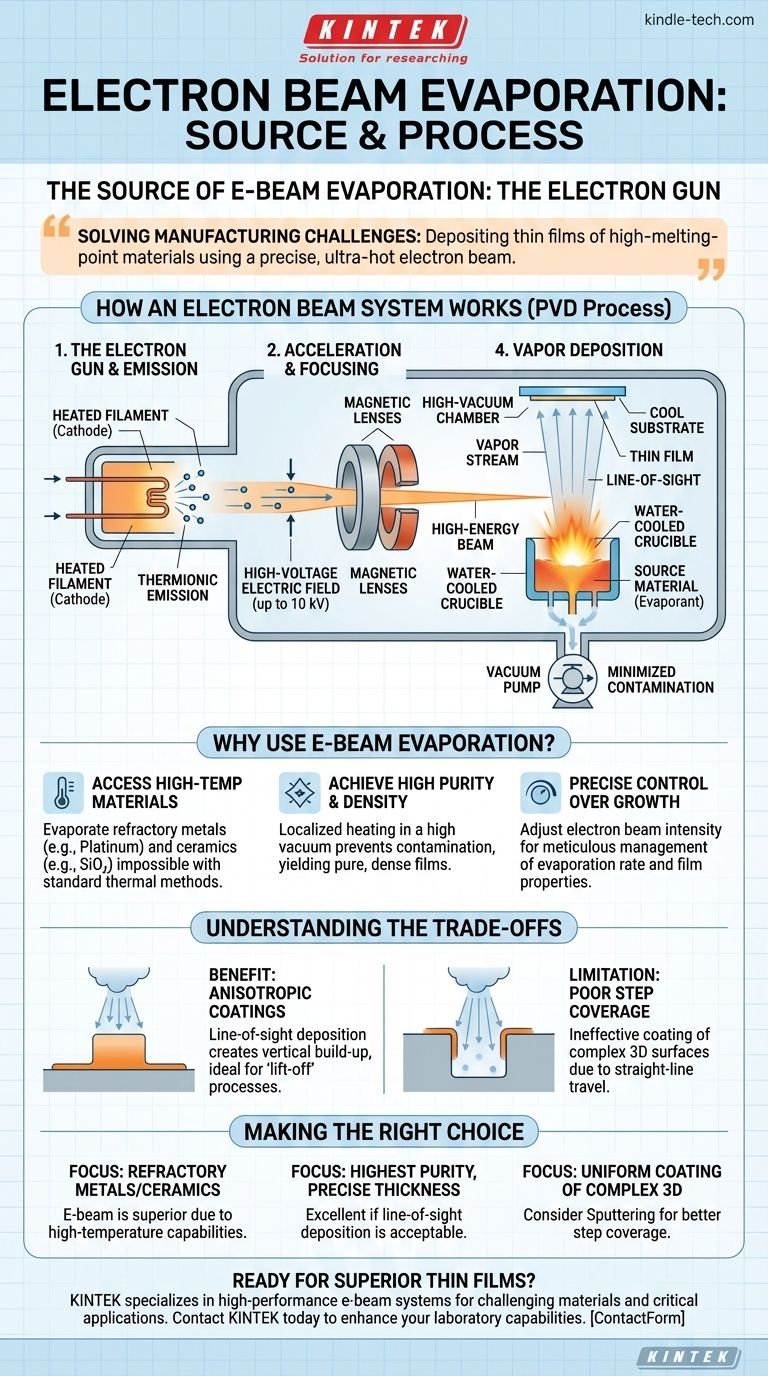
The fundamental source of electron beam evaporation is a specialized component known as an electron gun. This device uses a heated filament, or cathode, to release a high-flux stream of electrons. These electrons are then accelerated by a strong electric field and focused by magnets into an intense, high-energy beam that vaporizes the target material.
Electron beam evaporation solves a critical manufacturing challenge: how to deposit thin films of materials with extremely high melting points. It achieves this by using a precisely controlled beam of high-energy electrons as a localized, ultra-hot heat source, bypassing the temperature limitations of conventional heating methods.

How an Electron Beam System Works
Electron beam (e-beam) evaporation is a form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) that creates dense, high-purity thin films. The process relies on several key components working in concert within a high-vacuum environment.
The Electron Gun: Source of the Beam
The process begins with the electron gun. Inside the gun, a tungsten filament is heated to a high temperature, causing it to emit a cloud of electrons through a process called thermionic emission.
