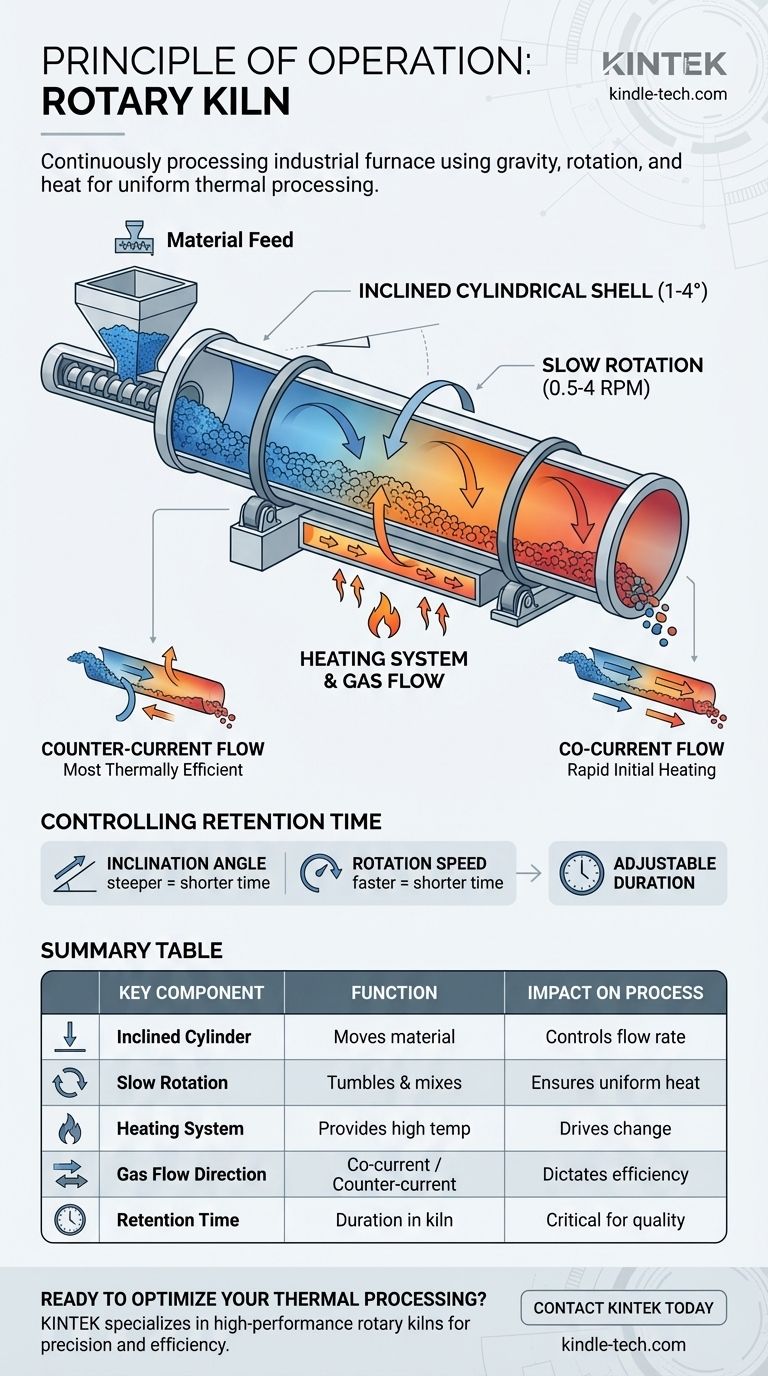
At its core, a rotary kiln is a continuously processing industrial furnace. It functions as a slowly rotating, inclined cylinder that uses gravity, mechanical tumbling, and high heat to induce a specific chemical reaction or physical change in solid materials as they pass from one end to the other.
The fundamental principle is to achieve perfectly uniform thermal processing. By combining a slight downward slope with slow rotation, the kiln tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to a precisely controlled temperature for a specific duration, known as the retention time.

The Mechanics of Material Transformation
A rotary kiln's design is deceptively simple, but each component plays a critical role in controlling the final product. Understanding how these elements work together is key to grasping its operational principle.
