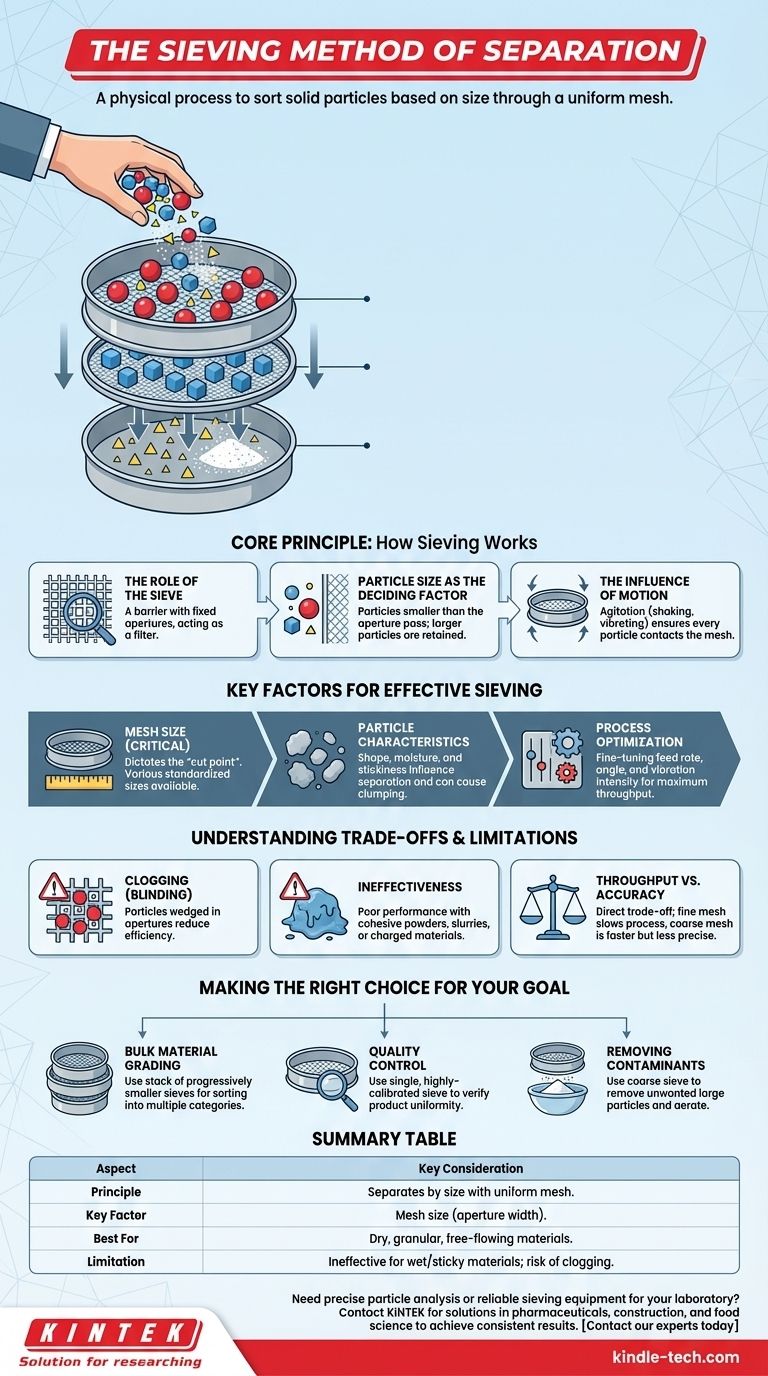
The sieving method of separation is a physical process used to distinguish and sort solid particles based on their size. It works by passing a mixture of materials through a screen or mesh with uniform openings; particles smaller than the openings pass through, while larger particles are retained on the surface.
The core principle of sieving is not merely filtering, but precise particle size classification. Its success depends entirely on the relationship between the particle size of the material and the aperture size of the chosen sieve mesh.

The Core Principle: How Sieving Works
Sieving is one of the oldest and most intuitive methods of separation, relying on simple mechanical principles to achieve its goal.
The Role of the Sieve
A sieve is a device, often a wire mesh or a perforated plate, that features apertures (openings) of a fixed, uniform size. This screen acts as a physical barrier.
Particle Size as the Deciding Factor
When a mixture of particles is introduced to the sieve, the separation occurs. Any particle with dimensions smaller than the sieve's apertures will fall through, while any particle larger will be held back.
The Influence of Motion
For the process to be efficient, the material is typically agitated. This is done by shaking, vibrating, or tumbling the sieve to ensure every particle has an opportunity to come into contact with the mesh and pass through if it is small enough.
Key Factors for Effective Sieving
Optimizing the sieving process requires controlling several variables to achieve the desired separation with accuracy and efficiency.
Mesh Size
This is the most critical factor. The mesh size, or aperture width, dictates the "cut point" of the separation. Sieves are available in a vast range of standardized mesh sizes to suit different materials and classification needs.
Particle Characteristics
The shape and condition of the particles heavily influence the outcome. Elongated or irregular particles may pass through a mesh they wouldn't if they were spherical. Furthermore, wet or sticky materials can clump together, preventing effective separation and clogging the sieve.
Process Optimization
In industrial applications, "optimizing the process" involves fine-tuning the rate of material feed, the angle of the sieve, and the intensity of vibration. This ensures maximum throughput without sacrificing the accuracy of the separation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieving is not a universal solution and comes with inherent limitations that must be considered.
The Risk of Clogging (Blinding)
When particles are very close in size to the mesh openings, they can become wedged in the apertures. This phenomenon, known as blinding, reduces the available surface area of the sieve and dramatically lowers its efficiency.
Ineffectiveness with Certain Materials
Sieving is most effective for dry, granular, and free-flowing materials. It performs poorly with cohesive powders, slurries, or materials that carry a static charge, as these tend to agglomerate rather than separate.
Throughput vs. Accuracy
There is a direct trade-off between the speed of the process and its precision. Using a very fine mesh to achieve high-purity separation will slow down the rate at which material can be processed. Conversely, a coarse mesh allows for high throughput but offers less precise classification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this method effectively, you must align the technique with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is bulk material grading (e.g., sand and gravel): Use a stack of sieves with progressively smaller mesh sizes to efficiently sort a single batch into multiple size categories at once.
- If your primary focus is quality control (e.g., in pharmaceuticals): Use a single, highly-calibrated analysis sieve with a precise mesh size to verify that a product meets particle uniformity standards.
- If your primary focus is removing contaminants (e.g., sifting flour): A simple, coarse sieve is sufficient to remove unwanted large particles and aerate the material.
Ultimately, mastering the sieving method lies in correctly matching the properties of your material to the specifications of the sieve.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Principle | Separates particles based on size using a mesh with uniform openings. |
| Key Factor | Mesh size (aperture width) is the most critical parameter. |
| Best For | Dry, granular, free-flowing materials like sand, gravel, or powders. |
| Limitation | Ineffective for wet, sticky, or cohesive materials; risk of clogging (blinding). |
Need precise particle analysis or reliable sieving equipment for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and particle analysis equipment designed for accuracy and durability. Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, construction materials, or food science, our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results in your quality control and R&D processes.
Let us help you optimize your separation process. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















