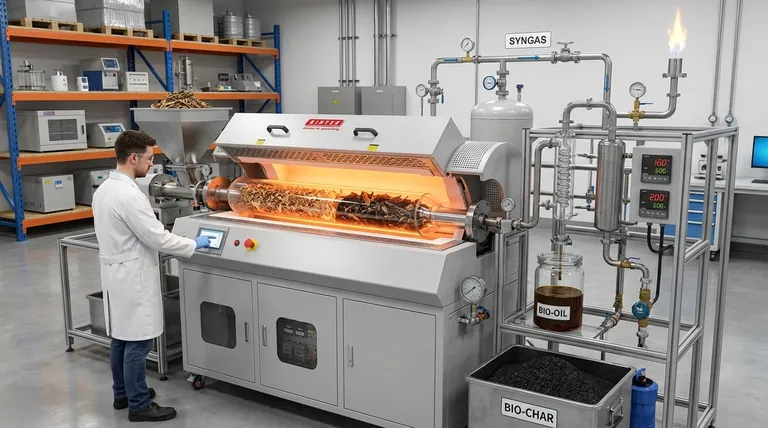
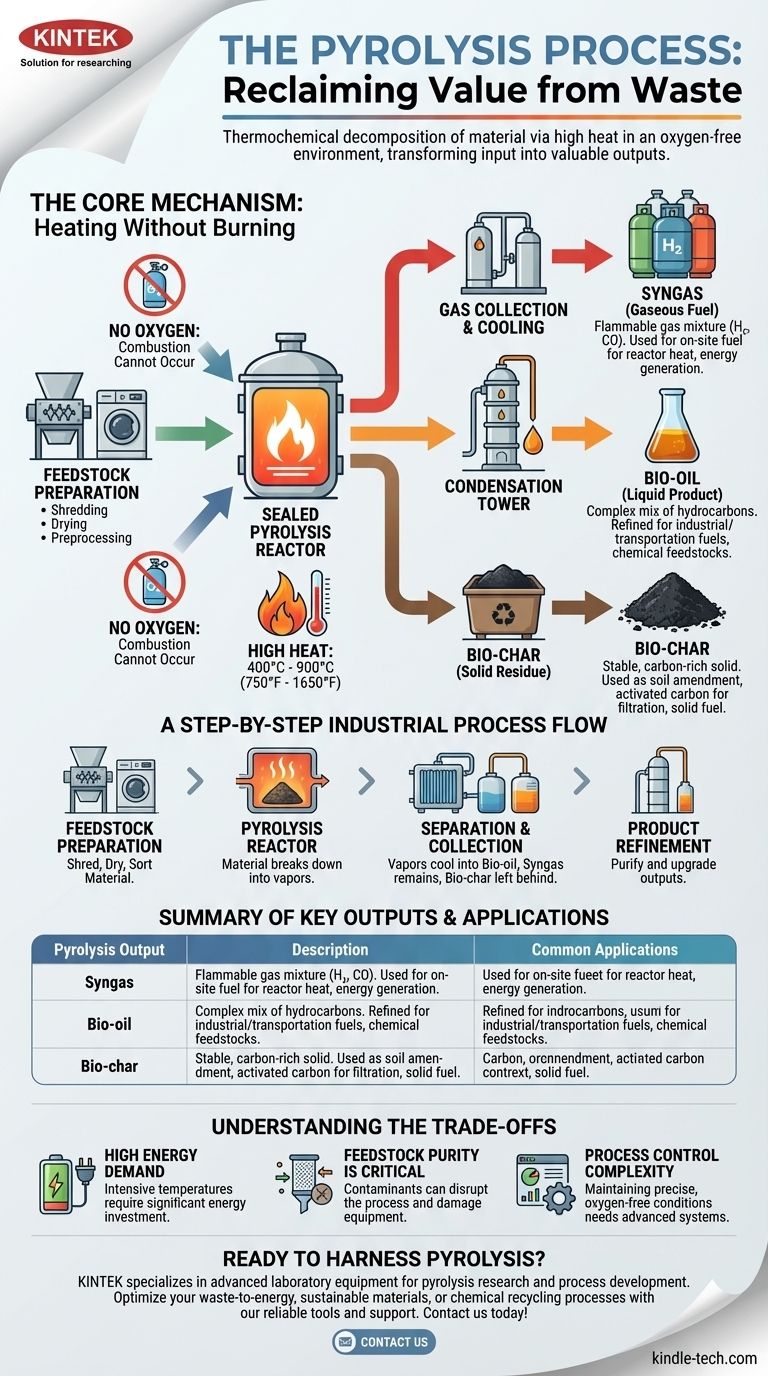
At its core, pyrolysis is the thermochemical decomposition of material through intense heat in a completely oxygen-free environment. Unlike incineration, which burns material, pyrolysis uses heat to break down complex substances like plastics or biomass into their fundamental chemical components. This process transforms a single input material into three distinct and valuable outputs: a gas mixture (syngas), a liquid (bio-oil), and a solid (bio-char).
