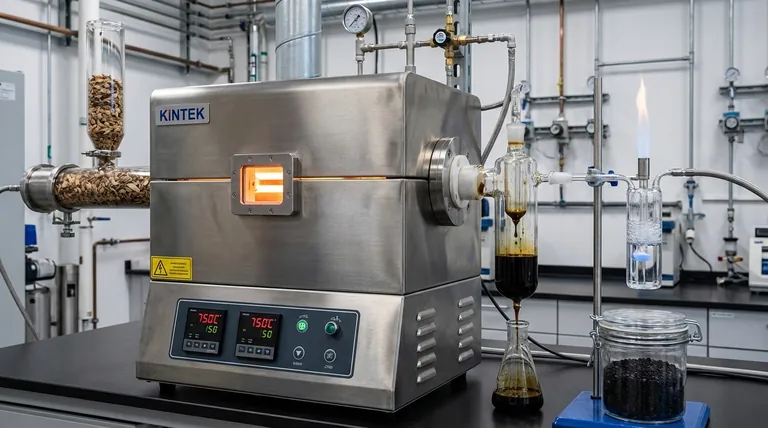
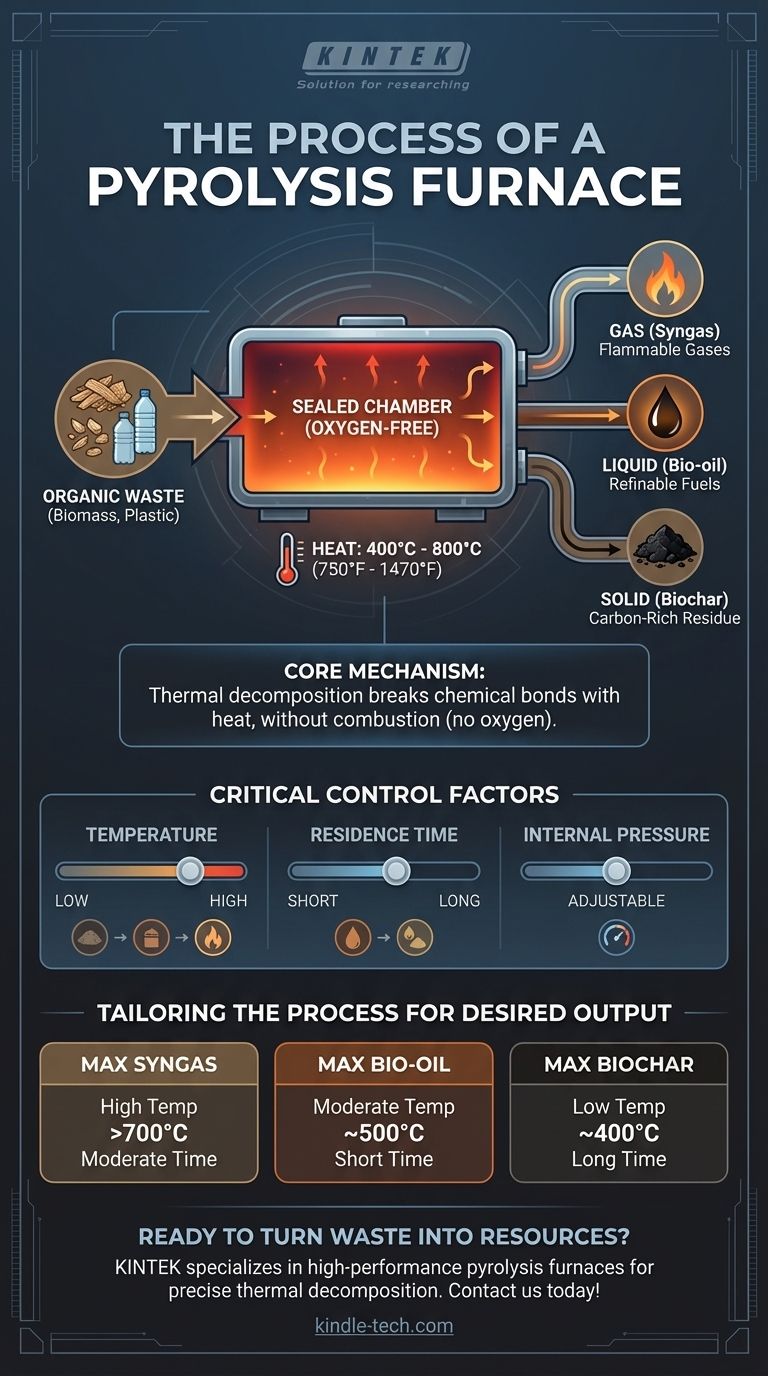
At its core, a pyrolysis furnace executes a process of thermal decomposition. It heats organic materials, such as biomass or plastic waste, to very high temperatures within a sealed, oxygen-free chamber, causing the material to break down into simpler, more valuable substances rather than burn.
