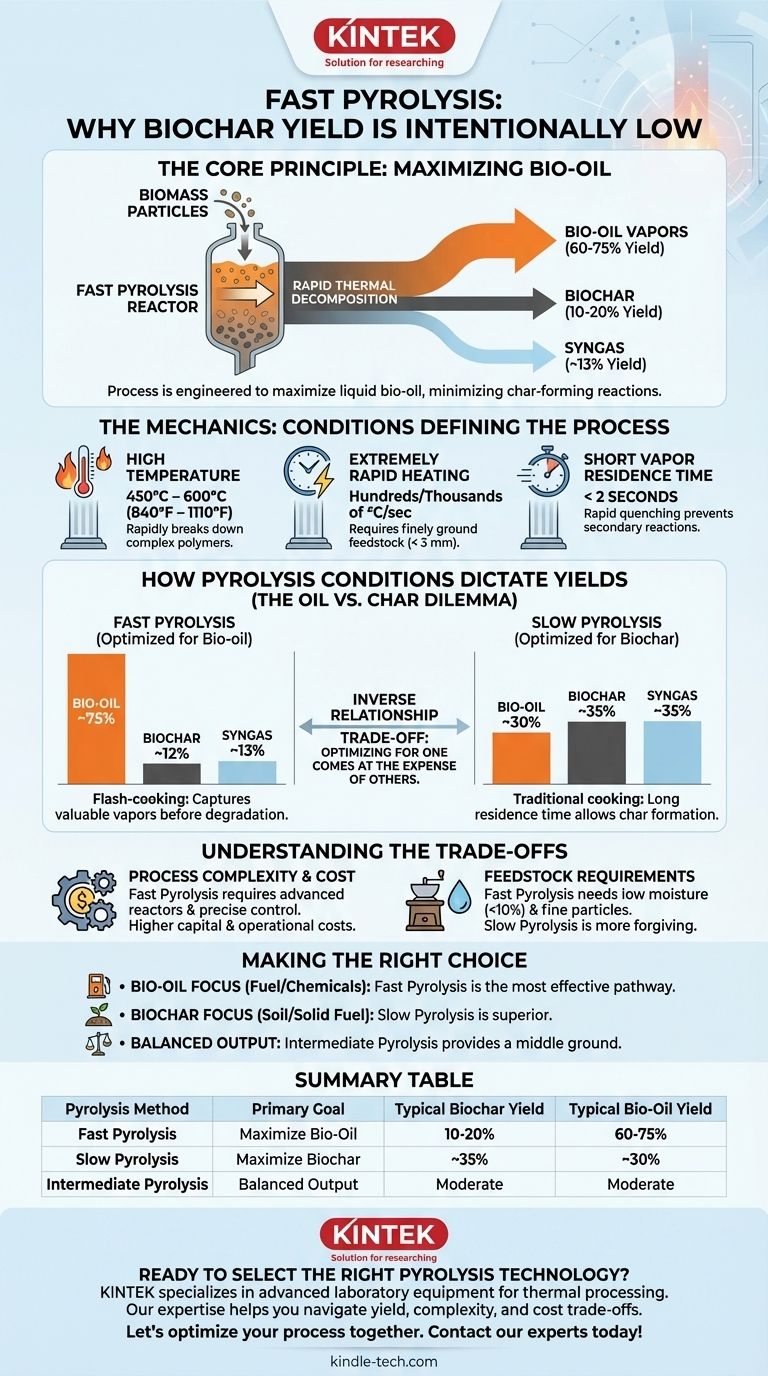
In fast pyrolysis, the yield of charcoal, more accurately termed biochar, is intentionally low, typically ranging from 10% to 20% of the initial biomass weight. This process is specifically engineered to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil, which often reaches yields of 60% to 75%. The remaining fraction consists of non-condensable syngas.
The core principle to grasp is that fast pyrolysis is not designed to produce charcoal. Its primary goal is the rapid thermal decomposition of biomass into vapors, which are then quickly cooled and condensed into liquid bio-oil, deliberately minimizing the time for char-forming reactions to occur.

The Mechanics of Fast Pyrolysis
To understand why biochar yield is low, you must first understand the specific conditions that define the fast pyrolysis process. It is a carefully controlled thermal reaction governed by three key parameters.
