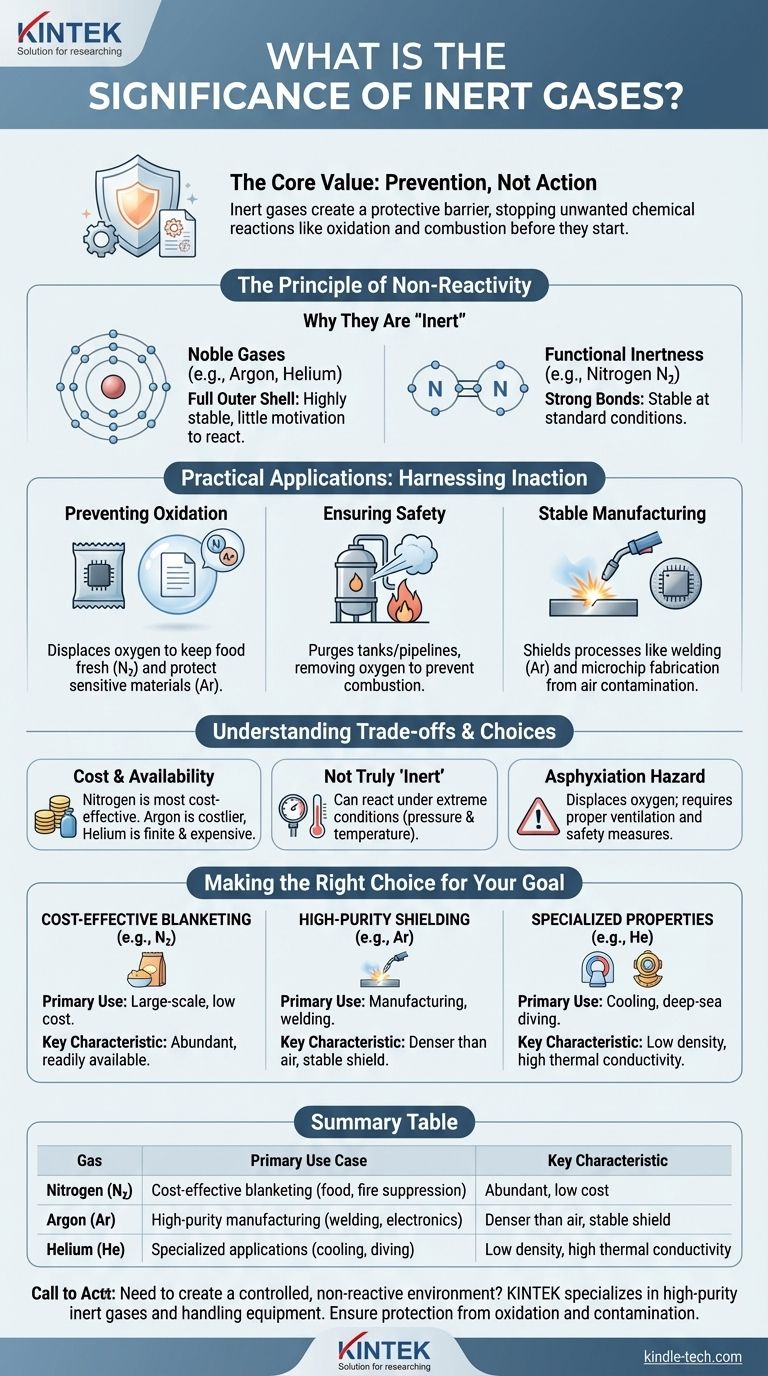
The significance of inert gases lies in their defining characteristic: a profound lack of chemical reactivity. Unlike reactive gases such as oxygen or chlorine, inert gases do not readily form chemical compounds with other substances. This stability makes them invaluable for creating controlled, non-reactive environments to protect sensitive materials and processes.
The core value of an inert gas is not what it does, but what it prevents. Its non-reactivity is a powerful tool used to create a protective shield, stopping unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and combustion before they can start.

The Principle of Non-Reactivity
To understand the significance of inert gases, we must first examine the chemical principle that governs their behavior. It is this fundamental stability that gives rise to all their practical applications.
What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
The inertness of a gas is determined by its atomic structure. The most stable and well-known inert gases are the noble gases (like argon, helium, and neon), which occupy Group 18 of the periodic table.
These elements have a full outer shell of electrons, which is a highly stable electronic configuration. Because this shell is complete, they have very little "motivation" to share, gain, or lose electrons by reacting with other elements.
