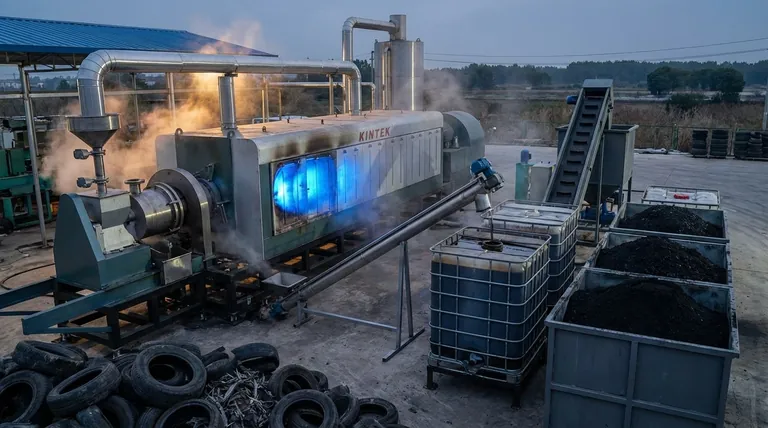
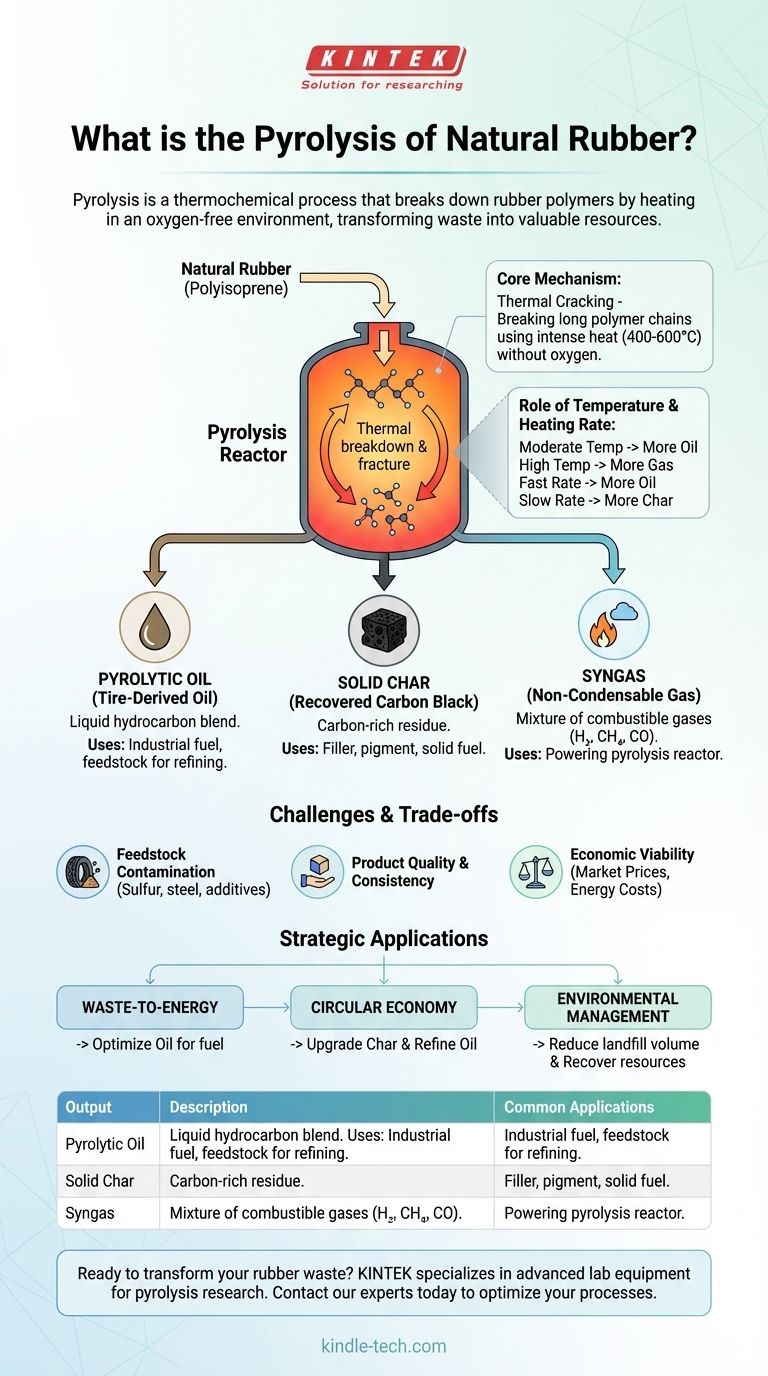
In essence, the pyrolysis of natural rubber is a thermochemical process that breaks down the complex polymer structure of rubber by heating it in an environment without oxygen. Instead of burning, the rubber decomposes into a mixture of a liquid oil, a solid char, and a combustible gas. This method is a cornerstone of modern tire recycling and waste rubber management.
