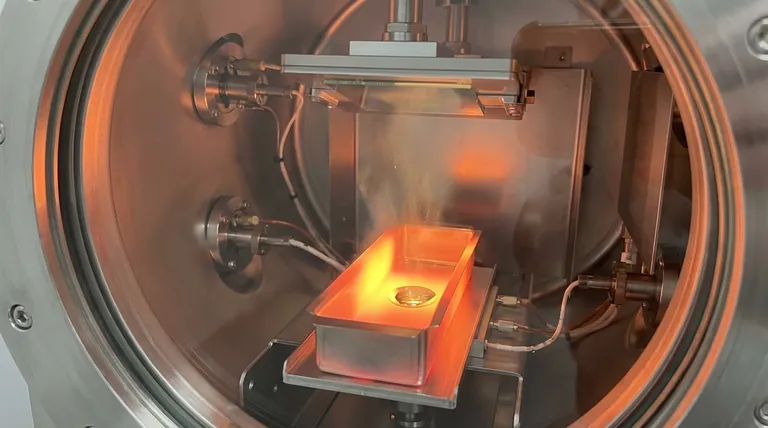
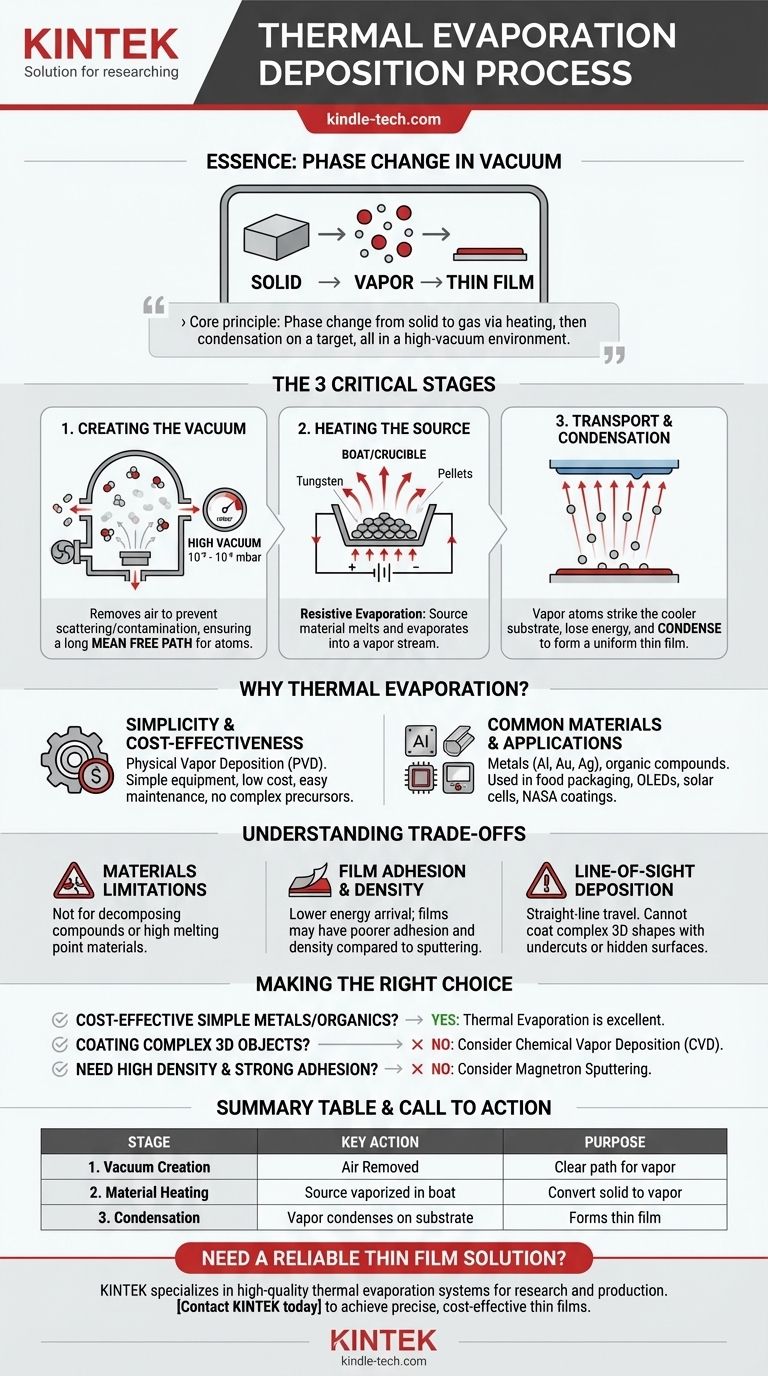
In essence, thermal evaporation deposition is a straightforward process where a material is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it turns into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the chamber and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming an extremely thin, solid film. It is one of the oldest and most fundamental methods used in the thin film industry.
