high-quality thin films requires sophisticated and expensive equipment operating in highly controlled environments, often under high vacuum. This makes the process significantly more complex and costly than working with bulk materials.
Durability and Adhesion
Because they are so thin, films can be susceptible to mechanical damage. Strong adhesion to the substrate is paramount for durability, and ensuring this bond is a primary engineering challenge in nearly every application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a thin film's material and deposition method is always driven by the intended function.
- If your primary focus is optics or photonics: You will manipulate film thickness and material refractive index to precisely control how light reflects, absorbs, or transmits.
- If your primary focus is electronics: You will select materials and deposition methods to achieve exact levels of electrical conductivity, insulation, or semiconducting behavior for creating circuits.
- If your primary focus is mechanical protection: You will prioritize deposition processes that create dense, hard, and strongly adhered layers for scratch, wear, and corrosion resistance.
Ultimately, the nature of a thin film is one of controlled, engineered functionality at an atomic scale.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Definition | A layer of material, from nanometers to micrometers thick, deposited on a substrate. |
| Core Nature | Properties are not inherent but engineered through interaction with the substrate and deposition process. |
| Key Effects | Dominated by surface effects, substrate influence, and precise thickness control. |
| Primary Methods | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). |
| Common Applications | Optical coatings, electronic circuits, and protective mechanical layers. |
Ready to engineer your next breakthrough with precision thin films?
The nature of thin film technology is complex, but achieving the perfect deposition for your specific application doesn't have to be. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for thin film deposition, serving the precise needs of research and industrial laboratories.
We provide the reliable tools and expert support you need to master surface effects, ensure strong adhesion, and tailor properties for optics, electronics, or mechanical protection. Let us help you turn material science into real-world innovation.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications


