Acceleration and Focusing
Once emitted, these free electrons are accelerated toward the target material by a high-voltage electric field, often up to 10 kV. A magnetic system then focuses these accelerated electrons into a tight, precise beam.
The Target: Heating the Source Material
This high-energy beam is directed into a water-cooled copper crucible containing the source material (the "evaporant"). The immense kinetic energy of the electrons is converted into thermal energy upon impact, rapidly heating the material past its melting and boiling points.
Deposition in a Vacuum
The material turns into a vapor and travels in a straight, line-of-sight path through the high-vacuum chamber. This vapor then condenses onto a cooler substrate, which is strategically placed above the source, forming a solid, thin film. The vacuum is critical for minimizing contamination and allowing the vapor to travel unimpeded.
Why Use Electron Beam Evaporation?
E-beam evaporation is chosen over other deposition methods for its distinct advantages, primarily related to temperature and purity.
Accessing High-Temperature Materials
This is the primary reason for its use. E-beam can achieve temperatures far greater than standard thermal evaporation, which relies on resistive heating. This allows it to evaporate refractory metals (like platinum) and dielectric materials (like silicon dioxide, SiO₂) that are impossible to deposit with other methods.
Achieving High Purity and Density
Because the electron beam heats only the source material in the crucible, the rest of the chamber remains relatively cool. This localized heating, combined with the high-vacuum environment, prevents contamination and results in exceptionally pure and dense films.
Precise Control Over Film Growth
The intensity of the electron beam can be controlled with high precision. This gives engineers direct control over the evaporation rate, which in turn allows for meticulous management of the final film's thickness and structural properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technology, e-beam evaporation has inherent characteristics that can be either an advantage or a limitation depending on the application.
The Benefit: Anisotropic Coatings
The vapor travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This "line-of-sight" deposition results in a highly anisotropic coating, meaning it builds up vertically without coating sidewalls. This is extremely useful for a microfabrication process called "lift-off," where a clean edge is required.
The Limitation: Poor Step Coverage
The same line-of-sight property becomes a disadvantage when trying to coat complex, three-dimensional surfaces. The process cannot effectively coat undercuts or the vertical sidewalls of trenches, an issue known as poor step coverage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method requires matching its capabilities to your specific material and geometric needs.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or ceramics: E-beam evaporation is often the superior or only viable PVD choice due to its high-temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity films with precise thickness: E-beam is an excellent candidate, provided the line-of-sight deposition profile is acceptable for your device's geometry.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating complex 3D surfaces: You should consider an alternative method like sputtering, which does not rely on line-of-sight and provides better step coverage.
Ultimately, choosing e-beam evaporation is a decision to prioritize material range and film purity when a directional coating process is beneficial or acceptable.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Electron Gun | Generates and directs the electron beam | Uses thermionic emission from a heated filament |
| Acceleration/Focusing System | Accelerates and focuses electrons | High-voltage electric field and magnetic lenses |
| Water-Cooled Crucible | Holds the source material (evaporant) | Prevents contamination from the crucible |
| High-Vacuum Chamber | Provides the environment for deposition | Minimizes contamination and allows line-of-sight travel |
Ready to Achieve Superior Thin Films with E-Beam Evaporation?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including advanced electron beam evaporation systems. Our solutions are designed for researchers and engineers who require the highest purity thin films from refractory metals and ceramics.
We help you:
- Deposit challenging materials like platinum and silicon dioxide with precision.
- Achieve exceptional film purity and density for critical applications.
- Gain precise control over film growth and thickness.
Let our experts help you select the right PVD technology for your specific material and geometric requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your thin film deposition goals and discover how our e-beam solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of e-beam deposition? Achieve High-Purity, High-Melting-Point Thin Films
- What is thermal evaporation of organic materials? The Gentle Method for OLED & Electronics
- How thick is thermal evaporation coating? Achieve Precision Thin Films for Your Lab
- How does the vacuum evaporation system work? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the effect of substrate temperature on sputtering? Master Film Density, Crystallinity, and Stress
- What is a thermal evaporation system? A Guide to Simple, Effective Thin-Film Deposition
- What are three applications of evaporation in different industries? From OLEDs to Automotive Parts
- How do you evaporate metal? Mastering Thermal vs. E-beam Evaporation for Thin Films



















