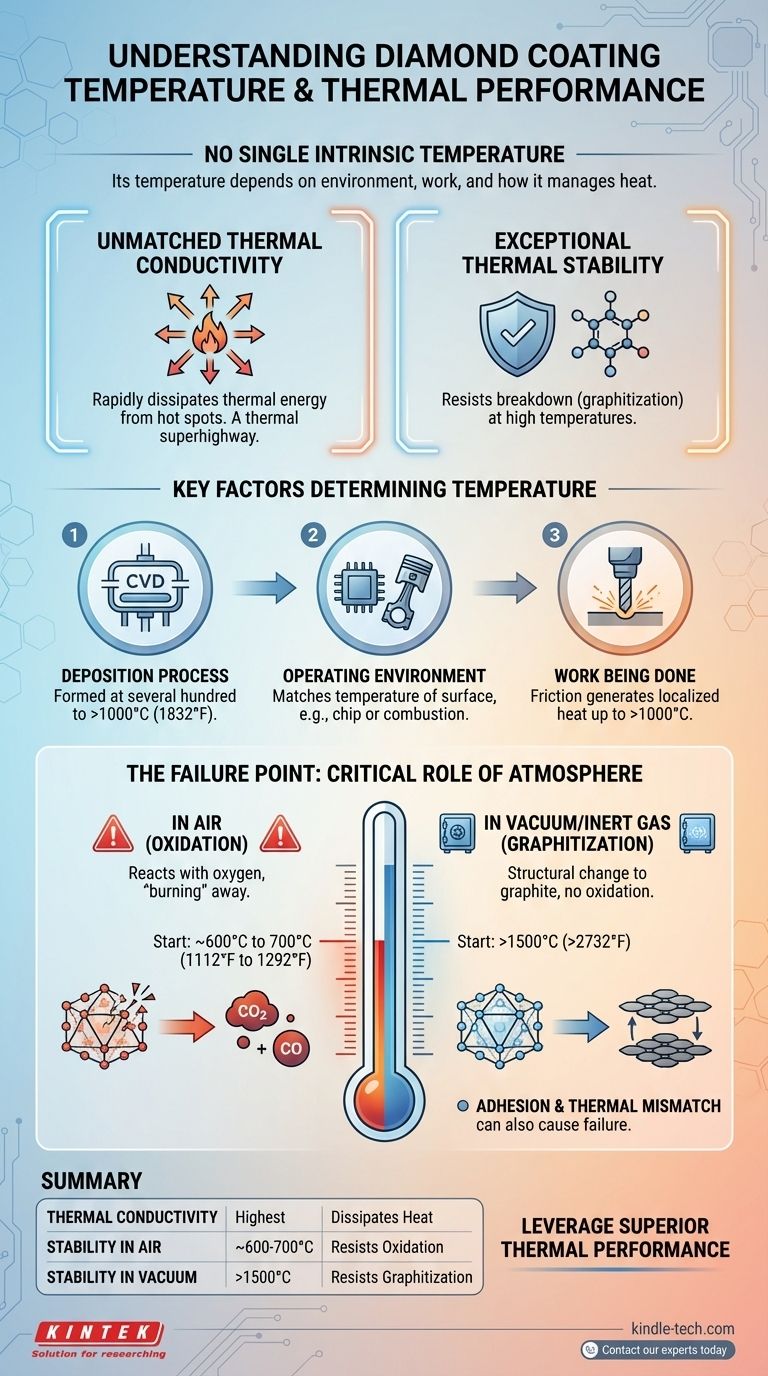
Critically, a diamond coating does not have a single, intrinsic temperature. Its temperature is entirely dependent on its environment and the work it is performing. The more important questions revolve around its two defining thermal characteristics: its ability to conduct heat away from a source (thermal conductivity) and the maximum temperature it can withstand before degrading (thermal stability).
The core issue is not a coating's inherent temperature, but how it manages heat. Diamond coatings are exceptional at rapidly dissipating thermal energy and can endure extremely high temperatures, but their ultimate limit is dictated almost entirely by the presence of oxygen.