A pyrolysis furnace is not an incinerator; it is a chemical reactor. Its primary function is to use controlled heat in an oxygen-starved environment to transform low-value organic waste into a mix of valuable gases, liquids, and a solid carbon-rich residue.

The Core Mechanism of Pyrolysis
The process hinges on a simple principle: heat can break chemical bonds. By removing oxygen, the furnace prevents combustion and instead forces the material to decompose into its fundamental components.
The Reaction Chamber
The entire process takes place in a sealed vessel. This containment is critical to ensure no oxygen can enter, which would otherwise cause the material to simply burn and produce ash instead of the desired outputs.
The Role of Heat (Without Oxygen)
Heating elements raise the temperature inside the chamber, typically between 400°C and 800°C (750°F and 1470°F). This intense heat, without the presence of oxygen, provides the energy needed to break down complex organic molecules into smaller, more stable ones.
The Three Key Products
The decomposition results in three distinct outputs that are collected separately:
- Gas: A mixture of flammable gases (often called syngas), including hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide, which can be used as fuel.
- Liquid: A dark, viscous liquid (pyrolysis oil or bio-oil) that can be refined into transportation fuels or used to produce chemicals.
- Solid: A stable, carbon-rich solid (char or biochar) that can be used as activated carbon for filtration or as a soil amendment.
Critical Factors for Controlling the Process
The final ratio and quality of gas, liquid, and solid products are not accidental. They are the direct result of carefully managing the conditions inside the furnace.
Furnace Temperature
Temperature is the most significant control factor. Higher temperatures tend to favor the production of gas, while lower temperatures and slower heating rates favor the production of solid char.
Residence Time
This refers to how long the material stays inside the hot chamber. A longer residence time allows for more complete decomposition, generally increasing the yield of gas and decreasing the yield of liquid and solid products.
Internal Pressure
The pressure inside the furnace also influences the process. While many systems operate at or near atmospheric pressure, adjusting it can affect heat transfer and the characteristics of the final products.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Modern Enhancements
Operating a pyrolysis furnace involves balancing competing priorities to achieve a specific goal. The process is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
The Goal: Product Optimization
The central trade-off is optimizing the parameters—temperature, pressure, and residence time—to maximize the yield of your desired product. A setup designed to produce maximum biochar will be different from one designed to produce maximum syngas.
Operational Challenges
Proper control and maintenance are crucial for both safety and efficiency. Uncontrolled reactions can be hazardous, and inefficient operation leads to poor product quality and wasted energy. This includes managing the removal of the solid char, a process sometimes called decoking.
Technological Improvements
Modern furnaces incorporate advanced technologies to improve performance. These include smart predictive models to anticipate outcomes, improved burner management for precise temperature control, and automated systems for processes like decoking to reduce downtime.
Tailoring the Process to Your Desired Output
The way you operate a pyrolysis furnace depends entirely on your end goal. The process is highly adaptable if you understand the key levers.
- If your primary focus is gas production (Syngas): Operate at higher temperatures (above 700°C) with a moderate residence time to maximize the thermal cracking of all components into gas.
- If your primary focus is liquid fuel (Bio-oil): Use a moderate temperature (around 500°C) and a very short residence time (fast pyrolysis) to quickly vaporize and then condense the material into liquid.
- If your primary focus is solid carbon (Biochar): Employ lower temperatures (around 400°C) and a long residence time (slow pyrolysis) to allow the carbon to form a stable, solid structure.
By precisely controlling these conditions, a pyrolysis furnace transforms the challenge of organic waste into an opportunity for creating value.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition of organic materials in an oxygen-free chamber. |
| Temperature Range | 400°C to 800°C (750°F to 1470°F). |
| Primary Products | Syngas (gas), Bio-oil (liquid), Biochar (solid). |
| Main Control Factors | Temperature, Residence Time, Pressure. |
Ready to turn your organic waste into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including pyrolysis furnaces designed for precise thermal decomposition. Whether your goal is to maximize syngas, bio-oil, or biochar production, our solutions offer the control and reliability your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how our pyrolysis technology can enhance your research and waste valorization projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning



















