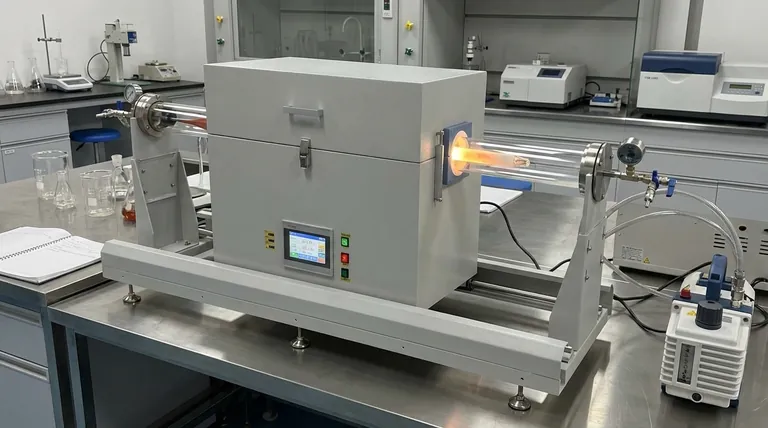
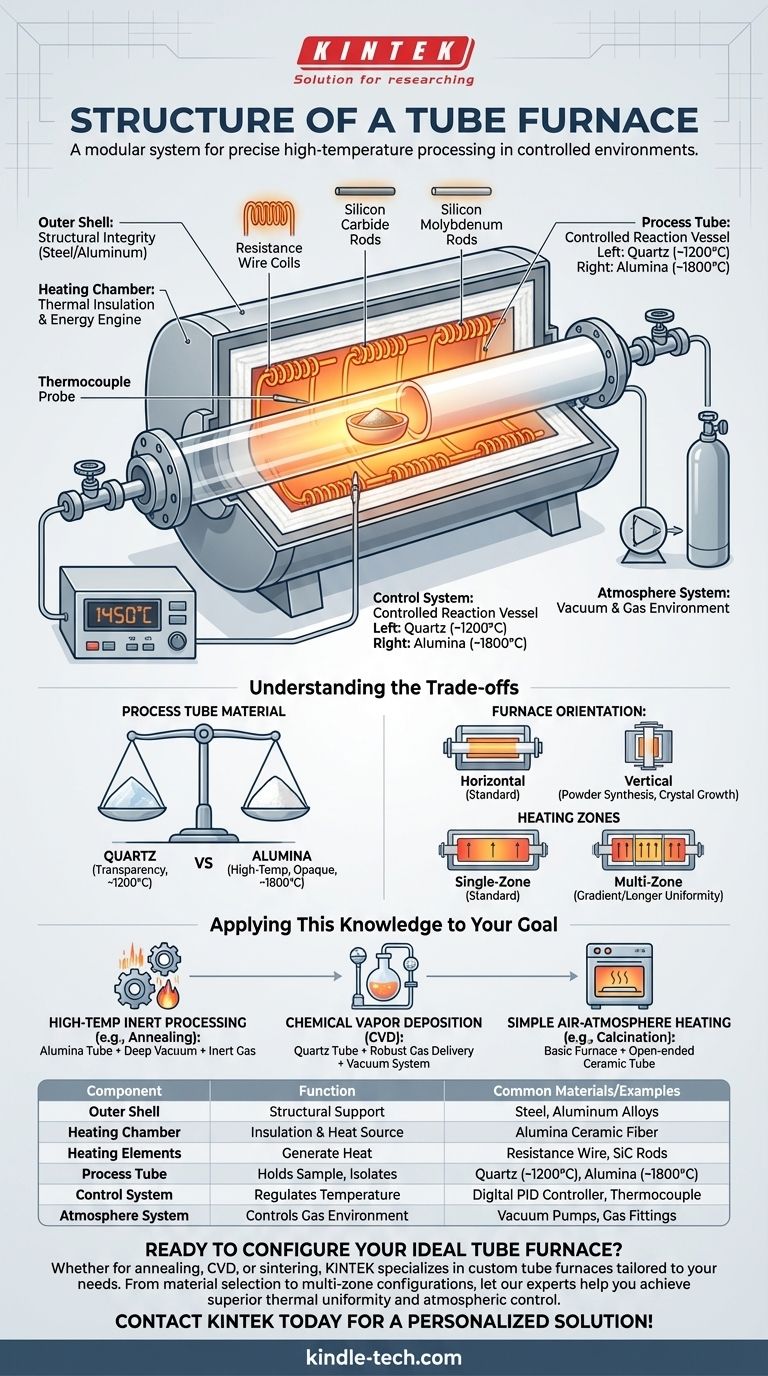
At its core, a tube furnace is a modular system designed to heat materials to precise temperatures within a controlled atmospheric environment. Its fundamental structure consists of an insulated furnace body containing heating elements, a central process tube that holds the sample, and a control system to regulate temperature. Additional components, such as vacuum pumps and gas fittings, are integrated to manage the atmosphere inside the tube.
