There is no single temperature for a furnace. The required temperature is dictated entirely by the furnace's specific application and the material being processed. Operating temperatures can range from a few hundred degrees Celsius for simple drying to over 1800°C for advanced materials testing, with each process demanding a precise level of heat.
A furnace's temperature is not a universal constant but a function of its purpose. The critical factor is the process temperature—the exact heat required to achieve a desired physical or chemical change in a material, whether it's binding, melting, or treating it.

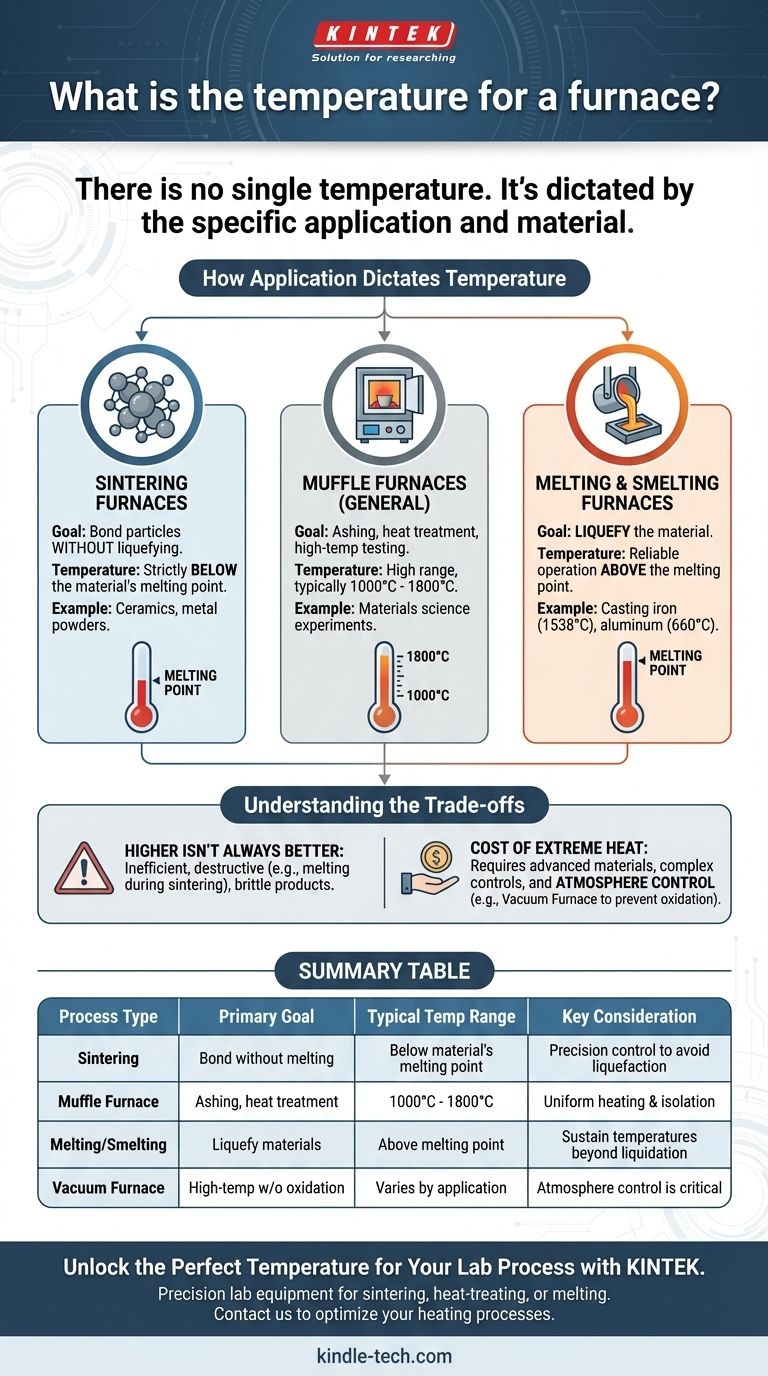
How Application Dictates Temperature
The core principle to understand is that a furnace is a tool designed to deliver a specific thermal profile to a material. The material and the desired outcome determine the temperature, not the other way around.