The core principle of thermal evaporation is a simple phase change: a source material is converted from solid to gas through heating, and then back to solid through cooling and condensation on a target surface. This entire process must occur in a vacuum to succeed.
The Core Mechanism: From Solid to Thin Film
The thermal evaporation process can be broken down into three critical stages that work in sequence to build the film layer by layer.
Creating the Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place within a sealed chamber under a high vacuum, typically at pressures between 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar.
This vacuum is not incidental; it is essential. It removes air and other gas molecules that would otherwise collide with the vaporized material, scattering the atoms and contaminating the final film. A high vacuum ensures a long "mean free path," allowing atoms to travel directly from the source to the substrate without interference.
Heating the Source Material
The solid material to be deposited, often in the form of pellets or wire, is placed in a small container known as a "boat" or "crucible."
This boat is made of a material with a very high melting point and electrical resistance, such as tungsten. A high electrical current is passed through the boat, causing it to heat up rapidly due to its resistance. This technique is often called resistive evaporation.
As the boat heats, the source material melts and then evaporates, releasing a stream of vapor into the chamber.
Vapor Transport and Condensation
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the source toward the substrate, which is strategically positioned above it.
When these energetic atoms strike the cooler surface of the substrate, they rapidly lose their thermal energy. This causes them to condense back into a solid state, gradually building up a thin and uniform film on the substrate's surface.
Why This Method is Widely Used
Thermal evaporation's longevity is a testament to its effectiveness and simplicity in a range of important applications.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other deposition technologies, thermal evaporation is relatively simple. It is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method that relies on basic thermodynamic principles.
It does not require complex chemical precursors or reactive gases, which often makes the equipment less expensive and easier to operate and maintain.
Common Materials and Applications
This technique is highly effective for depositing thin films of metals and certain organic compounds.
It is frequently used to apply metal layers like aluminum for food packaging and gold or silver for electronics. Other key applications include creating metal bonding layers in OLED displays and solar cells, as well as producing reflective coatings for materials used in NASA spacesuits and emergency blankets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, thermal evaporation is not the ideal solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Limitations on Materials
The process is limited to materials that will evaporate upon heating without decomposing. It is not suitable for compounds that break down at high temperatures or for materials with extremely high boiling points (refractory metals), which are difficult to evaporate thermally.
Film Adhesion and Density
The atoms in thermal evaporation arrive at the substrate with relatively low kinetic energy. This can sometimes result in films that are less dense and have poorer adhesion to the substrate compared to films created by higher-energy processes like sputtering.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, thermal evaporation is a "line-of-sight" technique. It cannot easily coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces. The film will only form on areas with a direct, unobstructed path from the source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the material properties and film quality you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple metals or organics: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, straightforward choice that delivers reliable results.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D object uniformly: You will need to consider a non-line-of-sight technique like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
- If your primary focus is creating a highly dense, durable film with strong adhesion: A higher-energy PVD process like magnetron sputtering is likely a better alternative.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation is a foundational thin-film technique that excels in applications where its simplicity, speed, and efficiency are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vacuum Creation | Air is removed from the chamber. | Creates a clear path for vapor atoms to travel without collisions. |
| 2. Material Heating | Source material is heated in a boat until it vaporizes. | Converts the solid material into a vapor for deposition. |
| 3. Condensation | Vapor travels to and condenses on a cooler substrate. | Forms a thin, solid film layer by layer. |
Need a reliable thin film coating solution for your lab?
Thermal evaporation is a cornerstone technique for depositing metals like aluminum, gold, and silver. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems, to meet your specific research and production needs.
Let us help you achieve precise and cost-effective thin films. Our experts can guide you to the right equipment for your application, whether it's for electronics, OLEDs, or solar cells.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What substrates are used for thin film deposition? Choosing the Right Foundation for Your Application
- How does e-beam deposition work? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- What are the applications of evaporation in industries? From Wastewater to Electronics
- What is the process of evaporation deposition? A Guide to High-Vacuum Thin Film Coating
- What is the process of evaporation coating? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the evaporation technique for deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- How does an electron beam evaporator work? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of e-beam evaporation? Achieve High-Purity, High-Rate Thin Film Deposition



