The Inclined Cylindrical Shell
The kiln is a long, hollow drum made of steel and lined with refractory brick to withstand extreme temperatures. Its entire body is positioned at a slight angle to the horizontal, typically between 1 and 4 degrees.
This inclination is the primary driver of material flow. It uses gravity to ensure the feedstock, once fed into the higher end, moves steadily toward the discharge port at the lower end.
The Rotational Mechanism
The kiln rotates slowly on its longitudinal axis, typically at speeds of 0.5 to 4 revolutions per minute (RPM). This is the most crucial mechanical action.
This slow rotation lifts the material partway up the side of the cylinder until gravity causes it to cascade, or tumble, back down. This constant stirring and mixing is essential for preventing hot spots and ensuring uniform heat exposure.
The Material Feed and Discharge
Material is continuously fed into the upper end of the kiln, often using a device like a screw feeder to ensure a consistent and quantifiable flow rate.
After traveling the full length of the kiln and undergoing its transformation, the finished product exits through a discharge port at the lower end.
The Heating System and Gas Flow
Heat is introduced by hot gases that pass through the length of the kiln. These gases can be generated by a large burner flame inside the kiln or by external heaters.
The direction of this gas flow relative to the material flow is a critical design choice, creating two primary modes of operation.
Understanding the Operational Modes and Trade-offs
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln depends entirely on the precise control of its variables. The most significant choice is the direction of the hot gas flow, which dictates the system's thermal efficiency and its suitability for a given process.
Counter-Current Flow
In a counter-current system, the hot gases are introduced at the lower (discharge) end and flow uphill, opposite to the direction of the material.
This is the most common and thermally efficient configuration. The hottest gases encounter the most processed material, while the cooler gases encounter the fresh, wet feedstock, effectively preheating it.
Co-Current Flow
In a co-current system, the hot gases enter at the same upper end as the feedstock and flow in the same direction, downhill.
This mode exposes the raw material to the highest temperatures immediately. It is ideal for processes like drying, where rapid heating is required, or for materials that are sensitive to overheating in their final state.
Controlling Retention Time
The retention time—how long the material spends inside the kiln—is the most critical process parameter. It is precisely controlled by adjusting two variables: the inclination angle and the rotation speed. A steeper slope or faster rotation will decrease retention time, while a shallower slope or slower rotation will increase it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of a rotary kiln comes from its ability to be finely tuned for a wide range of thermal processes, from simple drying to complex chemical transformations.
- If your primary focus is calcination (e.g., cement production): A counter-current configuration is ideal for maximizing thermal efficiency and achieving the precise, high-temperature profiles required for the chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is drying or thermal desorption: A co-current setup is often preferred to apply intense heat immediately to the wet feedstock, rapidly driving off moisture or volatile compounds.
- If your primary focus is uniform mixing and sintering: You will concentrate on controlling the rotation speed and internal lifters to ensure thorough tumbling and a consistent retention time for every particle.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's operational principle is a masterful integration of simple physics—gravity, rotation, and heat transfer—to create a powerful and highly controllable environment for transforming materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Inclined Cylinder | Uses gravity to move material | Controls the flow rate of material through the kiln |
| Slow Rotation | Tumbles and mixes the material | Ensures uniform heat exposure and prevents hot spots |
| Heating System | Provides high-temperature environment | Drives the desired chemical or physical change |
| Gas Flow Direction | Co-current or Counter-current flow | Dictates thermal efficiency and heating profile |
| Retention Time | Duration material stays in the kiln | Controlled by rotation speed and angle; critical for final product quality |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Understanding the principle of operation is the first step. The next is selecting the right equipment for your specific material and process goals. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including rotary kilns designed for precision, efficiency, and durability in your laboratory or pilot plant.
Our experts can help you choose the ideal configuration—whether you need the maximum efficiency of a counter-current system for calcination or the rapid heating of a co-current system for drying.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development, improve your product quality, and scale your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development



