A tube furnace’s structure is purpose-built for one primary goal: to apply uniform, high-temperature heat to a sample within a tightly controlled and isolated environment. Every component, from the outer shell to the inner tube, serves this dual function of thermal management and atmospheric isolation.

The Anatomy of a Tube Furnace
To understand how a tube furnace works, we must examine its key structural components and the function each one performs.
The Outer Shell: Structural Integrity
The furnace body, or shell, is the external casing that houses all other components. It is typically constructed from heavy-duty steel or aluminum alloys to provide structural support and durability. This shell often includes hinges for easy access to the heating chamber and process tube.
The Heating Chamber: The Engine of Thermal Energy
This is the heart of the furnace. The chamber is made of high-purity alumina ceramic fibers or another thermally insulating matrix. Its circular design ensures that heat is directed inward toward the central process tube.
Embedded within this ceramic matrix are the heating elements. These can be resistance wire coils, silicon carbon rods, or silicon molybdenum rods, chosen based on the furnace's maximum required temperature. Their even distribution around the chamber is critical for achieving high thermal uniformity.
The Process Tube: The Controlled Reaction Vessel
This is the cylindrical tube that passes through the center of the heating chamber. The material being processed is placed inside this tube, isolating it from the heating elements and the outside air.
The choice of tube material is critical and depends on the application. The most common materials are quartz, used for lower temperatures (up to ~1200°C), and high-purity alumina, which can withstand much higher temperatures (up to ~1800°C).
The Control System: Precision and Repeatability
The control system is the brain of the furnace. It consists of a thermocouple, a temperature sensor that extends into the heating zone, and a digital controller.
The thermocouple provides real-time temperature feedback to the controller, which then adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements. This feedback loop allows for precise temperature ramps, soaks, and controlled cooling, ensuring repeatable experimental conditions.
The Atmosphere System: Creating a Specific Environment
Many applications require an environment other than ambient air. To achieve this, tube furnaces are equipped with flanges, valves, and fittings at the ends of the process tube.
These fittings connect to a vacuum pump to remove air and create a vacuum, or to a gas supply to introduce specific inert (e.g., argon) or reactive gases. This transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a highly controlled reactor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The effectiveness of a tube furnace is determined by the interplay of its components. Making the right choice involves balancing key trade-offs.
Process Tube Material: Temperature vs. Transparency
Quartz is transparent, which can be useful for visual observation, but it softens at high temperatures. Alumina is opaque but offers superior performance and chemical stability at extreme temperatures, making it the standard for high-temperature annealing or sintering.
Furnace Orientation: Horizontal vs. Vertical
Most tube furnaces are horizontal. However, vertical orientations are also available and are preferable for applications like powder synthesis or certain crystal growth methods where gravity can be used to an advantage, or to prevent the sample from touching the tube walls.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone: Uniformity vs. Gradient
A standard furnace has a single heating zone. For longer samples or processes requiring exceptionally high uniformity, multi-zone furnaces are used. These have multiple, independently controlled heating sections that can create a longer uniform hot zone or a specific temperature gradient along the tube.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Goal
Your choice of furnace configuration depends entirely on the process you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature inert processing (e.g., annealing metals): You will need an alumina tube and a system capable of achieving a deep vacuum before backfilling with an inert gas like argon.
- If your primary focus is lower-temperature chemical vapor deposition (CVD): A quartz tube is often preferred for its chemical inertness, paired with a robust gas delivery and vacuum system to manage precursor gases and byproducts.
- If your primary focus is simple air-atmosphere heating (e.g., calcination): A basic furnace with an open-ended ceramic tube and a simple temperature controller may be all you need, forgoing the expense of a vacuum system.
Understanding this relationship between structure and function is the key to mastering high-temperature material processing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Common Materials/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Shell | Provides structural support and durability. | Steel, aluminum alloys. |
| Heating Chamber | Insulated core containing heating elements. | Alumina ceramic fiber insulation. |
| Heating Elements | Generate and radiate heat. | Resistance wire, silicon carbide rods. |
| Process Tube | Holds the sample; isolates it from the atmosphere. | Quartz (up to 1200°C), Alumina (up to 1800°C). |
| Control System | Precisely regulates temperature via a thermocouple. | Digital PID controller. |
| Atmosphere System | Controls the gas environment inside the tube. | Vacuum pumps, gas fittings, flanges. |
Ready to configure the ideal tube furnace for your application?
Whether your lab requires precise annealing, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or high-temperature sintering, the right furnace structure is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tube furnaces tailored to your specific process needs—from material selection (quartz or alumina tubes) to configuration (single or multi-zone).
Let our experts help you achieve superior thermal uniformity and atmospheric control. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















