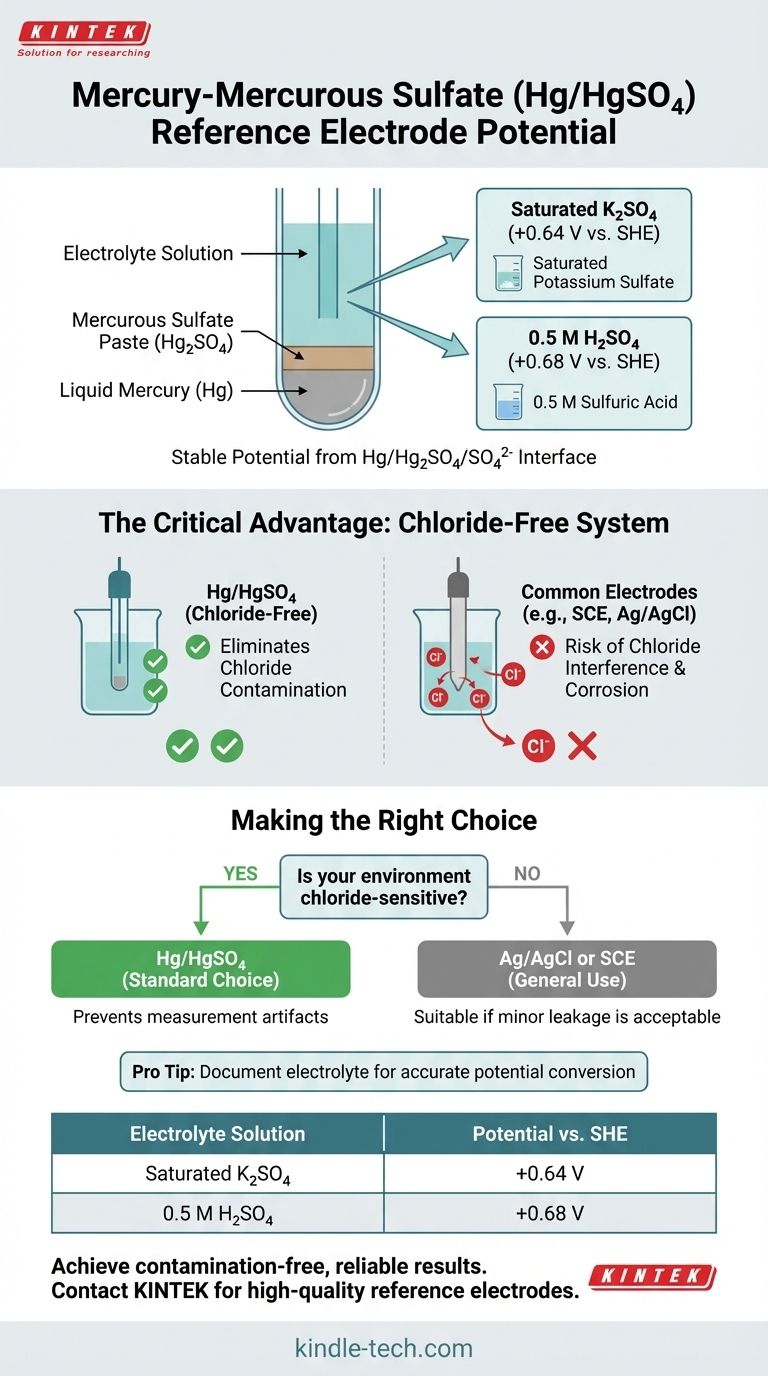
The accepted potential of a mercury-mercurous sulfate (Hg/HgSO4) reference electrode is typically +0.64 V versus the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) when using a saturated potassium sulfate (K2SO4) electrolyte. This value changes slightly to +0.68 V vs. SHE when a 0.5 M sulfuric acid (H2SO4) electrolyte is used.
The Hg/HgSO4 electrode is a specialized, highly stable reference electrode valued for one critical reason: it operates without chloride ions. This makes it the essential choice for electrochemical experiments where chloride contamination would interfere with results or damage the system.

What is a Mercury-Mercurous Sulfate Electrode?
The Core Components
A mercury-mercurous sulfate electrode consists of a pool of liquid mercury (Hg) in direct contact with a paste of solid mercurous sulfate (Hg₂SO₄).
The Role of the Electrolyte
This mercury and sulfate paste is immersed in an aqueous solution containing a high concentration of sulfate ions. This is most commonly a saturated potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄) solution or a 0.5 M sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) solution.
How It Provides a Stable Reference
The interface between the mercury, its sparingly soluble salt (Hg₂SO₄), and the sulfate ions in the electrolyte creates a stable and reproducible electrochemical half-reaction. This equilibrium generates a constant potential, which serves as a reliable benchmark against which the potential of a working electrode is measured.
Understanding its Potential vs. SHE
Potential in Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄)
When using a saturated potassium sulfate filling solution, the standard potential of the Hg/HgSO₄ electrode is +0.64 V relative to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE).
Potential in Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄)
In acidic environments, a 0.5 M sulfuric acid filling solution is often used. This shifts the potential slightly to +0.68 V vs. SHE. The change is due to the different activity of the sulfate ions in the two electrolyte solutions.
The Critical Advantage: A Chloride-Free System
The Problem with Common Electrodes
The most widely used reference electrodes, such as the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) and the Silver/Silver Chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode, are filled with concentrated potassium chloride (KCl) solutions.
Why Chloride Leaks are a Concern
During an experiment, a minuscule amount of this chloride-rich filling solution can leak from the electrode's junction into your test solution. This is a significant problem in systems where chloride ions can interfere with the reaction, poison a catalyst, or corrode stainless steel components.
The Hg/HgSO₄ Solution
The Hg/HgSO₄ electrode was developed specifically to solve this problem. By using a sulfate-based electrolyte instead of a chloride-based one, it completely eliminates the risk of chloride contamination, ensuring the integrity of your measurements in sensitive systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is working in chloride-sensitive environments: The Hg/HgSO₄ electrode is the correct and standard choice to prevent measurement artifacts and system damage.
- If your primary focus is general aqueous electrochemistry: A more common and often less expensive Ag/AgCl or SCE electrode is perfectly suitable, as long as minor chloride leakage is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is converting potentials: Always document the specific electrolyte used in your Hg/HgSO₄ electrode (e.g., saturated K₂SO₄ or 0.5 M H₂SO₄) to apply the correct conversion factor to the SHE scale.
Selecting the appropriate reference electrode is fundamental to achieving accurate and reliable electrochemical data.
Summary Table:
| Electrolyte Solution | Potential vs. Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) |
|---|---|
| Saturated Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄) | +0.64 V |
| 0.5 M Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) | +0.68 V |
Achieve contamination-free, reliable results in your sensitive electrochemical experiments. The Hg/HgSO4 reference electrode is the definitive choice for applications where chloride ions would interfere with your reaction, poison a catalyst, or damage your system. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable reference electrodes, to meet the precise needs of your laboratory. Ensure the integrity of your data — contact our experts today to find the perfect reference electrode for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the general precautions for using a reference electrode? Ensure Stable Potentials for Accurate Data
- Why and how should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be calibrated? Ensure Reliable Results
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
- Which electrode is used as a reference? A Guide to Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- Why is a Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) used as a reference electrode in microbial fuel cell research?



