The true value of pyrolysis is not in destroying waste but in reclaiming it. It is a controlled transformation process that unlocks the stored energy and chemical value within materials that would otherwise end up in a landfill.

How Pyrolysis Works: The Core Mechanism
To understand pyrolysis, you must first understand its core principle: heating without burning. This distinction is the key to the entire process.
The Essential Condition: High Heat, No Oxygen
Pyrolysis occurs inside a sealed reactor heated to temperatures between 400°C and 900°C (750°F to 1650°F).
Crucially, all oxygen is evacuated from this chamber. Without oxygen, combustion cannot occur. Instead of burning, the intense heat forces the chemical bonds within the material to break, a process known as thermal cracking.
The Feedstock Breakdown
The input material, or feedstock, is broken down into smaller, less complex molecules.
In biomass, the heat decomposes its primary components: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. For plastics, the long, repeating polymer chains are cracked into shorter hydrocarbon chains.
The Optional Role of Catalysts
In some advanced pyrolysis processes, a catalyst is introduced into the reactor. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up or directs a chemical reaction without being consumed by it.
Using a catalyst can help steer the process to maximize a specific output, such as increasing the yield and quality of bio-oil from plastic waste.
A Step-by-Step Look at an Industrial Process
While the core science is simple, a commercial pyrolysis plant operates through a precise, multi-stage process. Using plastic pyrolysis as an example, the steps are clear.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
The raw material is not fed directly into the reactor. It must be prepared to ensure efficiency and purity.
This involves shredding the material to increase surface area, drying it to remove moisture that hinders the process, and preprocessing it to separate out any non-pyrolyzable contaminants like metals or glass.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reactor
The prepared feedstock is fed into the oxygen-free reactor and heated. As the material breaks down, it vaporizes into a mixture of gases and aerosols.
Step 3: Separation and Collection
This hot vapor mixture is then channeled out of the reactor. As it cools, the different components are separated.
The condensable vapors cool into a liquid (bio-oil). The non-condensable gases remain as syngas. The solid, carbon-rich material left behind in the reactor is the bio-char.
Step 4: Product Refinement
The raw outputs are often purified to meet specific market standards. Bio-oil may be distilled to separate it into different fuel grades, and bio-char might be processed further to create high-grade activated carbon.
Understanding the Three Key Outputs
The success of a pyrolysis operation depends on the value derived from its three distinct products.
Syngas (The Gaseous Fuel)
Syngas is a mixture of flammable gases, primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide. It is often used on-site as fuel to provide the very heat needed for the pyrolysis reactor, dramatically improving the plant's overall energy efficiency.
Bio-oil (The Liquid Product)
Also known as pyrolysis oil, this liquid is a complex mix of hydrocarbons. It can be refined for use as an industrial fuel or further processed into more valuable products like transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks.
Bio-char (The Solid Residue)
Bio-char is a stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal. It has excellent applications as a soil amendment to improve soil health and water retention, as a base material for producing activated carbon for filtration, or simply as a solid fuel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pyrolysis is a powerful technology, but it is not without its challenges. Objectivity requires acknowledging its operational realities.
High Energy Demand
Achieving and maintaining temperatures up to 900°C is highly energy-intensive. While using the syngas output can offset this, the initial energy investment and system design are significant considerations.
Feedstock Purity is Critical
The efficiency and output quality of pyrolysis are highly sensitive to the composition of the feedstock. Contaminants can disrupt the chemical reactions or damage equipment, making the initial preparation and sorting steps vital but costly.
Process Control Complexity
Operating a pyrolysis reactor is a delicate balance. Maintaining a completely oxygen-free environment while precisely controlling temperature requires sophisticated, reliable, and expensive monitoring and safety systems.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding pyrolysis allows you to see its potential application from several different angles.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is a premier technology for converting non-recyclable plastics and organic waste into valuable resources, offering a direct alternative to landfills.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: The syngas and bio-oil outputs represent a decentralized energy source, capable of powering the system itself or contributing energy back to the grid.
- If your primary focus is sustainable materials: The bio-char produced is a valuable commodity for agriculture and manufacturing, serving as a key ingredient for soil enhancement or advanced filtration products.
By understanding pyrolysis not as destruction but as controlled deconstruction, we can effectively reclaim value from waste and engineer more sustainable systems.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Output | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Flammable gas mixture (H₂, CO) | On-site fuel for reactor heat, energy generation |
| Bio-oil | Liquid hydrocarbon mixture | Industrial fuel, transportation fuel, chemical feedstocks |
| Bio-char | Solid, carbon-rich residue | Soil amendment, activated carbon for filtration, solid fuel |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and process development. Whether you are exploring waste-to-energy solutions, sustainable materials, or chemical recycling, our experts can provide the reliable tools and support you need to optimize your pyrolysis processes. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve your sustainability and research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing



















