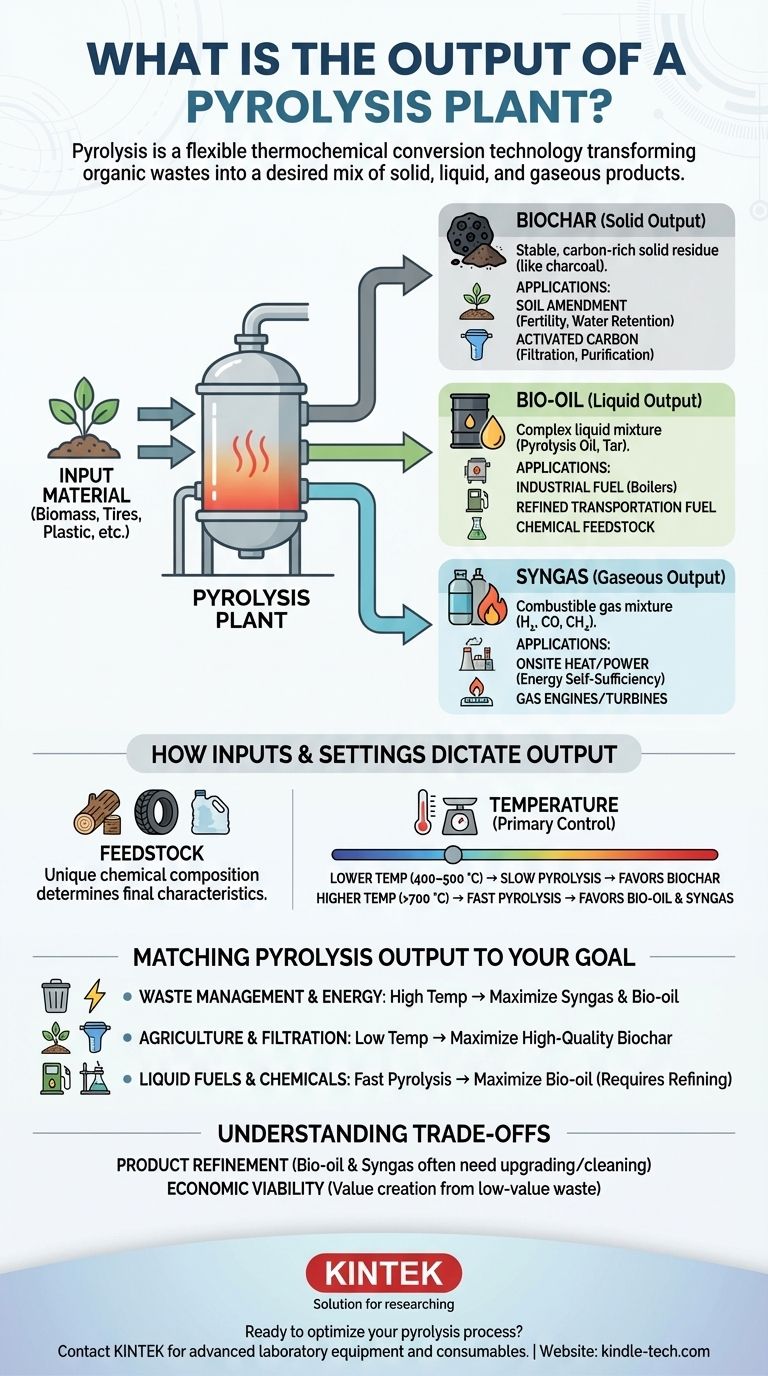
A pyrolysis plant primarily produces three core outputs: a solid carbon-rich material called biochar, a liquid known as bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), and a combustible gas called syngas. The exact proportion and chemical makeup of these products are not fixed; they are deliberately manipulated based on the input material—such as biomass, tires, or plastic—and the specific operating conditions of the plant, like temperature and heating rate.
