In thin film deposition, the substrate is the foundational material or surface onto which a new layer of material is grown or deposited. While many materials can serve this purpose, the most common choices for advanced applications include silicon (Si), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), and quartz, each selected for its specific properties. The choice of substrate is as critical as the choice of the film material itself.
The substrate is not merely a passive holder for the thin film. It is an active component in the deposition system that directly influences the film's structural integrity, properties, and ultimate performance in its intended application.

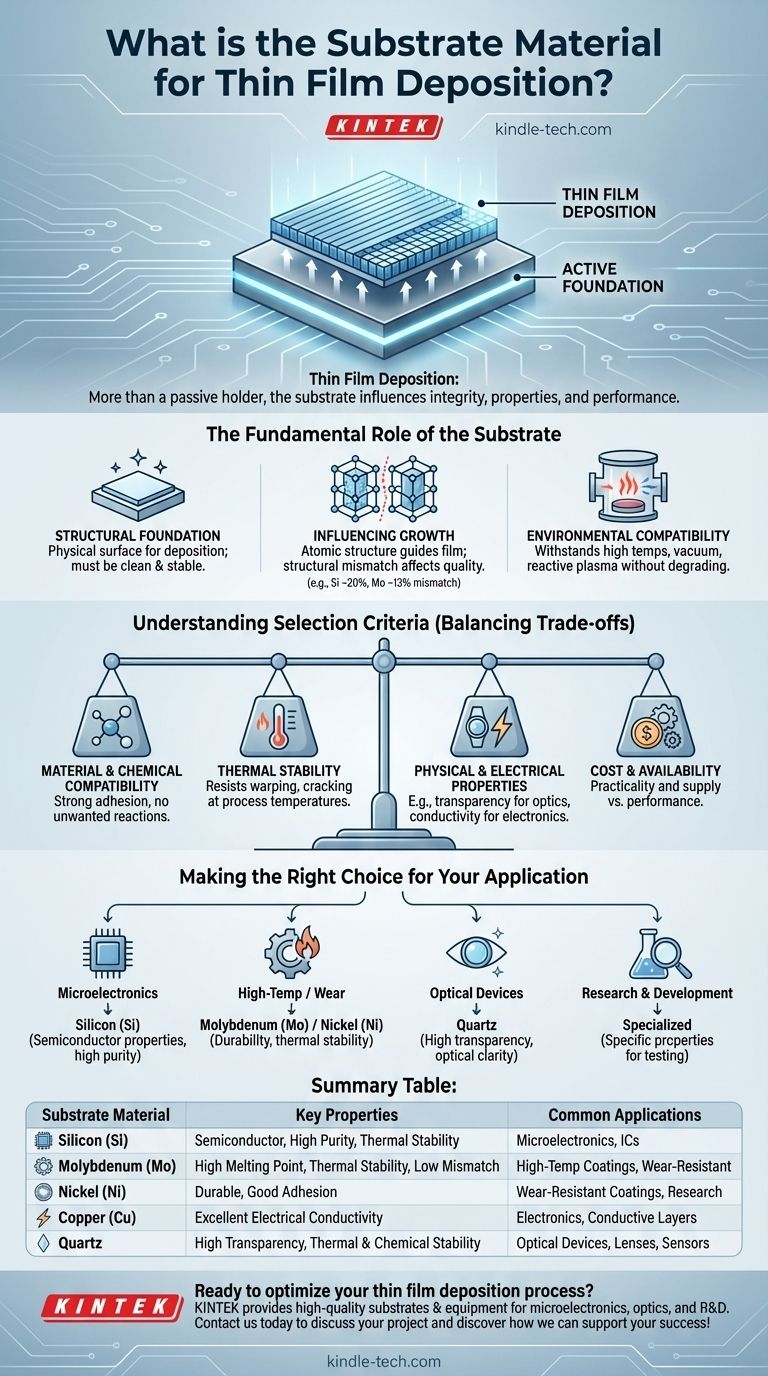
The Fundamental Role of the Substrate
Understanding the function of the substrate moves beyond seeing it as a simple base. It is an integral part of the final engineered product, dictating what is possible during and after deposition.