The Two Pillars of Thermal Performance
To understand how a diamond coating behaves under thermal stress, we must separate its function into two distinct properties.
Unmatched Thermal Conductivity
A diamond coating's primary thermal superpower is its ability to spread heat. It possesses the highest thermal conductivity of any known material at room temperature.
This means it excels at pulling heat away from a concentrated "hot spot" and distributing it over a wider area, preventing localized heat buildup. Think of it as a thermal superhighway.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
This refers to the temperature at which the diamond's carbon structure begins to break down. Diamond is a metastable form of carbon; under enough heat, it will revert to a more stable form, graphite.
In the absence of oxygen, this transformation temperature is incredibly high, often cited as being above 1500°C (2732°F).
Key Factors That Determine a Coating's Temperature
In any real-world application, a diamond coating's temperature is a dynamic value determined by three factors.
The Deposition Process
Diamond coatings, typically created through Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), are formed at very high temperatures. The substrate being coated must be able to withstand temperatures ranging from several hundred to over 1000°C (1832°F) during the coating process itself.
The Operating Environment
A coating on a computer chip's heat spreader will be close to the chip's operating temperature. A coating on an engine piston will cycle through the extreme temperatures of fuel combustion. The coating will always attempt to match the temperature of the surface it protects.
The Work Being Done
For applications like cutting tools, the immense friction at the cutting edge generates localized temperatures that can reach well over 1000°C. The coating's job is both to survive this heat and to conduct it away from the cutting edge and into the body of the tool as quickly as possible.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Failure Point
The theoretical stability of diamond is impressive, but its practical limitations are crucial for any engineering application. The single greatest factor determining its failure temperature is the atmosphere.
The Critical Role of Oxygen
In the presence of air, a diamond coating's durability is significantly reduced. Like any form of carbon, diamond will react with oxygen (oxidize) at high temperatures, essentially "burning" away into carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
This oxidation process typically begins to occur at temperatures around 600°C to 700°C (1112°F to 1292°F). This is often the most important limiting factor for diamond-coated tools used in open-air machining.
Performance in a Vacuum or Inert Atmosphere
When oxygen is removed from the equation, the diamond coating can reach its true potential. In a vacuum or an inert gas environment (like argon), the failure point is no longer oxidation but graphitization.
This structural change from diamond to graphite occurs at much higher temperatures, generally above 1500°C (2732°F), allowing the coating to be used in extreme applications like space components or vacuum electronics.
Adhesion and Thermal Mismatch
A coating can also fail if it separates from the material it is bonded to (the substrate). If the substrate expands and contracts with heat at a very different rate than the diamond coating, the induced stress can cause the coating to crack or peel off long before it begins to oxidize.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your focus should not be on a single temperature value, but on how the coating's thermal properties match your application's demands.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation (e.g., electronics, optics): The key metric is its unparalleled thermal conductivity, which prevents hot spots from forming.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature wear resistance in air (e.g., cutting tools): Your critical limit is the onset of oxidation, roughly 600-700°C.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme, oxygen-free environments (e.g., space, vacuum systems): You can leverage diamond's full thermal stability, pushing towards the graphitization limit of over 1500°C.
Ultimately, leveraging a diamond coating effectively means treating it not as a material with a fixed temperature, but as a powerful tool for thermal management.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Temperature Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Highest of any material; rapidly dissipates heat from hot spots. | N/A (Functional property) |
| Stability in Air | Resists oxidation (burning) in the presence of oxygen. | ~600-700°C (1112-1292°F) |
| Stability in Vacuum/Inert Gas | Resists graphitization in oxygen-free environments. | >1500°C (>2732°F) |
Ready to leverage the superior thermal performance of diamond coatings in your lab or manufacturing process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions that utilize cutting-edge materials like diamond coatings. Whether you're developing high-performance electronics, durable cutting tools, or components for extreme environments, our expertise can help you achieve optimal thermal management and durability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and enhance your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques



















