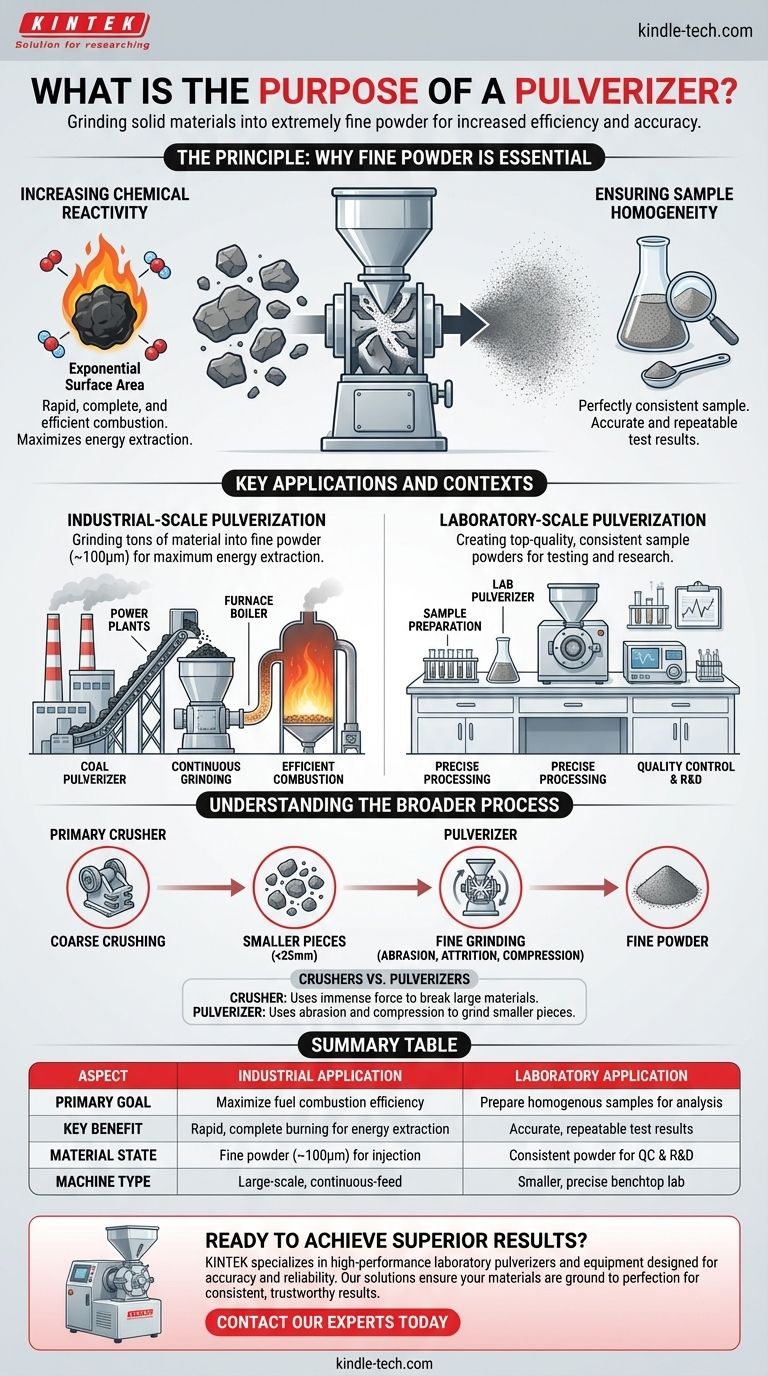
In short, the purpose of a pulverizer is to grind solid materials into an extremely fine powder. This process, known as pulverization, dramatically increases the material's surface area. This is a critical step for a wide range of applications, from ensuring efficient fuel combustion in power plants to preparing precise samples for laboratory analysis.
A pulverizer's core function isn't just to make things smaller, but to fundamentally change a material's properties to achieve a specific goal. Whether for maximizing energy extraction or creating a perfectly consistent sample for testing, pulverization enables greater reactivity, consistency, and efficiency.