Noble Gases vs. Other Inert Gases
While the term "inert gas" was historically synonymous with noble gases, the definition is functional. Any gas can be considered inert if it does not react under a specific set of conditions.
Nitrogen (N₂), for example, is often used as an inert gas. While it is not a noble gas and can be made to react under high energy conditions, its strong triple bond makes it very stable and non-reactive at standard temperatures and pressures.
Practical Applications: Harnessing Inaction
The ability to displace reactive air (which is ~21% oxygen) with a non-reactive gas is critical across numerous scientific and industrial fields. This process is often called blanketing or purging.
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
One of the most common unwanted reactions is oxidation, where a substance reacts with oxygen. This is the process that causes iron to rust and food to spoil.
Inert gases create an oxygen-free atmosphere to prevent this. For example, bags of potato chips are filled with nitrogen to displace oxygen, keeping the contents fresh and preventing them from going stale. Similarly, sensitive historical documents are often stored in argon-filled cases.
Ensuring Safety in Hazardous Environments
In industrial settings, an inert gas can be used to purge tanks and pipelines that contained flammable liquids or gases. By displacing the oxygen, the inert gas removes a key component required for combustion, rendering the environment safe for maintenance or inspection.
Creating Stable Atmospheres for Manufacturing
Many advanced manufacturing processes are highly sensitive to contamination from the air.
In welding, particularly TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, a constant stream of argon shields the molten metal from oxygen and water vapor. Without this shield, the weld would become brittle and weak. A similar principle applies to the manufacturing of silicon wafers for microchips, which requires an exceptionally pure and non-reactive environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, the selection and use of inert gases require an understanding of their limitations and potential hazards.
Cost and Availability
The most abundant and cost-effective gas for inerting applications is nitrogen. Noble gases like argon are more expensive, and helium is a finite resource with a significantly higher cost, reserved for specialized applications.
Not Truly "Inert"
It's a crucial distinction that "inert" simply means non-reactive under a given set of conditions. Under extreme pressure and temperature, even noble gases like xenon and krypton have been forced to form chemical compounds. For nearly all practical purposes, however, they are reliably stable.
The Danger of Asphyxiation
A critical safety consideration is that inert gases are asphyxiants. They are not toxic, but they displace the oxygen necessary for breathing. In a poorly ventilated or confined space, a leak of any inert gas can lead to oxygen deficiency, causing unconsciousness and death without warning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate inert gas depends entirely on the specific requirements of the application, balancing performance, cost, and safety.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective blanketing: Nitrogen is almost always the optimal choice for large-scale applications like food packaging or fire suppression due to its low cost and high availability.
- If your primary focus is high-purity manufacturing or welding: Argon is the industry standard because it is denser than air, providing a more effective and stable shield over a work area.
- If your primary focus requires unique physical properties: Helium is used for specialized applications like deep-sea diving mixtures or as a coolant for MRI magnets due to its low density and excellent thermal conductivity.
By understanding that stability is a tool, you can use these non-reactive gases to precisely control the chemical world around you.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Cost-effective blanketing (food packaging, fire suppression) | Abundant, low cost |
| Argon (Ar) | High-purity manufacturing (welding, electronics) | Denser than air, stable shield |
| Helium (He) | Specialized applications (cooling, diving mixtures) | Low density, high thermal conductivity |
Need to create a controlled, non-reactive environment for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity inert gases and the equipment to handle them safely and effectively. Whether you require nitrogen for cost-effective blanketing or argon for high-purity welding and manufacturing, our expertise ensures your sensitive materials are protected from oxidation and contamination. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect inert gas solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
People Also Ask
- Why is a controlled atmosphere furnace with a quartz tube used for W-SiC thin films? Optimize Phase Transformation
- How do four-way valves and flow meters function together to control the atmosphere? Master Gas-Solid Reaction Kinetics
- What is furnace atmosphere? A Guide to Controlled Heating for Superior Results
- Why is a reaction system with gas protection required for Fe3O4 co-precipitation? Ensure Pure Magnetite Synthesis
- What is the pressure inside a furnace? Mastering Controlled Environments for Your Lab
- What is a retort furnace for heat treating? Achieve Superior Atmospheric Control for Your Materials
- What is vacuum inerting? A Safer Method for Preventing Explosions and Oxidation
- Why is an atmosphere-controlled reduction experimental device required? Precision in Ore Pellet Swelling Analysis
















