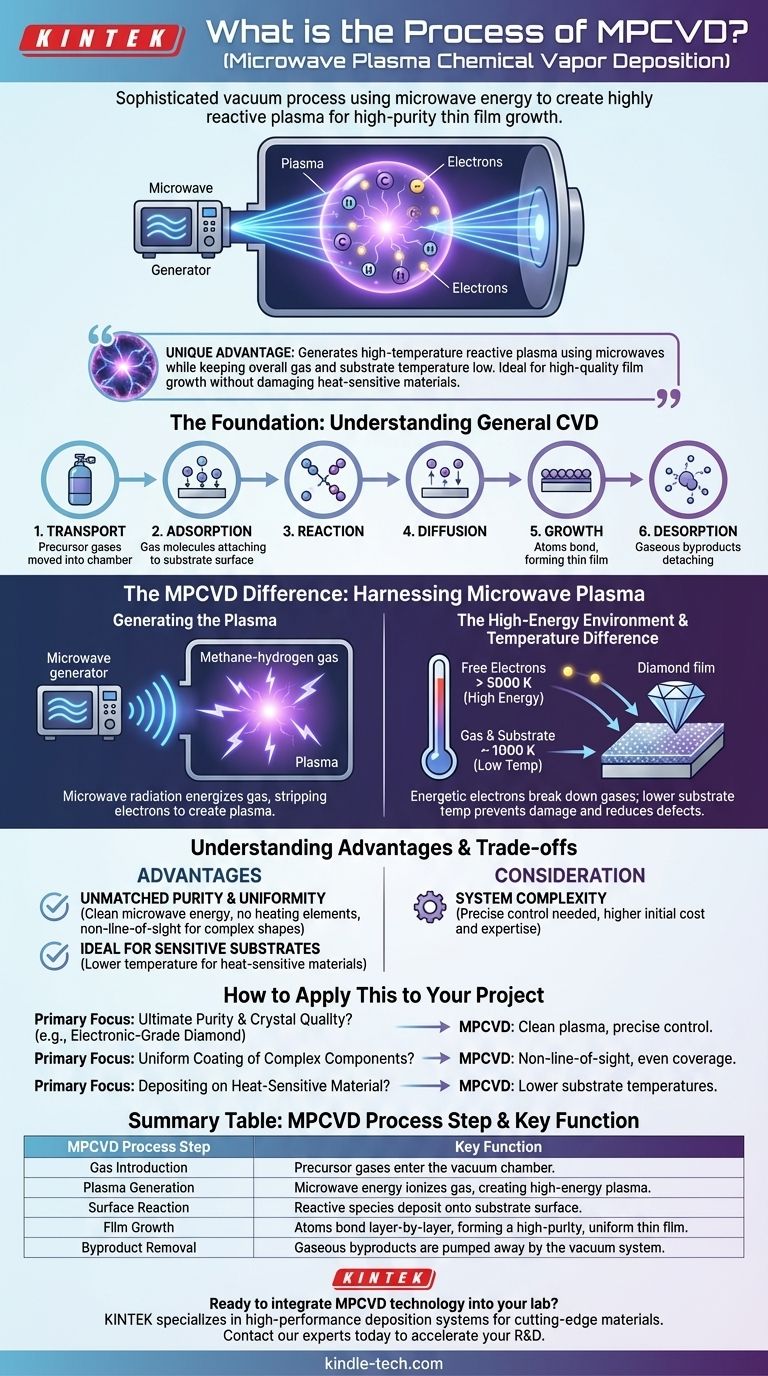
At its core, Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) is a sophisticated process that uses microwave energy to create a highly reactive plasma from a precursor gas. This plasma contains the necessary chemical species to grow high-purity thin films, such as synthetic diamond, onto a substrate within a vacuum chamber. The process is valued for its precision and its ability to deposit films at lower temperatures than many alternative methods.
MPCVD's unique advantage lies in its ability to generate a high-temperature, reactive plasma using microwaves while keeping the overall gas and substrate temperature relatively low. This creates an ideal environment for high-quality film growth without damaging heat-sensitive materials.
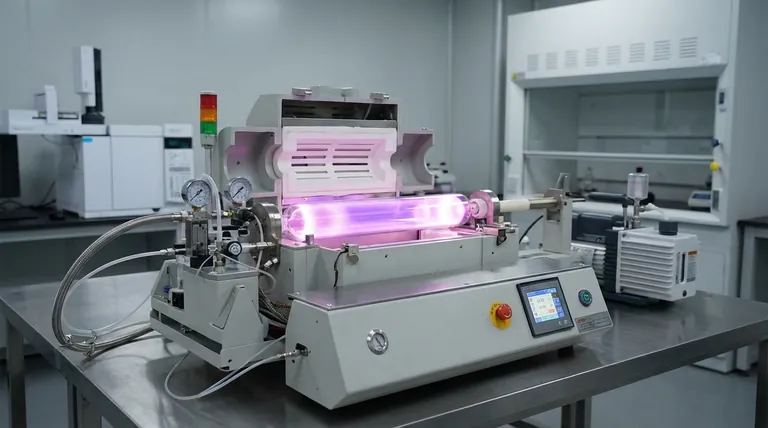

The Foundation: Understanding General CVD
Before detailing the specifics of MPCVD, it's crucial to understand the principles of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) in general. MPCVD is a specialized subtype of this foundational technology.
