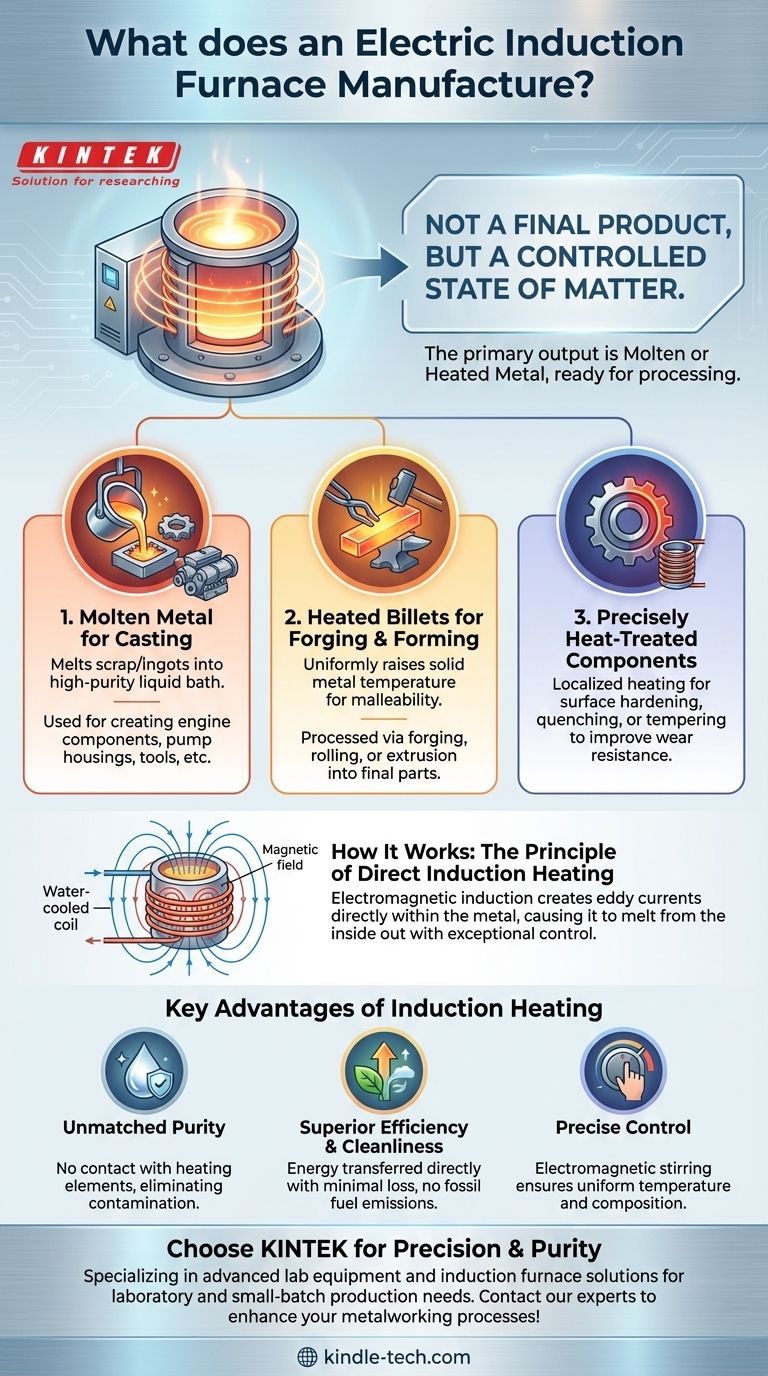
At its core, an electric induction furnace does not manufacture a final consumer product. Instead, its primary output is molten metal of a specific composition and temperature or, alternatively, solid metal heated precisely for further processing. This furnace is a critical piece of equipment in foundries and metalworking industries, using electromagnetic induction to melt or heat materials with exceptional control and cleanliness.
The true "product" of an induction furnace is not a physical item, but a controlled state of matter: metal transformed into a liquid or heated to a precise temperature, ready for the next stage of manufacturing like casting or forging.
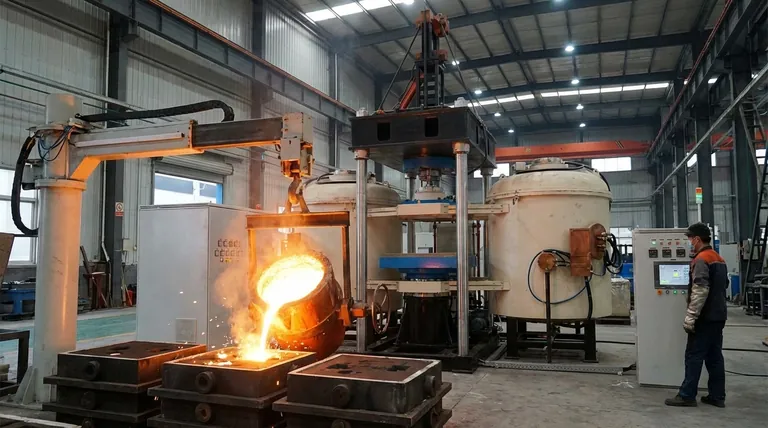

How an Induction Furnace Produces Its Output
An induction furnace's function is best understood not as creating a finished good, but as a sophisticated process for transforming raw metal. This process yields different outputs depending on the industrial application.
