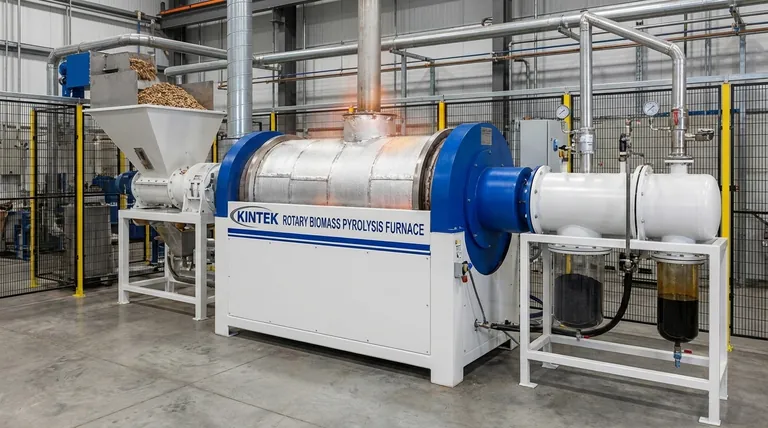
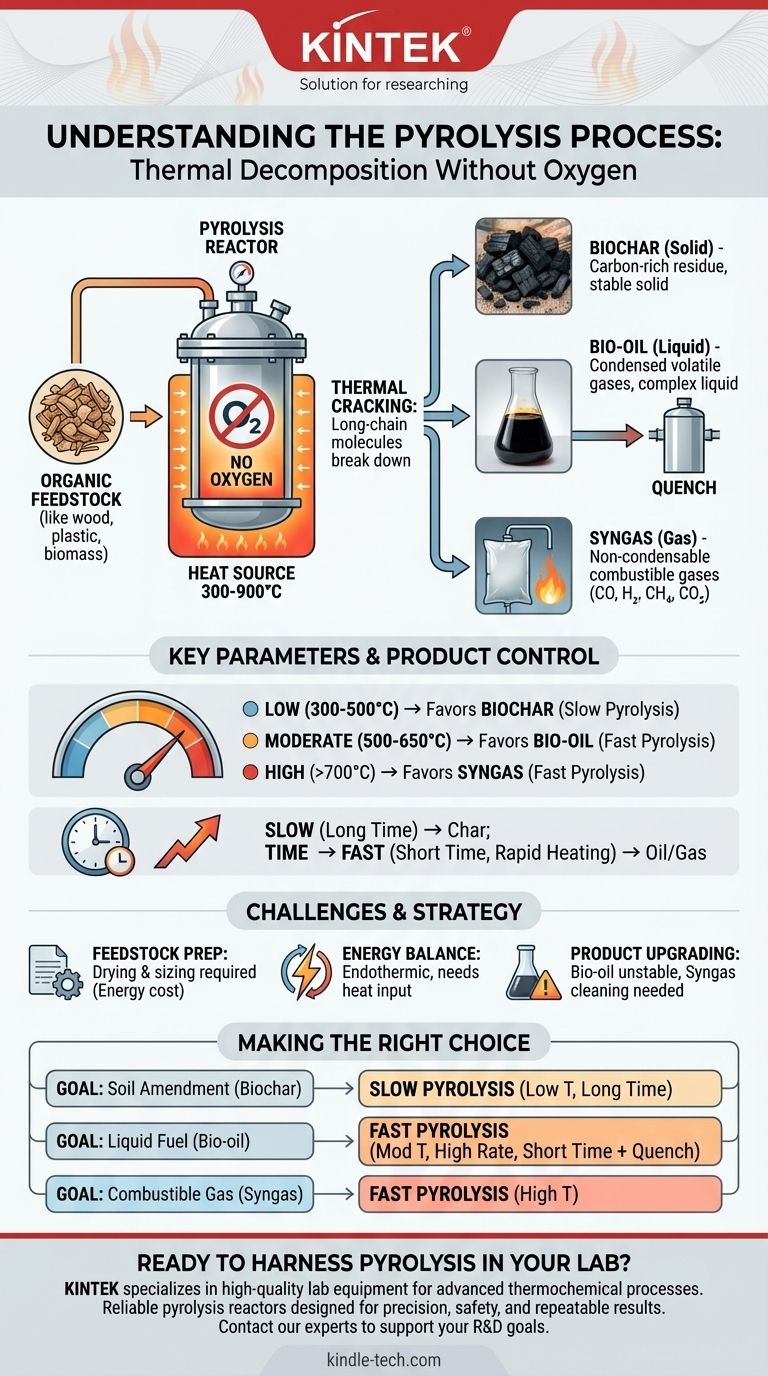
At its core, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic-based materials at elevated temperatures in a near-total absence of oxygen. Unlike combustion, which is a reaction with oxygen, pyrolysis uses heat to break down complex molecules like cellulose, lignin, or plastics into simpler, more valuable products. It is not burning; it is a controlled chemical breakdown.
The fundamental principle of pyrolysis is to prevent combustion. By heating material without oxygen, you force its long-chain molecules to crack apart into a mixture of solid carbon (char), liquid hydrocarbons (oil), and combustible gases (syngas) instead of turning into ash and smoke.

