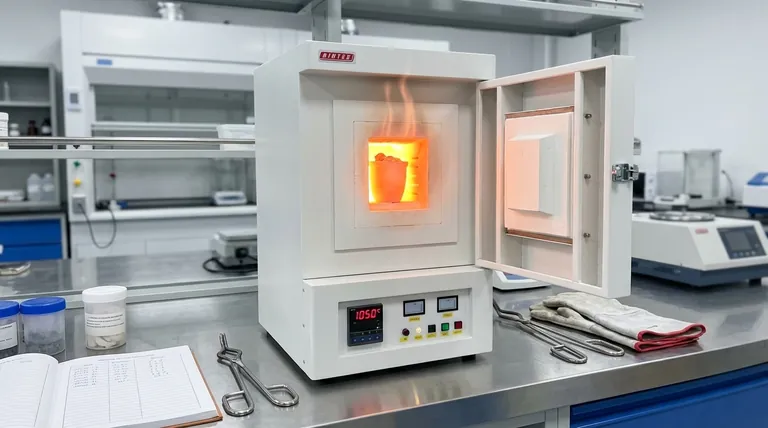
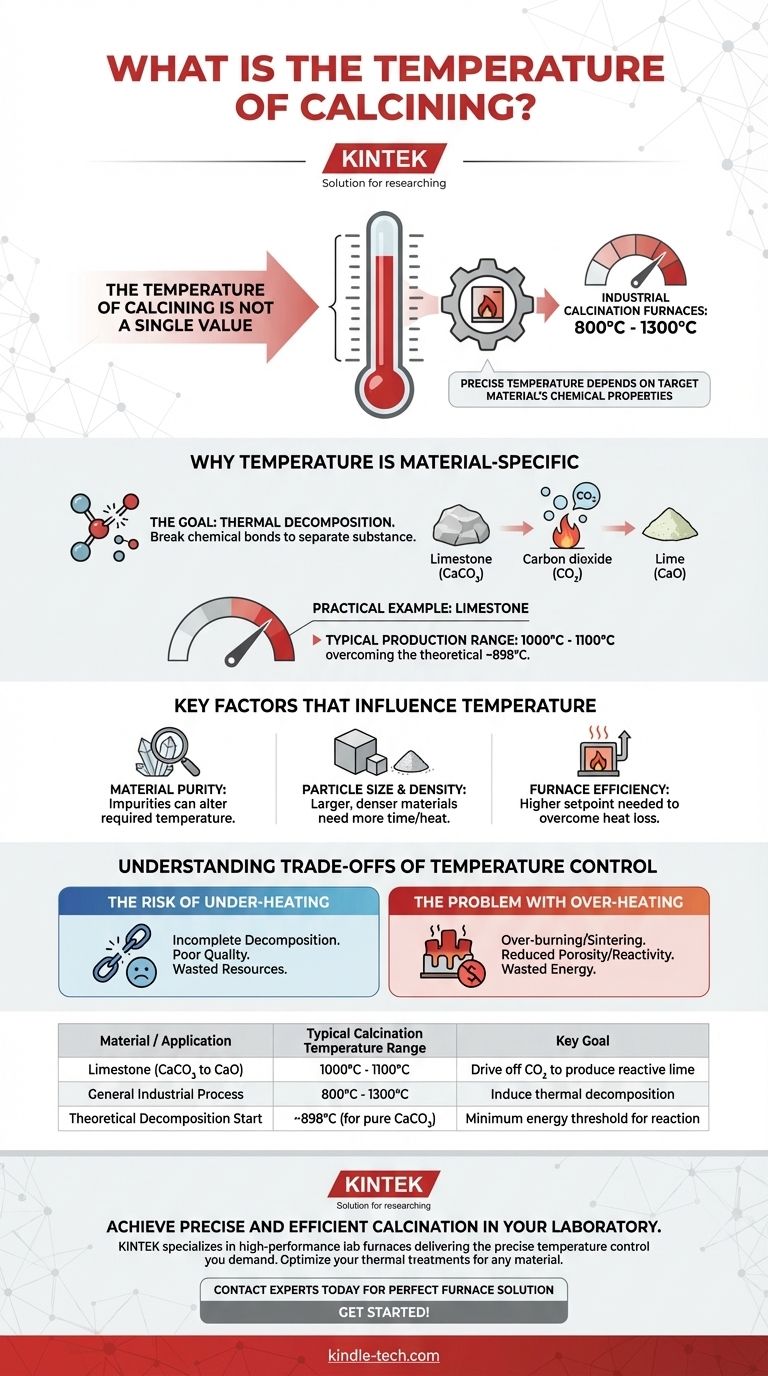
The temperature of calcination is not a single value but a specific range dictated by the material being processed. While industrial calcination furnaces typically operate between 800°C and 1300°C, the precise temperature depends entirely on the target material's chemical properties. For a common application like processing limestone, the temperature is often controlled within 1000°C to 1100°C in a production environment.