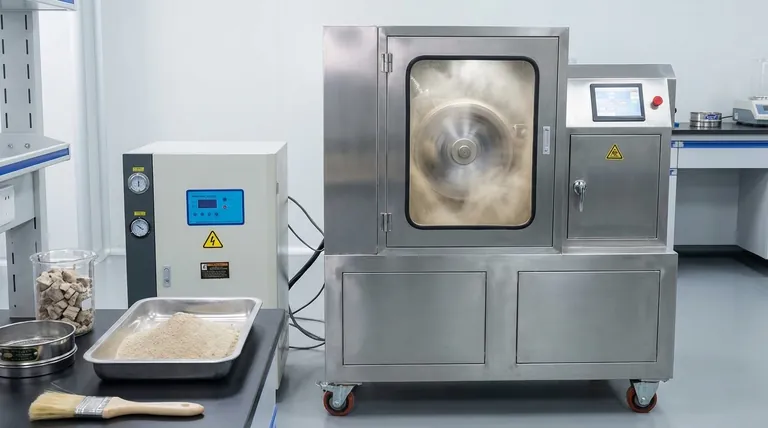

The Principle: Why Fine Powder is Essential
The value of pulverization comes down to a simple concept: increasing the available surface area of a material. Grinding a solid lump into a fine dust exposes vastly more of that material to its environment.
Increasing Chemical Reactivity
When a material like coal is pulverized, its surface area increases exponentially. This allows oxygen to interact with the fuel particles almost instantaneously.
The result is a far more rapid, complete, and efficient combustion compared to trying to burn a larger piece of coal, which would burn slowly and unevenly from the outside in.
Ensuring Sample Homogeneity
In a laboratory setting, the goal is often quality control or research. Analysts need to be certain that the tiny sample they test is a perfect representation of the entire batch.
Pulverizing the material creates a homogenous powder, ensuring that any portion taken for analysis has the exact same composition as the rest. This is fundamental for accurate and repeatable test results.
Key Applications and Contexts
While the principle is the same, the application of pulverization is split between two main contexts: large-scale industrial processes and precise laboratory work.
Industrial-Scale Pulverization
The most common industrial example is the coal pulverizer used in power plants. These are massive machines designed to continuously grind tons of coal into a fine powder (around 100μm).
This powder is then blown into a boiler, where it ignites and burns with high efficiency, maximizing the energy extracted from the fuel.
Laboratory-Scale Pulverization
A lab pulverizer is a smaller, more precise instrument used for sample preparation. It allows researchers and technicians to quickly and simply process a wide variety of materials.
The goal here is not bulk processing, but the creation of top-quality, consistent sample powders for quality control testing and R&D trials.
Understanding the Broader Process
It's important to understand that a pulverizer is often the final stage in a multi-step size reduction process. It is not designed to handle large, raw chunks of material.
A Final Step in Size Reduction
Typically, a sample is first broken down by a primary crusher, such as a jaw or hammer crusher. These machines handle the initial, coarse crushing.
Only after the material is reduced to a manageable size (e.g., smaller than 25mm) is it fed into a pulverizer for the final, fine grinding.
Crushers vs. Pulverizers
A crusher uses immense force and impact to break large rocks or materials into smaller pieces. A pulverizer takes these smaller pieces and uses abrasion, attrition, and compression to grind them into a fine powder.
Applying This to Your Goal
The need for a pulverizer is dictated entirely by your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency in combustion: You need an industrial pulverizer to create fine fuel particles that ignite quickly and burn completely.
- If your primary focus is accurate material analysis: You need a laboratory pulverizer to prepare homogenous, representative samples for quality control or research.
- If your primary focus is processing large, raw material: You must recognize that a pulverizer is the final step, requiring a primary crusher to do the initial size reduction first.
Ultimately, a pulverizer is a precision tool used to unlock the full potential of a solid material by transforming its physical form.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Industrial Application | Laboratory Application |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize fuel combustion efficiency | Prepare homogenous samples for analysis |
| Key Benefit | Rapid, complete burning for energy extraction | Accurate, repeatable test results |
| Material State | Fine powder (~100μm) for injection into boilers | Consistent powder for quality control & R&D |
| Machine Type | Large-scale, continuous-feed pulverizers | Smaller, precise benchtop lab pulverizers |
Ready to achieve superior sample preparation or material processing?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory pulverizers and equipment designed for accuracy and reliability. Whether you are in quality control, research, or need to prepare homogenous samples, our solutions ensure your materials are ground to perfection for consistent, trustworthy results.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal pulverizing solution for your specific needs and unlock the full potential of your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Jar Ball Mill with Alumina Zirconia Grinding Jar and Balls
- lab cryogenic grinding use liquid-nitrogen for pulverizing plastic raw materials and heat sensitive materials
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of a grinding machine? Achieve Superior Precision and Surface Finishes
- How does a Vibratory Mill improve niobium recovery efficiency? Optimize Waste Pre-treatment for Maximum Yield
- Does milling reduce particle size? Achieve Precise Control Over Your Material's Properties
- What is a ceramic mill? A Guide to Rust-Proof, Flavor-Pure Grinding
- What is the difference between grinding and pulverizing? Achieve the Perfect Particle Size for Your Application



















