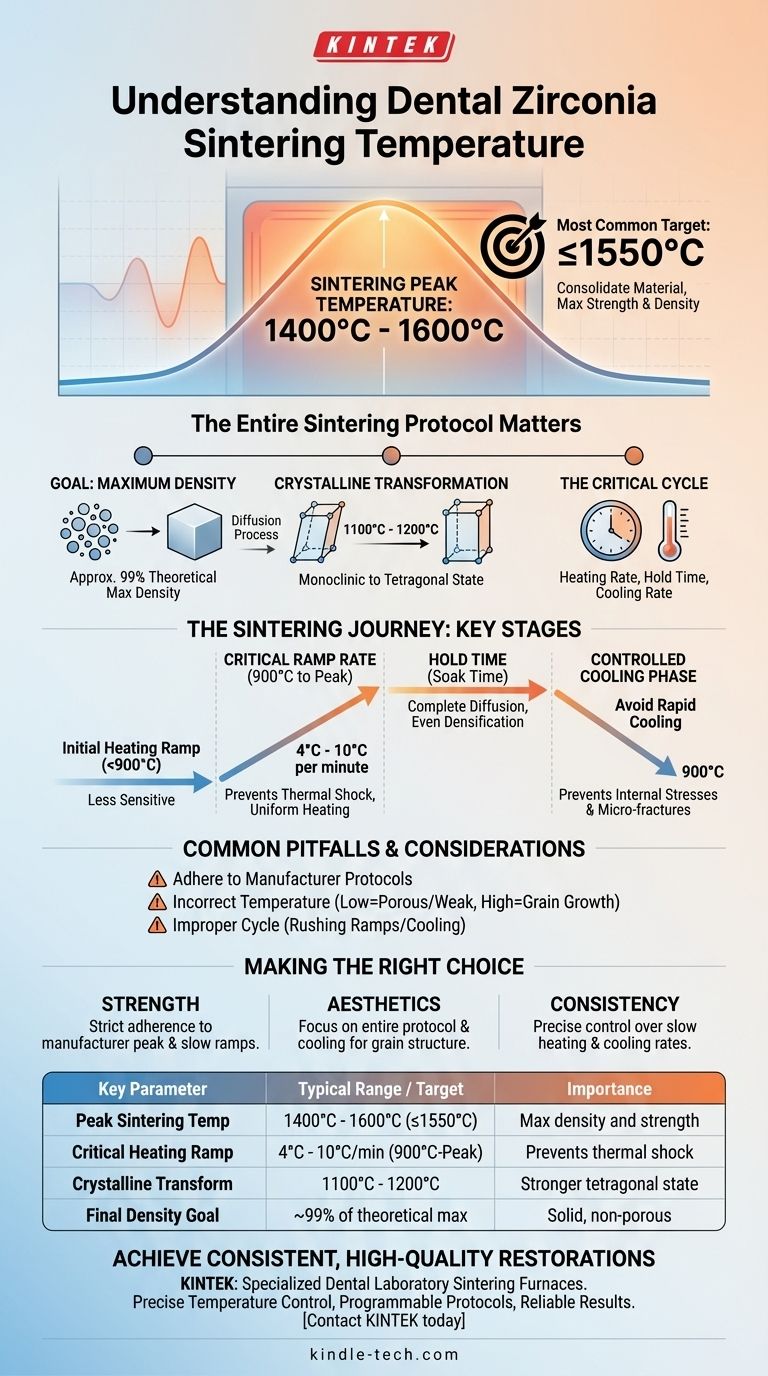
For most dental zirconia, the final sintering temperature is typically between 1400°C and 1600°C. The most common target is at or below 1550°C, a temperature required to consolidate the material and achieve its maximum strength and density.
The specific peak temperature is only one part of the equation. True success in sintering zirconia comes from understanding and controlling the entire heating and cooling cycle—the sintering protocol—as this governs the final physical and aesthetic properties of the restoration.

Why Sintering is More Than Just a Peak Temperature
Sintering is a process of thermal transformation. For zirconia, it's not simply about melting and fusing material but about inducing specific changes at a microscopic level. The goal is a dense, strong, and stable final product.
The Goal: Achieving Maximum Density
The primary objective of sintering is to transform the porous, "chalky" pre-sintered zirconia into a solid, non-porous ceramic. The high temperatures facilitate a process called diffusion, where atoms move and bond, eliminating the spaces between particles. This process aims to achieve a final restoration that is close to 99% of its theoretical maximum density.
The Crystalline Transformation
A key event occurs between 1100°C and 1200°C, where zirconia's crystal structure transforms from its monoclinic state to the much stronger tetragonal state. While this transformation is essential, the temperature must continue to rise well beyond this point to complete the densification process.
