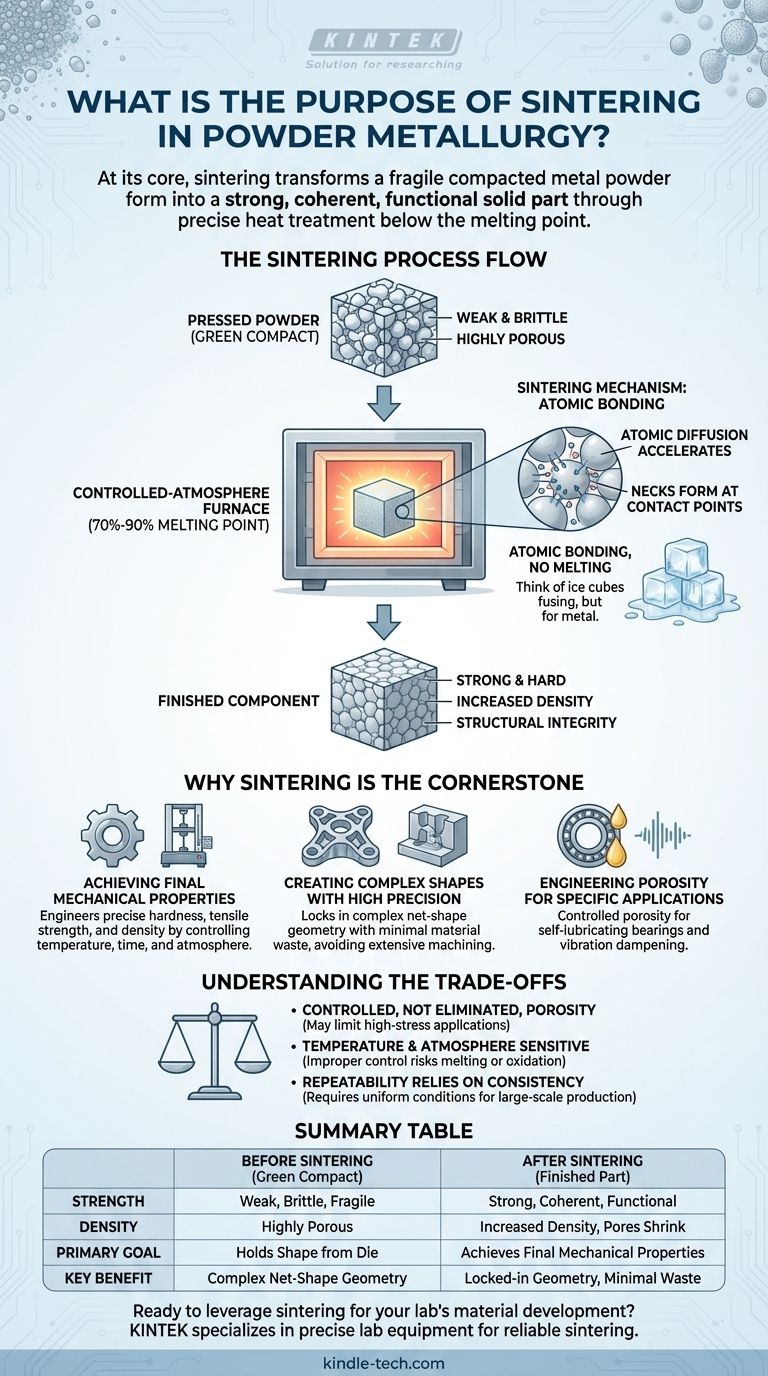
At its core, the purpose of sintering is to transform a compacted, fragile metal powder form into a strong, coherent, and functional solid part. This is achieved through a precise heat treatment process that occurs below the material's melting point, causing the individual powder particles to bond together and densify.
Sintering is the critical step in powder metallurgy that imparts strength, hardness, and final mechanical properties to a component. It is not about melting the metal, but rather using heat to fuse particles together, turning a loosely-held "green compact" into a finished, engineered product.