The core purpose of rubber pyrolysis is not destruction, but transformation. It is a controlled process designed to deconstruct waste rubber into valuable raw materials, converting an environmental liability into potential assets like fuel and industrial carbon.

The Core Mechanism: How Rubber Decomposes Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is a fundamentally different process from incineration. While incineration uses oxygen to burn material for heat, pyrolysis uses heat to break chemical bonds in the absence of oxygen, preserving the chemical value of the byproducts.
The Chemical Breakdown of Polyisoprene
Natural rubber is primarily made of long polymer chains of polyisoprene. Applying intense heat (typically 400-600°C) without oxygen causes these long chains to vibrate and fracture into a wide array of smaller, less complex hydrocarbon molecules.
The process is a form of thermal cracking, breaking down a large, solid material into smaller liquid and gaseous components.
The Role of Temperature and Heating Rate
The specific outputs of pyrolysis are highly dependent on the operating conditions.
- Temperature is the most critical factor. Moderate temperatures tend to maximize the yield of liquid oil, while very high temperatures favor the production of gas.
- Heating Rate also influences the product distribution. A rapid heating rate (fast pyrolysis) generally increases the liquid oil yield, while a slow rate can produce more solid char.
The Valuable Outputs of Rubber Pyrolysis
The process is engineered to create three distinct product streams, each with its own potential market and application.
Pyrolytic Oil (Tire-Derived Oil)
This liquid fraction is a complex blend of hydrocarbons, similar in some respects to crude oil. It can be used directly as a heavy fuel oil in furnaces or boilers.
With further refining, this oil can be upgraded into more valuable products like diesel, gasoline, or as a feedstock for the chemical industry.
Solid Char (Recovered Carbon Black)
The solid residue left after pyrolysis is a carbon-rich material known as char or recovered carbon black (rCB). It contains most of the original carbon from the rubber.
While its quality is lower than virgin carbon black, it can be used as a pigment, a reinforcing filler in lower-grade rubber products, or as a solid fuel similar to coal.
Syngas (Non-Condensable Gas)
The gaseous product is a mixture of combustible gases like hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
This syngas has a significant energy value and is almost always captured and used to power the pyrolysis reactor itself. This makes the entire process more energy-efficient and can even make it self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, rubber pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for evaluating its real-world viability.
Feedstock Contamination
Waste tires and rubber products are not pure polyisoprene. They contain significant amounts of sulfur (from the vulcanization process), steel wiring, and other additives.
These contaminants end up in the final products. Sulfur in the pyrolytic oil is a major issue, as burning it can lead to acid rain. Removing this sulfur adds significant cost and complexity.
Product Quality and Consistency
The output products, particularly the oil and char, can vary widely in quality depending on the exact type of rubber feedstock and the specific process conditions used.
This lack of a consistent, standardized product makes it difficult to integrate into existing industrial supply chains that demand reliable specifications.
Economic Viability
The profitability of a pyrolysis plant is a delicate balance. It depends on the cost of acquiring and preparing the waste rubber, the operational cost (especially energy), and the market value of the resulting oil, char, and gas. Fluctuations in oil prices can dramatically impact the economic feasibility.
Applying Pyrolysis to Your Strategic Goal
The value you derive from pyrolysis depends entirely on what you want to achieve.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: Prioritize optimizing the yield and quality of the pyrolytic oil for use as a fuel, while ensuring the syngas makes the operation energy-neutral.
- If your primary focus is a circular economy: Concentrate on upgrading the recovered carbon black for reuse in manufacturing and refining the oil into valuable chemical feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is environmental management: View pyrolysis as a superior alternative to landfilling, as it dramatically reduces waste volume while recovering valuable resources that would otherwise be lost.
Pyrolysis stands as a key technology for reframing our perspective on rubber waste, turning a persistent environmental problem into a valuable resource stream.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Output | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolytic Oil | A liquid hydrocarbon blend similar to crude oil. | Industrial fuel, feedstock for refining into diesel/gasoline. |
| Solid Char (rCB) | Carbon-rich residue from the rubber. | Filler for lower-grade rubber products, pigment, solid fuel. |
| Syngas | Mixture of combustible gases (e.g., hydrogen, methane). | Used to power the pyrolysis reactor for energy efficiency. |
Ready to transform your rubber waste into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focused on waste-to-energy, circular economy goals, or environmental management, our solutions help you optimize pyrolysis processes for maximum efficiency and product quality. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in sustainable material transformation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