The Critical Role of the Sintering Cycle
Achieving optimal results depends less on a single temperature and more on the entire programmed cycle. This includes the rate of heating, the time spent at the peak temperature, and the rate of cooling. Each stage has a distinct and critical purpose.
The Key Stages of a Sintering Protocol
A successful sintering outcome is built on a precise and controlled temperature journey. The phases between 900°C and the peak temperature are the most sensitive.
The Initial Heating Ramp
From room temperature up to about 900°C, the zirconia restoration is not particularly sensitive. The heating rate during this initial phase is less critical than what follows.
The Critical Ramp Rate (900°C to Peak)
The rate at which the furnace temperature increases from 900°C to its final hold temperature is paramount. A slow and steady heat rise, typically between 4°C and 10°C per minute, is recommended. This prevents thermal shock and ensures the entire restoration heats uniformly, which is crucial for a predictable outcome.
The Hold Time (Soak Time)
Once the furnace reaches its peak temperature (e.g., 1550°C), it holds that temperature for a specified period. This "soak time" allows the diffusion process to complete throughout the restoration, ensuring even and complete densification.
The Controlled Cooling Phase
Just as important as the heating phase is the cooling phase, particularly the rate of cooling back down to about 900°C. Cooling too rapidly can introduce internal stresses and micro-fractures, severely compromising the structural integrity and longevity of the final restoration.
Common Pitfalls and Variables to Consider
While the principles are straightforward, several factors can lead to suboptimal results. Awareness of these variables is key to consistency.
Adhering to Manufacturer Protocols
Different zirconia formulations, such as those optimized for high translucency versus high strength, have slightly different compositions. As a result, they may require different sintering protocols. Always treat the manufacturer's specific instructions as your primary guide.
The Risk of Incorrect Temperature
Sintering at a temperature that is too low will result in incomplete densification. The restoration will be porous, weak, and may not have the desired color or translucency. Conversely, sintering at a temperature that is too high can cause excessive grain growth, which can sometimes reduce strength and alter the material's aesthetic properties.
The Impact of an Incorrect Cycle
Even with the correct peak temperature, rushing the ramp-up or cool-down phases is a common cause of failure. An improper cycle is a primary source of internal stress that can lead to fractures long after the restoration has been placed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve predictable and high-quality results, align your sintering protocol with your primary objective for the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Strictly adhere to the manufacturer's recommended peak temperature and slow ramp rates to ensure you achieve the highest possible density.
- If your primary focus is optimal aesthetics: Pay close attention to the entire protocol, as the peak temperature and cooling cycle significantly impact the final grain structure, which governs light transmission and translucency.
- If your primary focus is consistency and avoiding failures: The most critical factor is precise control over the slow heating and cooling rates, especially between 900°C and the peak temperature.
Mastering the full sintering protocol is the key to unlocking the full potential of your zirconia restorations.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Typical Range / Target | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Sintering Temperature | 1400°C - 1600°C (Common: ≤1550°C) | Achieves maximum density and strength |
| Critical Heating Ramp Rate | 4°C - 10°C per minute (900°C to Peak) | Prevents thermal shock, ensures uniform heating |
| Crystalline Transformation | 1100°C - 1200°C | Transforms to stronger tetragonal state |
| Final Density Goal | ~99% of theoretical maximum | Ensures restoration is solid and non-porous |
Achieve consistent, high-quality zirconia restorations with precise thermal control.
At KINTEK, we specialize in laboratory sintering furnaces designed specifically for the dental industry. Our equipment provides the exact temperature control and programmable protocols necessary to perfectly sinter zirconia for maximum strength, optimal aesthetics, and unwavering consistency.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your dental lab:
- Precise Temperature Control: Ensure you hit the critical 1400-1600°C range accurately every time.
- Programmable Protocols: Easily set and replicate the slow ramp rates and soak times required for different zirconia formulations.
- Reliable Results: Eliminate failures and achieve the density and translucency your restorations demand.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect sintering solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature for zirconia? Unlock Maximum Strength and Aesthetics
- What is a burnout furnace? The Key to Flawless Precision Casting
- What is the shrinkage of zirconia during sintering? Mastering the 20-25% Dimensional Change
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- What is the difference between porcelain and ceramic restoration? Choose the Right Material for Your Smile
- What is the firing of porcelain in dentistry? The Lab Process for Strong, Life-like Crowns & Veneers
- What are the materials used in dental ceramics? Choosing the Right Material for Strength & Aesthetics
- What is the strongest type of zirconia? A Guide to Choosing the Right Dental Zirconia



