Molten Metal for Casting
The most common output is liquid metal. Solid metal scrap, ingots, or alloys are placed in a crucible within the furnace. The induction process melts this charge into a homogenous liquid bath.
This high-purity molten metal is then poured into molds to create a vast range of cast products, from engine components and pump housings to tools and decorative items. This application is central to iron foundries.
Heated Billets for Forging and Forming
Induction furnaces are also used for through-heating of solid metal pieces, such as billets or bars. The goal here isn't to melt the metal, but to raise its temperature uniformly until it becomes malleable.
These hot billets are immediately transferred to other machines for processes like forging, rolling, or extrusion, where they are shaped into final parts.
Precisely Heat-Treated Components
A specialized application is surface hardening, quenching, or tempering. The furnace's induction coil can be designed to heat only a specific area of a finished metal part with incredible speed and precision.
This localized heating and subsequent cooling (quenching) alters the metal's crystalline structure, hardening it to improve wear resistance without affecting the core properties of the component.
Why This Process is So Effective
The value of an induction furnace comes from how it heats the metal. The underlying principles give it distinct advantages over other furnace types.
The Principle of Direct Induction Heating
The furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil through which a powerful alternating current flows. This creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around the crucible.
This magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
Unmatched Purity and Control
Because heat is generated directly within the metal, there is no physical contact with a heating element or flame. This eliminates contamination from fuel, combustion gases, or electrodes (a key difference from electric arc furnaces).
The result is an exceptionally clean melt. The electromagnetic stirring caused by the eddy currents also ensures the molten bath has a highly uniform temperature and chemical composition, which is critical for producing high-quality alloys.
Superior Efficiency and Cleanliness
This heating method is highly energy-efficient because the energy is transferred directly to the workpiece with minimal thermal loss to the surrounding environment.
Furthermore, with no burning of fossil fuels, the process is clean and produces no smoke or polluting exhaust gases, making it a preferred technology in modern, environmentally-conscious industrial settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an induction furnace is not the universal solution for all metal heating and melting needs. Understanding its context is key to appreciating its role.
Induction Furnace vs. Electric Arc Furnace
It is crucial not to confuse these two technologies. An electric arc furnace (EAF) melts metal using an intense electric arc that forms between graphite electrodes and the metal charge.
EAFs are extremely powerful and are the workhorses for melting massive quantities of scrap steel. However, they are less controlled and can introduce impurities from the electrodes. Induction furnaces offer higher purity and precision, making them ideal for specialty alloys and applications where quality is paramount.
Capacity and Scale
Induction furnaces are perfectly suited for small-to-medium batch sizes, typical of specialized foundries. For the mass production of commodity steel in volumes of hundreds of tons per batch, the electric arc furnace or basic oxygen furnace remains the dominant technology.
Reliance on the Control System
The effectiveness of an induction furnace is heavily dependent on its sophisticated power supply and control systems. These systems manage the frequency and power to ensure stable, efficient melting and protect the equipment from over-voltage or over-current conditions. While modern systems are highly reliable, they represent a complex electronic core that requires specialized maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on the desired outcome and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys and precise composition control: An induction furnace is the definitive choice due to its clean, non-contact heating and natural stirring action.
- If your primary focus is mass-melting of steel scrap at the lowest cost per ton: An electric arc furnace is generally more suitable for its high power and large-volume capacity.
- If your primary focus is rapid, localized heating for forging or heat treatment: A specialized induction heating furnace offers unparalleled speed and precision, minimizing energy waste and cycle time.
Understanding that an induction furnace produces a controlled material state, not a finished part, is the key to leveraging its unique advantages in modern metalworking.
Summary Table:
| Output Type | Primary Application | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Molten Metal | Casting (e.g., engine parts) | High purity, uniform composition |
| Heated Billets | Forging and Forming | Uniform, rapid heating |
| Heat-Treated Parts | Surface Hardening | Precise, localized heating |
Need precise, high-purity metal melting or heating for your laboratory or foundry? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnace solutions tailored for laboratory and small-batch production needs. Our technology ensures the clean, controlled heating essential for developing high-quality alloys and components. Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can enhance your metalworking processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Superior Density in Cu-Y Composites
- Why is a high-precision temperature control system in a vacuum hot press furnace critical? Perfect Cu-Ti3SiC2 Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve Superior Lithium Niobate Piezoelectric Density
- Why is a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace required for Ni-Cr-Co-Ti-V alloys? Achieve High Density & Purity



