The Principle of Process Temperature
The "process temperature" is the temperature at which the material itself must be held to achieve the intended transformation. A furnace's primary job is to reach and maintain this temperature uniformly and accurately. This is its most critical performance metric.
Example 1: Sintering Furnaces
Sintering is a process that uses heat to bond particles of a material, like a ceramic or metal powder, into a solid mass. The goal is to create a solid shape without liquefying the material.
Therefore, a sintering furnace must operate at a temperature high enough to promote atomic diffusion between particles but remain strictly below the material's melting point. Exceeding this limit would ruin the product.
Example 2: Muffle Furnaces
Muffle furnaces are general-purpose lab and industrial furnaces often used for high-temperature applications. They are designed to isolate the material being heated from the heating elements, preventing contamination.
These typically operate in a high range, often between 1000°C and 1800°C. This capability allows them to be used for processes like ashing materials, heat-treating steel, or conducting high-temperature materials science experiments.
Example 3: Melting and Smelting Furnaces
In direct contrast to sintering, the purpose of a melting or smelting furnace is to liquefy a material. These are used in foundries for casting metal or in refineries for separating ores.
For these applications, the furnace must be capable of reliably operating above the melting point of the target metal, such as iron (1538°C) or aluminum (660°C).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a furnace involves balancing temperature requirements against physical limitations and costs. Higher temperatures are not always better and often come with significant consequences.
Higher Temperature Isn't Always Better
Applying more heat than the process requires is inefficient and often destructive. For a process like sintering, overshooting the temperature target will cause the material to melt, defeating the purpose. For heat treating, incorrect temperatures can result in a brittle or weak final product.
The Cost of Extreme Heat
Furnaces capable of achieving and sustaining very high temperatures are significantly more complex and expensive. They require advanced insulating materials, exotic metal alloys for heating elements, and sophisticated control systems to maintain temperature uniformity.
Atmosphere Control
For many advanced processes, temperature is only one part of the equation. A vacuum furnace, for example, removes air and other gases from the chamber to prevent oxidation at high temperatures. In these systems, controlling the atmosphere is just as critical as controlling the heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the correct temperature, you must first define your objective. The material and the desired transformation are your guide.
- If your primary focus is shaping materials without liquefying them (e.g., sintering): Your temperature must be precisely controlled to remain just below the material's melting point.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature testing or heat treatment (e.g., using a muffle furnace): The temperature will be dictated by the specific material standard or protocol, often in the 1000°C to 1800°C range.
- If your primary focus is to melt a material (e.g., casting or smelting): Your furnace must be capable of safely operating and maintaining a temperature above the material's full liquidation point.
Ultimately, the right temperature is not a feature of the furnace, but a requirement of your process.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Primary Goal | Typical Temperature Range | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Bond particles without melting | Below material's melting point | Precision control to avoid liquefaction |
| Muffle Furnace (General) | Ashing, heat treatment, testing | 1000°C - 1800°C | Uniform heating and contamination isolation |
| Melting/Smelting | Liquefy materials (e.g., metals) | Above melting point (e.g., Al: 660°C, Fe: 1538°C) | Must sustain temperatures beyond liquidation |
| Vacuum Furnace | High-temperature processes without oxidation | Varies by application | Atmosphere control is as critical as temperature |
Unlock the Perfect Temperature for Your Lab Process
Choosing the right furnace temperature is critical to your material's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables designed to meet your specific thermal processing needs—whether you're sintering ceramics, heat-treating alloys, or melting metals.
Our experts will help you select a furnace that delivers accurate, uniform heat for your application, ensuring efficiency and repeatability. Don't leave your results to chance.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can optimize your lab's heating processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is required for calcination? Master Material-Specific Thermal Decomposition
- What is furnace lining? The Engineered System Protecting Your High-Temperature Processes
- What is the calcination process? A Guide to Thermal Purification and Material Transformation
- What is the theory of calcination? Master Precise Thermal Decomposition for Your Materials
- What is the main purpose of a furnace? A Guide to Heating, Comfort, and Material Transformation



