The Core Principle: Precursor Gas to Solid Film
CVD is a process that transforms a volatile chemical precursor, introduced as a gas, into a solid material that is deposited as a thin film onto a substrate. This occurs within a vacuum chamber when the gas is energized, causing it to react or decompose.
The Fundamental Steps
All CVD processes, including MPCVD, generally follow a sequence of six key events:
- Transport: The precursor gases are moved into the reaction chamber.
- Adsorption: The gas molecules attach to the surface of the substrate.
- Reaction: The adsorbed molecules react on the hot surface, breaking down into the desired film material and byproducts.
- Diffusion: The film-forming atoms move across the surface to stable nucleation sites.
- Growth: The atoms bond together, forming a continuous thin film layer by layer.
- Desorption: Gaseous byproducts detach from the surface and are transported away by the vacuum system.
The MPCVD Difference: Harnessing Microwave Plasma
MPCVD refines the general CVD process by using a specific energy source—microwaves—to drive the chemical reactions. This provides a level of control that is essential for producing high-performance materials.
Generating the Plasma
In an MPCVD system, a precursor gas (like a methane-hydrogen mix for diamond growth) is introduced into a vacuum chamber. Microwave radiation is then channeled into the chamber, energizing the gas and stripping electrons from the atoms and molecules, instantly creating plasma.
The High-Energy Environment
This plasma is a dynamic "soup" of charged particles, including electrons, ions, neutral atoms, and molecular fragments. The intense microwave energy creates highly reactive carbon species and atomic hydrogen, which are the critical building blocks for diamond film deposition.
The Key to Quality: High Electron Temp, Low Gas Temp
A defining feature of MPCVD is the massive temperature difference it creates. The free electrons in the plasma can reach temperatures over 5000 K, while the overall gas and substrate temperature can remain much lower, often around 1000 K.
This is highly advantageous. The energetic electrons efficiently break down the precursor gases to create reactive species, but the lower substrate temperature prevents damage to the material being coated and reduces defects in the growing film.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
Like any specialized technology, MPCVD offers distinct benefits but also comes with considerations that must be weighed for any given application.
Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Uniformity
Because the reaction is driven by clean microwave energy rather than direct heating elements, contamination is minimized, leading to exceptionally pure films. The gaseous nature of the process allows it to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with a highly uniform thickness, as it is not a line-of-sight technique.
Advantage: Ideal for Sensitive Substrates
The ability to maintain a lower substrate temperature makes MPCVD suitable for coating materials that cannot withstand the extreme heat of other deposition methods. This expands its applicability to a wider range of substrates.
Consideration: System Complexity
MPCVD reactors are sophisticated systems that require precise control over microwave power, gas flow, pressure, and temperature. This complexity can translate to higher initial equipment costs and a need for specialized operational expertise compared to simpler thermal CVD setups.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a deposition method requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and crystal quality (e.g., electronic-grade diamond): MPCVD is a leading choice due to its clean plasma environment and precise control over growth chemistry.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex component uniformly: The non-line-of-sight nature of MPCVD ensures even coverage that is difficult to achieve with physical deposition methods.
- If your primary focus is depositing on a heat-sensitive material: The lower substrate temperatures used in MPCVD offer a significant advantage over high-temperature CVD or combustion-based methods.
Ultimately, understanding the mechanism of MPCVD empowers you to select the right tool for creating advanced materials with exacting specifications.
Summary Table:
| MPCVD Process Step | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Gas Introduction | Precursor gases (e.g., methane/hydrogen) enter the vacuum chamber. |
| Plasma Generation | Microwave energy ionizes the gas, creating a high-energy plasma. |
| Surface Reaction | Reactive species from the plasma deposit onto the substrate surface. |
| Film Growth | Atoms bond layer-by-layer, forming a high-purity, uniform thin film. |
| Byproduct Removal | Gaseous byproducts are pumped away by the vacuum system. |
Ready to integrate MPCVD technology into your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced deposition systems. Our expertise can help you achieve the ultimate purity and uniformity required for cutting-edge materials like synthetic diamond. Whether your project demands electronic-grade films or complex 3D coatings, we provide the solutions and support to ensure your success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our MPCVD systems can accelerate your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries



