High Temperature
Fast pyrolysis operates at moderate to high temperatures, typically between 450°C and 600°C (840°F to 1110°F). This high thermal energy rapidly breaks down the complex polymers in biomass, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Extremely Rapid Heating
This is a critical factor. The biomass particles are heated at an exceptionally high rate, often hundreds or thousands of degrees Celsius per second. This requires the feedstock to be finely ground (typically < 3 mm) to ensure heat penetrates the entire particle almost instantly.
Short Vapor Residence Time
This is the most important variable for maximizing bio-oil. The hot gases (vapors) created during decomposition are removed from the hot reactor zone in less than two seconds. This rapid quenching prevents secondary reactions, where the initial vapors would further break down into more stable, lower-value products like additional char and syngas.
How Pyrolysis Conditions Dictate Product Yields
The trade-off between bio-oil, biochar, and syngas is a direct function of temperature, heating rate, and time. Different pyrolysis methods manipulate these variables to optimize for a specific product.
Fast Pyrolysis: Optimized for Bio-oil
As discussed, high heat, rapid heating, and short vapor residence time crack the biomass into condensable vapors. This is like "flash-cooking" the biomass to capture the valuable intermediate products before they can degrade further.
- Typical Yield: ~75% Bio-oil, ~12% Biochar, ~13% Syngas.
Slow Pyrolysis: Optimized for Biochar
This is the traditional method for making charcoal. It uses much lower temperatures and significantly slower heating rates. The biomass is allowed to "cook" for hours or even days.
This long residence time allows the secondary reactions to proceed, leading to the formation of a stable, carbon-rich solid structure—charcoal.
- Typical Yield: ~30% Bio-oil, ~35% Biochar, ~35% Syngas.
Intermediate Pyrolysis: A Balanced Approach
Operating between the fast and slow extremes, intermediate pyrolysis uses moderate heating rates and residence times. This results in a more balanced distribution of the three primary products, without maximizing any single one.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a pyrolysis method involves navigating a "yield trilemma." You cannot simultaneously maximize the output of all three products; optimizing for one comes at the expense of the others.
The Oil vs. Char Dilemma
The relationship between bio-oil and biochar yield is inversely proportional. The short vapor residence time that is essential for high bio-oil yield is precisely what prevents the formation of additional biochar. Conversely, the long reaction times needed for high biochar yield will inevitably degrade valuable oil vapors into non-condensable gas.
Process Complexity and Cost
Fast pyrolysis is a technically sophisticated process. Achieving and controlling rapid heating rates and short residence times requires advanced reactors (e.g., fluidized bed or ablative reactors) and precise operational control. This typically involves higher capital and operational costs compared to simpler, robust slow pyrolysis kilns.
Feedstock Requirements
Fast pyrolysis is also more sensitive to feedstock preparation. The need for rapid heat transfer mandates that the biomass be dried to a low moisture content (e.g., < 10%) and ground into fine particles. Slow pyrolysis is far more forgiving of variable particle sizes and higher moisture levels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis method is entirely dependent on your desired primary product. The low charcoal yield in fast pyrolysis is not a flaw, but a feature of a process designed for a different outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuel or chemical feedstocks (bio-oil): Fast pyrolysis is the most effective and direct pathway.
- If your primary focus is producing a solid soil amendment or solid fuel (biochar): Slow pyrolysis is the superior technology by a significant margin.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility or a balanced output: Intermediate pyrolysis provides a viable middle ground between the two extremes.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the precise thermal conversion technology that aligns with your strategic objective.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Method | Primary Goal | Typical Biochar Yield | Typical Bio-Oil Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | Maximize Bio-Oil | 10-20% | 60-75% |
| Slow Pyrolysis | Maximize Biochar | ~35% | ~30% |
| Intermediate Pyrolysis | Balanced Output | Moderate | Moderate |
Ready to select the right pyrolysis technology for your biomass conversion goals?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment for thermal processing. Whether you're researching fast pyrolysis for bio-oil or slow pyrolysis for biochar, our reactors and systems are designed for precision and reliability. Our expertise helps you navigate the trade-offs between yield, complexity, and cost to achieve your specific objectives.
Let's optimize your process together. Contact our experts today to discuss your lab's pyrolysis needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What role do laboratory autoclaves play in pectin extraction? Optimize Prebiotic Yield from Citrus and Apple Biomass
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment



















