At its core, ion plating is an advanced Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process that creates exceptionally dense and well-adhered thin-film coatings. It works by vaporizing a source material into a plasma within a vacuum, then using a high-voltage electrical field to accelerate these material ions, causing them to bombard and embed into the substrate's surface, forming a superior coating.
The critical distinction of ion plating is not just depositing material, but actively using high-energy ion bombardment during deposition. This simultaneous action cleans the surface and compacts the coating on an atomic level, yielding significantly improved adhesion and density compared to standard PVD methods.

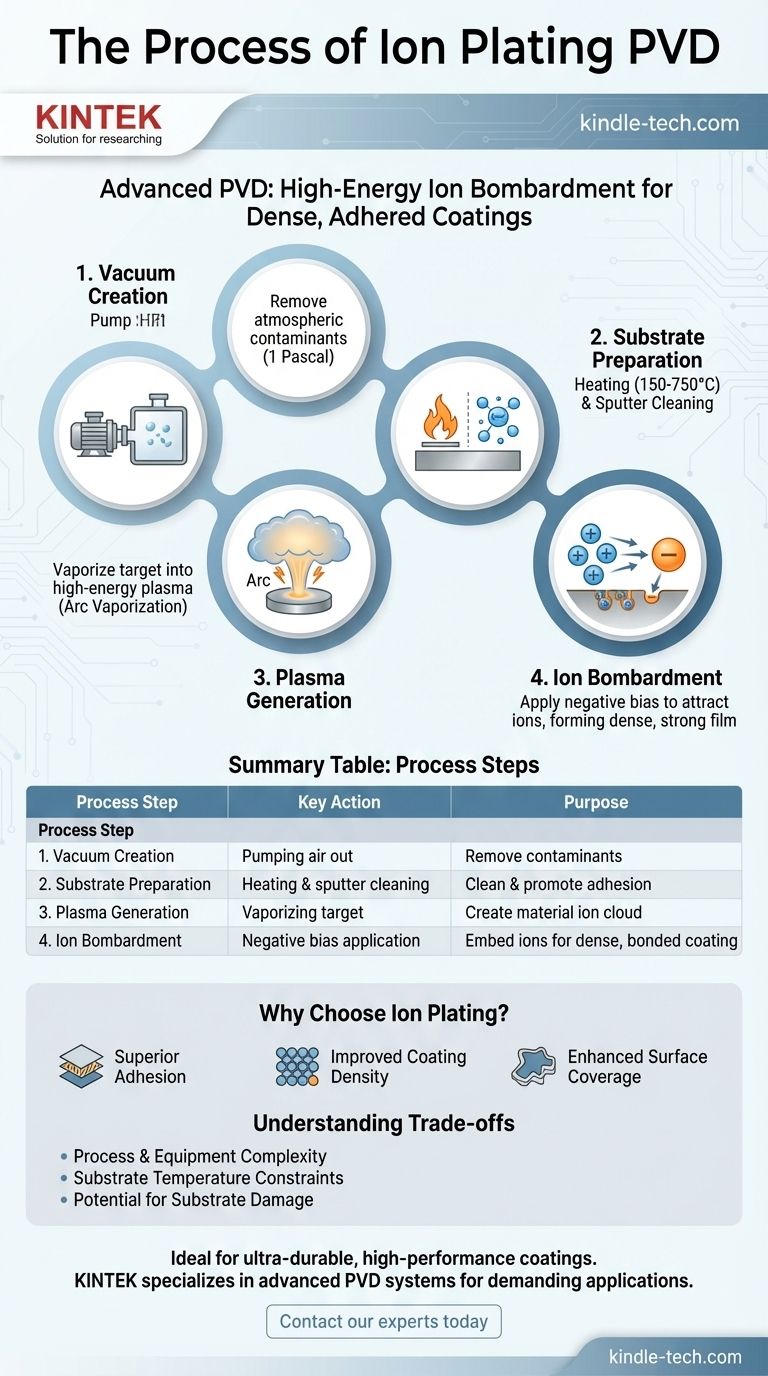
Deconstructing the Ion Plating Process
Ion plating is a multi-stage process conducted within a high-vacuum chamber. Each step is precisely controlled to engineer the final properties of the coating.
Step 1: Creating the Vacuum Environment
The component to be coated, known as the substrate, is placed inside a reaction chamber. The chamber is sealed and air is pumped out to create a high vacuum, typically around 1 Pascal.