The most critical concept to understand is that pyrolysis is not a single process with a static output. Instead, it is a flexible thermochemical conversion technology that operators can tune to transform a wide range of organic wastes into a desired mix of solid, liquid, and gaseous products.

The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis works by superheating organic materials in an oxygen-free environment. This thermal decomposition, often called "cracking," breaks down large, complex molecules into simpler, more valuable substances.
The Solid Output: Biochar
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. It is analogous to charcoal.
Its primary applications include use as a potent soil amendment to improve fertility and water retention, or as a feedstock for producing activated carbon, a powerful filtration and purification agent.
The Liquid Output: Bio-oil
Bio-oil is a complex liquid mixture of water, tars, and hundreds of different organic compounds. Depending on the feedstock, it may also be referred to as pyrolysis oil, tar, or wood vinegar.
This liquid can be refined into transportation fuels, used directly as an industrial boiler fuel, or serve as a source for specialty chemicals.
The Gaseous Output: Syngas
Syngas (synthesis gas) is a mixture of combustible gases, primarily hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane.
It has significant energy value and is often captured and reused to provide the heat needed for the pyrolysis process itself, making many plants partially or fully energy self-sufficient.
How Inputs and Settings Dictate the Output
A pyrolysis plant is not a black box with a fixed output. The operator has several key levers to pull that fundamentally change the product yields, allowing them to target the most economically viable output for their specific feedstock.
The Role of the Feedstock
The material fed into the reactor is the single most important factor. Pyrolyzing plastic waste will yield different types of oils and gases compared to pyrolyzing wood waste or agricultural residue.
Each feedstock has a unique chemical composition that determines the final product characteristics.
The Critical Impact of Temperature
Temperature is the primary control mechanism for determining the final product ratio. This allows operators to steer the process toward their desired outcome.
A general rule is that lower temperatures (400–500 °C) favor the production of solid biochar. This is known as "slow" pyrolysis.
Conversely, higher temperatures (above 700 °C) favor the production of liquid bio-oil and syngas. This is known as "fast" pyrolysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While pyrolysis is a powerful technology, its outputs are not finished products ready for immediate, widespread use. Understanding their limitations is key to a successful operation.
Product Quality and Refinement
The raw outputs of a pyrolysis plant require processing. Bio-oil is often acidic and unstable, needing significant upgrading before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Similarly, syngas may need to be cleaned of impurities before it can be used in sensitive equipment like gas engines or turbines.
Economic Viability
The profitability of a pyrolysis plant depends entirely on creating a higher-value product from a lower-value (or negative-value) waste stream.
A plant's economic model must account for the costs of feedstock acquisition, processing, and the market value of its specific outputs, whether that's low-grade industrial fuel or high-grade activated carbon.
Matching Pyrolysis Output to Your Goal
The optimal setup for a pyrolysis plant depends entirely on its intended purpose. There is no single "best" configuration; the process must be engineered to meet a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is waste management and energy generation: Operating at higher temperatures to maximize syngas and bio-oil for onsite heat and power is the most direct path.
- If your primary focus is agricultural improvement or filtration: Operating at lower, slower-heating conditions to maximize the yield of high-quality biochar is the correct approach.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuels or chemical feedstocks: Fast pyrolysis at high temperatures is necessary to maximize the liquid bio-oil fraction, which will then require a dedicated refining process.
Ultimately, a pyrolysis plant is a versatile conversion tool, transforming low-value inputs into a tailored set of valuable energy and material outputs.
Summary Table:
| Output Product | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Carbon-rich solid residue | Soil amendment, activated carbon production |
| Bio-Oil | Complex liquid mixture | Industrial fuel, refined transportation fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Syngas | Combustible gas mixture (H2, CO, CH4) | Onsite heat/power for the pyrolysis process |
Ready to tailor a pyrolysis solution for your specific waste stream and output goals? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you're researching biochar for agriculture, refining bio-oil for fuel, or analyzing syngas composition, our precision tools help you achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your pyrolysis R&D and scale-up needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















