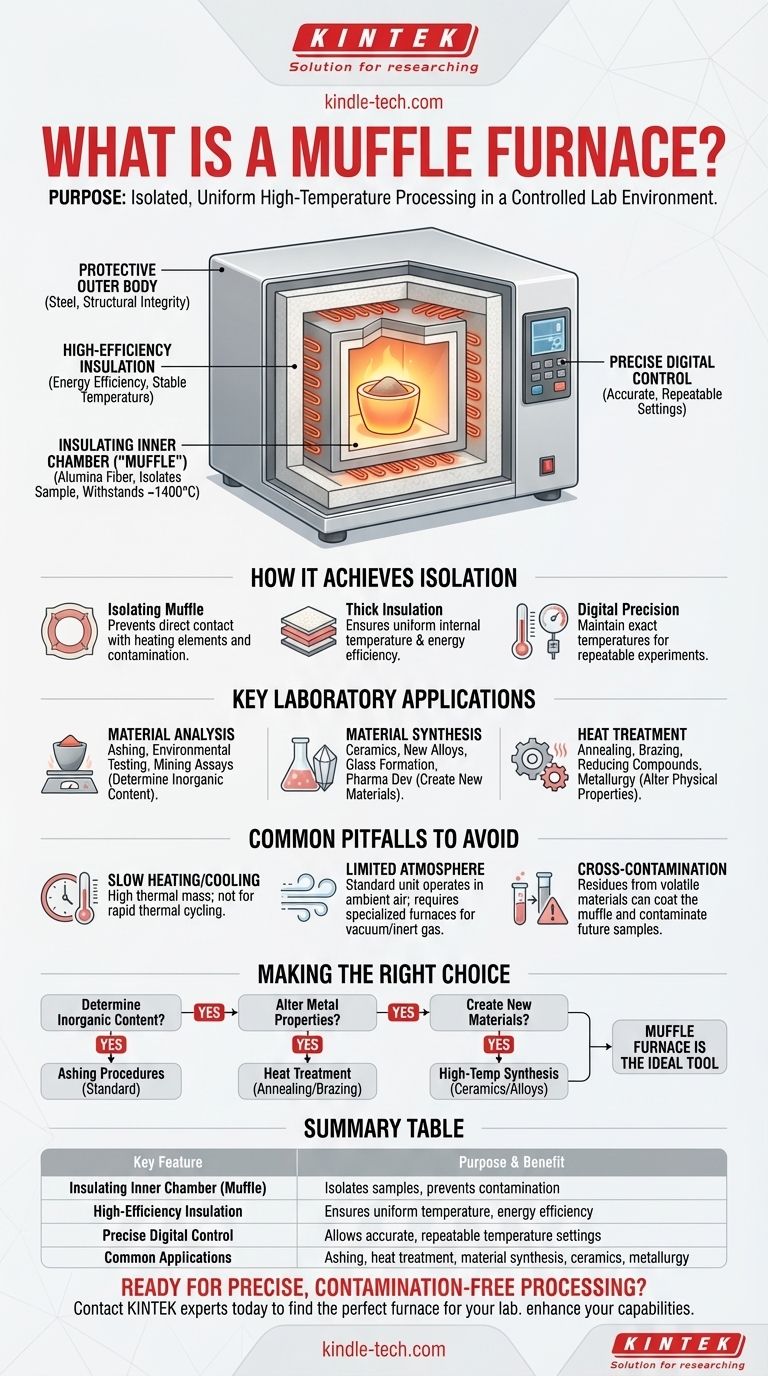
The primary purpose of a muffle furnace is to heat samples to extremely high temperatures inside a self-contained, insulated chamber. Its defining feature is that the material being tested is isolated from the direct heat source, which prevents contamination and ensures highly uniform temperature distribution.
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; it is a controlled environment. Its key advantage lies in the "muffle"—an insulating retort or chamber that protects samples from direct heating elements, providing uniform temperature and preventing contamination during processes like ashing, heat-treating, or material synthesis.

How a Muffle Furnace Achieves High-Temperature Isolation
The effectiveness of a muffle furnace comes from its simple but robust construction, where each component serves a critical function.
The Insulating Inner Chamber (The "Muffle")
The core of the furnace is the inner chamber, or "muffle," which is constructed from a high-purity ceramic material like alumina fiber.
This ceramic design is crucial because it can withstand extremely high temperatures, often up to 1400°C, without melting or degrading. It is this chamber that isolates the sample.
High-Efficiency Insulation
Surrounding the inner ceramic muffle is a thick layer of insulation.
This material prevents heat from escaping into the lab, ensuring both energy efficiency and highly stable internal temperatures during operation.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern muffle furnaces are managed by a digital controller.
This component allows the user to set and maintain a precise temperature required for a specific scientific process, ensuring repeatability and accuracy in experiments.
The Protective Outer Body
An outer chamber, typically made of steel, houses all the internal components. This provides structural integrity and protects the operator from the extreme internal heat.
Key Laboratory Applications
The ability to provide pure, uniform, high-temperature heat makes the muffle furnace a versatile tool across many scientific and industrial fields.
Material Analysis and Quantification
Many processes use a muffle furnace to burn away organic components to analyze what remains.
Applications include ashing samples to determine inorganic content, performing environmental testing on materials, and conducting mining assays.
Material Synthesis and Transformation
The furnace creates an ideal environment for forming new materials.
This is essential for research in ceramics, creating new alloys, glass formation, and even specialized applications like nuclear fuel disposal and pharmaceutical development.
Heat Treatment and Conditioning
The controlled heat can be used to alter the physical properties of a material.
Common industrial uses include heat treatment of metals, brazing, reducing compounds, and general metallurgy research.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every high-temperature application. Understanding its limitations is key to proper use.
Slow Heating and Cooling Cycles
The same heavy insulation that makes the furnace efficient also gives it significant thermal mass.
This means it cannot change temperature quickly. It is not suitable for experiments that require rapid thermal cycling.
Limited Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air.
If your process requires a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen), you will need a more specialized and expensive type of furnace.
Cross-Contamination Between Samples
The muffle protects samples from the heating elements but not from each other.
If volatile materials are heated, residues can coat the inside of the ceramic chamber and potentially contaminate future samples run in the same furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a muffle furnace depends entirely on whether your goal requires uniform, isolated heat.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample: A muffle furnace is the standard and essential instrument for ashing procedures.
- If your primary focus is altering the properties of a metal: The furnace provides the controlled, high-temperature environment necessary for heat-treating processes like annealing or brazing.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials like ceramics or alloys: The uniform, isolated heat is ideal for the high-temperature synthesis of these materials.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the indispensable tool when your process demands pure and uniform high-temperature heat in a controlled chamber.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Purpose & Benefit |
|---|---|
| Insulating Inner Chamber (Muffle) | Isolates samples from heating elements, preventing contamination. |
| High-Efficiency Insulation | Ensures uniform temperature distribution and energy efficiency. |
| Precise Digital Control | Allows for accurate, repeatable temperature settings for experiments. |
| Common Applications | Ashing, heat treatment, material synthesis, ceramics, and metallurgy. |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free high-temperature processing in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment, including high-performance muffle furnaces designed for accuracy and durability. Whether your work involves material analysis, heat treatment, or synthesis, our solutions are built to meet the rigorous demands of your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific application and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- What is the main purpose of a furnace? A Guide to Heating, Comfort, and Material Transformation
- Why the melting temperature of ceramic is higher than for most metals? Unpacking Atomic Bond Strength
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and induction furnace? Choosing the Right Heat Source for Your Lab
- What is the meaning of debinding? Master the Critical Step to High-Performance Parts



