From Pressed Powder to Solid Component
Sintering is the bridge between a shaped powder and a usable metal part. Understanding this transformation requires looking at the state of the material before and after the process.
The "Green Compact": The Starting Point
After metal powder is pressed into a die, the resulting shape is called a green compact. This part has the desired geometry but is mechanically weak and brittle, held together only by the interlocking of the particles.
It is highly porous and lacks the strength and integrity required for any functional application.
The Sintering Mechanism: Atomic Bonding Without Melting
The green compact is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature typically between 70% and 90% of the metal's melting point.
At this elevated temperature, atomic diffusion accelerates dramatically. Atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles, causing the contact points to grow into solid "necks."
Think of two ice cubes in a glass of water. Even below freezing, they will slowly fuse together at their contact points. Sintering achieves a similar effect for metal particles, but much more rapidly and completely.
The Result: Strength, Density, and Integrity
As the particles bond and fuse, the voids or pores between them shrink, increasing the part's density. This process of atomic bonding is what gives the component its final strength, hardness, and structural integrity.
The part emerges from the sintering furnace as a solid metallic component, ready for use or for secondary finishing operations.
Why Sintering is the Cornerstone of Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is not just a heating step; it is the process that unlocks the unique advantages of the powder metallurgy method. Without it, you simply have a fragile brick of pressed powder.
Achieving Final Mechanical Properties
The primary goal of sintering is to develop the required physical and mechanical properties. By carefully controlling the temperature, time, and furnace atmosphere, manufacturers can precisely engineer the final hardness, tensile strength, and density of the part.
Creating Complex Shapes with High Precision
Powder metallurgy excels at producing complex external and internal shapes directly from the mold. Sintering locks in this geometry, solidifying the net-shape part with minimal material waste.
This avoids the extensive machining and material loss associated with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Engineering Porosity for Specific Applications
While sintering reduces porosity, it doesn't always eliminate it. This can be a significant advantage. The remaining interconnected pores can be filled with oil to create self-lubricating bearings.
The inherent porosity also gives sintered parts excellent vibration-dampening characteristics, a benefit in many mechanical systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that create both advantages and limitations.
Controlled, Not Eliminated, Porosity
The residual porosity in most sintered parts means they may not achieve the same maximum strength or ductility as a fully dense wrought or cast component. This makes them unsuitable for certain high-stress structural applications.
Temperature and Atmosphere are Critical
The sintering process is highly sensitive. Improper temperature control can lead to incomplete bonding or, in a worst-case scenario, melting and distortion.
Furthermore, the furnace atmosphere must be tightly controlled to prevent oxidation, which would inhibit proper bonding and ruin the component's properties.
Repeatability Relies on Consistency
The success of sintering for large-scale production hinges on extreme consistency in the powder, compaction pressure, and furnace conditions. Any deviation can lead to variations in the final part's dimensions and mechanical performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is the essential process that gives powder metallurgy its value. Your specific goal determines which aspect of sintering is most critical.
- If your primary focus is complex, net-shape parts: Sintering is the key to solidifying intricate designs with high precision and minimal material waste.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: The process enables high repeatability for large volumes with lower energy consumption compared to casting, as the metal is never fully melted.
- If your primary focus is unique material properties: Sintering enables the creation of parts with controlled porosity for applications like self-lubrication and vibration dampening.
Ultimately, sintering is the metallurgical engine that converts precisely shaped powder into a high-performance engineered component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Before Sintering (Green Compact) | After Sintering (Finished Part) |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Weak, brittle, fragile | Strong, coherent, functional |
| Density | Highly porous | Increased density, pores shrink |
| Primary Goal | Holds shape from die | Achieves final mechanical properties |
| Key Benefit | Complex net-shape geometry | Locked-in geometry, minimal waste |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material development? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable sintering processes. Whether you are researching new materials or producing high-performance components, our solutions ensure consistent results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's powder metallurgy and sintering needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