This step is critical for removing atmospheric contaminants like moisture and oxygen, which would otherwise interfere with the process and compromise the quality of the final coating.
Step 2: Substrate Preparation
The substrate is heated to temperatures ranging from 150°C to 750°C. This heating cleans the surface of residual contaminants and provides thermal energy that promotes better diffusion and adhesion of the coating material.
Simultaneously, the substrate is often subjected to an initial "sputter cleaning" by bombarding it with inert gas ions (like Argon) to remove any microscopic oxides or impurities.
Step 3: Generating the Material Plasma
The coating material, called the target, is vaporized to create a dense plasma—a high-energy gas of ions and electrons. This can be achieved through several methods, with arc vaporization being common.
In arc vaporization, a high-current, low-voltage arc (~100 Amperes) is struck on the target's surface. This creates an intense, localized heat point that vaporizes the metal into a plasma.
Step 4: The Ion Bombardment and Deposition
This is the defining step of ion plating. The substrate is given a strong negative electrical charge (bias voltage). This negative potential attracts the positively charged metal ions from the plasma.
These ions accelerate toward the substrate at high speed, bombarding its surface with significant energy. This bombardment has two simultaneous effects:
- It continues to sputter-clean the surface, ensuring a pristine interface for bonding.
- The ions embed themselves into the substrate, forming a dense, tightly packed film with an exceptionally strong bond.
If a compound coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) is desired, a reactive gas (like Nitrogen) is introduced into the chamber, which reacts with the metal ions as they deposit onto the surface.
Why Choose Ion Plating?
Ion plating is chosen when the performance and longevity of the coating are paramount. The energetic bombardment process provides distinct advantages over simpler deposition techniques.
Superior Adhesion
The high energy of the impacting ions creates a graded interface between the substrate and the coating, rather than a sharp, distinct boundary. This atomic-level mixing results in an unparalleled mechanical bond that is highly resistant to flaking or chipping.
Improved Coating Density
The constant bombardment during deposition is like "sandblasting" on an atomic scale. It compacts the deposited atoms, eliminating the microscopic voids and columnar structures often found in standard PVD coatings. This results in a denser, less porous, and more durable film.
Enhanced Surface Coverage
The plasma environment helps the coating material "wrap around" the substrate more effectively than simple line-of-sight deposition methods. This allows for more uniform coverage on complex shapes, sharp edges, and even some internal surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, ion plating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Process and Equipment Complexity
Ion plating systems require high-vacuum chambers, high-current arc power supplies, and high-voltage DC bias systems. This makes the equipment and process control more complex and costly than some alternative methods.
Substrate Temperature Constraints
The process often requires heating the substrate to several hundred degrees Celsius. This can be problematic for heat-sensitive materials like certain plastics or tempered alloys, which could warp, melt, or lose their engineered properties.
Potential for Substrate Damage
The same high-energy ion bombardment that improves adhesion can, if not properly controlled, induce stress or damage in the substrate's surface layer. This is a critical parameter that must be optimized for each specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right coating process depends entirely on your end goal. Use these guidelines to determine if ion plating is the correct approach for your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and hardness: The dense, non-porous films created by ion plating are ideal for demanding applications like cutting tools and industrial components.
- If your application requires exceptional coating adhesion: For components subject to high stress, impact, or thermal cycling, the atomically bonded interface from ion plating provides superior reliability.
- If you are coating complex geometries: The excellent "throw power" of ion plating ensures more uniform protection on parts with sharp edges, grooves, or non-flat surfaces.
- If your substrate is a heat-sensitive polymer or your budget is minimal: You may need to evaluate lower-temperature PVD variants or simpler deposition methods that trade some performance for lower cost and process temperature.
Ultimately, ion plating is a premier surface engineering tool for creating coatings where failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vacuum Creation | Pumping air out of the chamber | Remove atmospheric contaminants for a pure process environment. |
| 2. Substrate Preparation | Heating & sputter cleaning with inert gas ions | Clean the surface and promote adhesion. |
| 3. Plasma Generation | Vaporizing the target material (e.g., via arc vaporization) | Create a cloud of coating material ions. |
| 4. Ion Bombardment & Deposition | Applying a negative bias to the substrate to attract ions | Embed ions into the substrate for a dense, strongly bonded coating. |
Need a coating where failure is not an option?
The ion plating process detailed above is ideal for creating ultra-durable, high-performance coatings. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including PVD systems, to help you achieve superior results for your most demanding applications, from cutting tools to precision components.
Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