How Pyrolysis Fundamentally Works
To understand the process, we must look at the roles of heat and the oxygen-free environment, which together dictate the transformation of the input material, or feedstock.
The Role of Heat: Cracking Molecules
The process begins by heating the feedstock in a closed reactor. As the temperature rises (typically between 300-900°C), the intense thermal energy causes the long, complex polymer chains that make up the material to vibrate and break apart.
This thermal "cracking" initially breaks the solid feedstock down into smaller, volatile components. These components then either escape as gas or cool and condense into a liquid. What remains behind is a solid, carbon-rich residue.
The Critical Factor: Absence of Oxygen
The entire process must occur in an inert atmosphere. If oxygen were present, the organic material would simply combust, releasing its energy as heat and producing carbon dioxide, water, and ash.
By removing oxygen, we prevent this oxidation reaction. This forces the chemical change from a destructive burning process to a controlled deconstruction process, preserving the chemical energy in the resulting products.
The Three Core Products: Solid, Liquid, and Gas
Pyrolysis consistently yields three distinct product streams, the proportions of which are determined by the process conditions.
- Biochar (Solid): A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It is the residue left after volatile components have been driven off.
- Bio-oil/Pyrolysis Oil (Liquid): A dark, viscous liquid created when the hot, volatile gases are rapidly cooled and condensed. It is a complex mixture of oxygenated hydrocarbons.
- Syngas (Gas): A mix of non-condensable, combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Key Parameters That Control the Outcome
The ratio and specific composition of the three products are not fixed. They can be precisely controlled by manipulating three key process parameters.
Temperature: The Primary Driver
Temperature has the most significant influence on the product distribution.
- Low Temperatures (300-500°C): Favors the production of solid biochar.
- Moderate Temperatures (500-650°C): Maximizes the yield of liquid bio-oil.
- High Temperatures (>700°C): Favors the production of gaseous syngas, as the higher heat causes further cracking of the liquid components.
Heating Rate & Residence Time
How quickly the material is heated (heating rate) and how long it is kept at the target temperature (residence time) are also critical.
- Slow Pyrolysis: A slow heating rate and long residence time (hours) allows for more solid-to-solid reactions, maximizing the yield of biochar. This is the traditional method for making charcoal.
- Fast Pyrolysis: A very rapid heating rate and short residence time (seconds) quickly vaporizes the feedstock. When these vapors are rapidly cooled (quenched), it maximizes the yield of bio-oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, pyrolysis is a technically demanding process with several inherent challenges that must be managed for successful operation.
Feedstock Preparation
Pyrolysis reactors are sensitive to the physical properties of the feedstock. Materials must often be dried to a low moisture content and ground to a consistent particle size to ensure uniform heating and efficient conversion. This pre-processing adds energy cost and complexity.
Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a continuous input of energy to maintain the high temperatures needed to break the chemical bonds. A portion of the syngas produced is often used to heat the reactor, but ensuring a positive net energy balance remains a key engineering challenge.
Product Complexity and Upgrading
The outputs of pyrolysis are not final, refined products. Bio-oil is acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable, often requiring significant upgrading (e.g., hydrotreating) before it can be used as a drop-in fuel. Syngas also typically requires cleaning to remove tars and other impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis strategy depends entirely on the desired end product.
- If your primary focus is producing a stable soil amendment or carbon sequestration product (biochar): Employ slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures (~450°C) and long residence times to maximize the solid yield.
- If your primary focus is creating a liquid fuel intermediate (bio-oil): Use fast pyrolysis with moderate temperatures (~500°C), extremely high heating rates, and short vapor residence times followed by rapid quenching.
- If your primary focus is generating a combustible fuel gas (syngas): Utilize fast pyrolysis at very high temperatures (>700°C) to encourage the secondary cracking of vapors into non-condensable gases.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a versatile thermochemical tool for converting low-value organic materials into a spectrum of valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Impact on Pyrolysis Process |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Primary driver for product distribution (char, oil, or gas). |
| Heating Rate | Fast heating maximizes liquid oil; slow heating maximizes solid char. |
| Oxygen Absence | Critical to prevent combustion and enable chemical decomposition. |
| Residence Time | Duration at temperature affects the completeness of the conversion. |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced thermochemical processes. Whether you are researching biochar production, bio-oil optimization, or syngas analysis, our reliable pyrolysis reactors and supporting apparatus are designed for precision, safety, and repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve your research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of the rotary furnace? It Depends on the Heating Method
- What are the advantages of bio oil pyrolysis? Turn Waste into Renewable Energy & Carbon Sinks
- What are the steps of pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the 3-Phase Process
- What is the pyrolysis method for biochar production? A Guide to Maximizing Carbon-Rich Char Yield
- What is the byproduct of calcination? Uncovering the Gases Released in Thermal Decomposition
- How does the process of pyrolysis work? Unlock the Power of Chemical Recycling and Energy Recovery
- What is the history of pyrolysis technology? From Wood Distillation to Modern Waste Valorization
- What is the heat required for calcination? A Guide to Accurate Energy Calculations



