Providing the Structural Foundation
The substrate provides the physical surface where the deposition process, whether chemical or physical, takes place. It must be clean, stable, and often precisely engineered to serve as a template for the film.
Influencing Film Growth and Structure
The atomic arrangement of the substrate's surface can guide the growth of the thin film. A key factor is structural mismatch, or the difference in the crystalline lattice spacing between the substrate and the film material.
For example, silicon has a ~20% structural mismatch with certain film materials, while molybdenum has a ~13% mismatch. This difference can introduce stress and defects, affecting the film's quality.
Compatibility with the Deposition Environment
Deposition processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) often involve extreme conditions. The substrate must be able to withstand high temperatures, vacuum environments, and potentially reactive plasmas without degrading.
Understanding the Selection Criteria
Selecting the correct substrate is a process of balancing trade-offs. No single material is perfect for every situation; the choice depends on a careful analysis of multiple interacting factors.
Material and Chemical Compatibility
The thin film must adhere strongly to the substrate. This requires chemical compatibility, ensuring that the film material bonds to the substrate surface without unwanted reactions that could compromise the interface.
Thermal Stability
Many deposition techniques use thermal energy from resistive heaters or infrared lamps to drive the reaction. The substrate must have a melting point and thermal expansion coefficient suitable for the process temperatures to prevent warping, cracking, or delamination.
Physical and Electrical Properties
The substrate's own properties are critical for the final device's function. For optical applications, a transparent substrate like quartz is necessary. For electronics, the exceptional purity and semiconductor properties of silicon wafers are indispensable.
Cost and Availability
Practical considerations are always a factor. Materials like silicon are widely available in high purity due to their dominance in the semiconductor industry, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications. More exotic substrates may offer superior performance but at a significantly higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal substrate is determined by the primary goal of your project. The material you deposit onto is as important as the material you are depositing.
- If your primary focus is microelectronics: Silicon (Si) is the default choice due to its well-understood semiconductor properties, high purity, and established manufacturing ecosystem.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or wear-resistant coatings: A metallic substrate like molybdenum (Mo) or nickel (Ni) may be chosen for its durability and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is optical devices: A transparent material with excellent optical clarity, such as quartz or specialized glass, is the required foundation.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The choice will be driven by the specific properties you wish to induce in the film, often leading to less common substrates to test material interactions.
Ultimately, selecting the right substrate is the first step in engineering the performance of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Substrate Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) | Semiconductor properties, high purity, thermal stability | Microelectronics, integrated circuits |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | High melting point, thermal stability, low structural mismatch | High-temperature coatings, wear-resistant layers |
| Nickel (Ni) | Durable, good adhesion for many films | Wear-resistant coatings, research |
| Copper (Cu) | Excellent electrical conductivity | Electronics, conductive layers |
| Quartz | High transparency, thermal and chemical stability | Optical devices, lenses, sensors |
Ready to optimize your thin film deposition process? The right substrate is critical for your film's performance, whether for microelectronics, optics, or R&D. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including substrates and deposition systems, to meet your specific laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect materials to ensure strong adhesion, thermal stability, and superior results. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer CaF2 Substrate Window Lens
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How should the quartz optical windows of the electrolytic cell be cleaned? A Guide to Maintaining Optical Clarity
- What do the optical properties of thin film depend on? Mastering Material, Thickness, and Process
- What role does the dielectric window play in MW-SWP CVD equipment? Ensuring Stable Plasma Generation with Quartz
- What is chemical vapor deposition substrate material? The Foundation for High-Quality Thin Films
- What are the ideal storage conditions for a side-window optical electrolytic cell? Ensure Long-Term Accuracy and Performance



