The core principle is that calcination temperature must be high enough to induce thermal decomposition in a specific material, but not so high that it damages the final product or wastes energy. It is a calculated balance determined by chemistry, physics, and operational goals.

Why Temperature is Material-Specific
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a chemical change, typically by driving off a volatile component. Understanding this core function is key to understanding the temperature requirements.
The Role of Thermal Decomposition
The goal of calcination is to heat a material to its thermal decomposition temperature. This is the point at which chemical bonds break, causing the substance to separate into simpler compounds.
For example, calcining limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO). This chemical reaction requires a specific amount of energy, which is delivered via heat.
A Practical Example: Limestone
The theoretical decomposition temperature of pure calcium carbonate is around 898°C. However, in actual industrial production, the temperature is set higher, often between 1000°C and 1100°C.
This higher temperature is a practical adjustment to overcome real-world variables and ensure the reaction is completed efficiently throughout the entire batch of material.
Key Factors That Influence Temperature
Setting the correct temperature is a balancing act that accounts for several variables beyond the basic chemical formula.
Material Purity
Impurities within the raw material can alter the required calcination temperature. Some impurities may require higher temperatures to break down, while others can act as fluxes, potentially lowering the required energy.
Particle Size and Density
Larger, denser blocks of material require more time or a higher furnace temperature for heat to penetrate to the core. A fine powder will calcine much faster and at a lower temperature than a large stone of the same material due to its greater surface area.
Furnace Efficiency
No system is perfectly efficient. Heat loss from the furnace to the surrounding environment means the temperature setpoint must be higher than the theoretical decomposition temperature to ensure the material itself reaches the necessary heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Temperature Control
Selecting a calcination temperature is not just about meeting a minimum threshold; it's about optimizing the process to avoid common pitfalls.
The Risk of Under-heating
If the temperature is too low or the heating time is too short, the decomposition will be incomplete. This results in a final product contaminated with unreacted raw material, leading to poor quality and wasted resources.
The Problem with Over-heating
Exceeding the optimal temperature, or "over-burning," is equally problematic. It wastes a significant amount of energy and can damage the final product by causing it to sinter, reducing its porosity and chemical reactivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine the ideal calcination temperature, you must first define your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Start with the material's theoretical decomposition temperature and gradually increase it to find the minimum effective point for your specific equipment and raw material, minimizing energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is maximum product quality: Conduct pilot tests to identify the temperature range that ensures complete calcination without causing sintering or other degradation of the final product's desired properties.
- If you are working with inconsistent raw materials: A slightly higher temperature buffer, such as the 1000°C to 1100°C range used for limestone, may be necessary to ensure complete decomposition across batches with varying sizes and impurities.
Ultimately, mastering the calcination process is achieved through precise and deliberate temperature control tailored to your material and goals.
Summary Table:
| Material / Application | Typical Calcination Temperature Range | Key Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone (CaCO₃ to CaO) | 1000°C - 1100°C | Drive off CO₂ to produce reactive lime |
| General Industrial Process | 800°C - 1300°C | Induce thermal decomposition |
| Theoretical Decomposition Start | ~898°C (for pure CaCO₃) | Minimum energy threshold for reaction |
Achieve precise and efficient calcination in your laboratory.
Determining the exact temperature for your specific material is critical for complete decomposition, energy efficiency, and superior product quality. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces that deliver the precise temperature control and uniform heating your calcination processes demand.
Whether you are processing limestone, ores, or other solid materials, our equipment is designed to help you optimize your thermal treatments. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect furnace solution for your lab's needs.
Contact Us Today to Get Started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What do you use a muffle furnace for? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the hottest temperature a furnace? From 1100°C to 2000°C+
- Does melting require increase in temperature? Understanding Latent Heat and Phase Changes
- What is the use of muffle oven in laboratory? For Clean, High-Temperature Material Processing
- What should be considered when performing melting point determination? Ensure Accurate Compound Identification and Purity Assessment



















