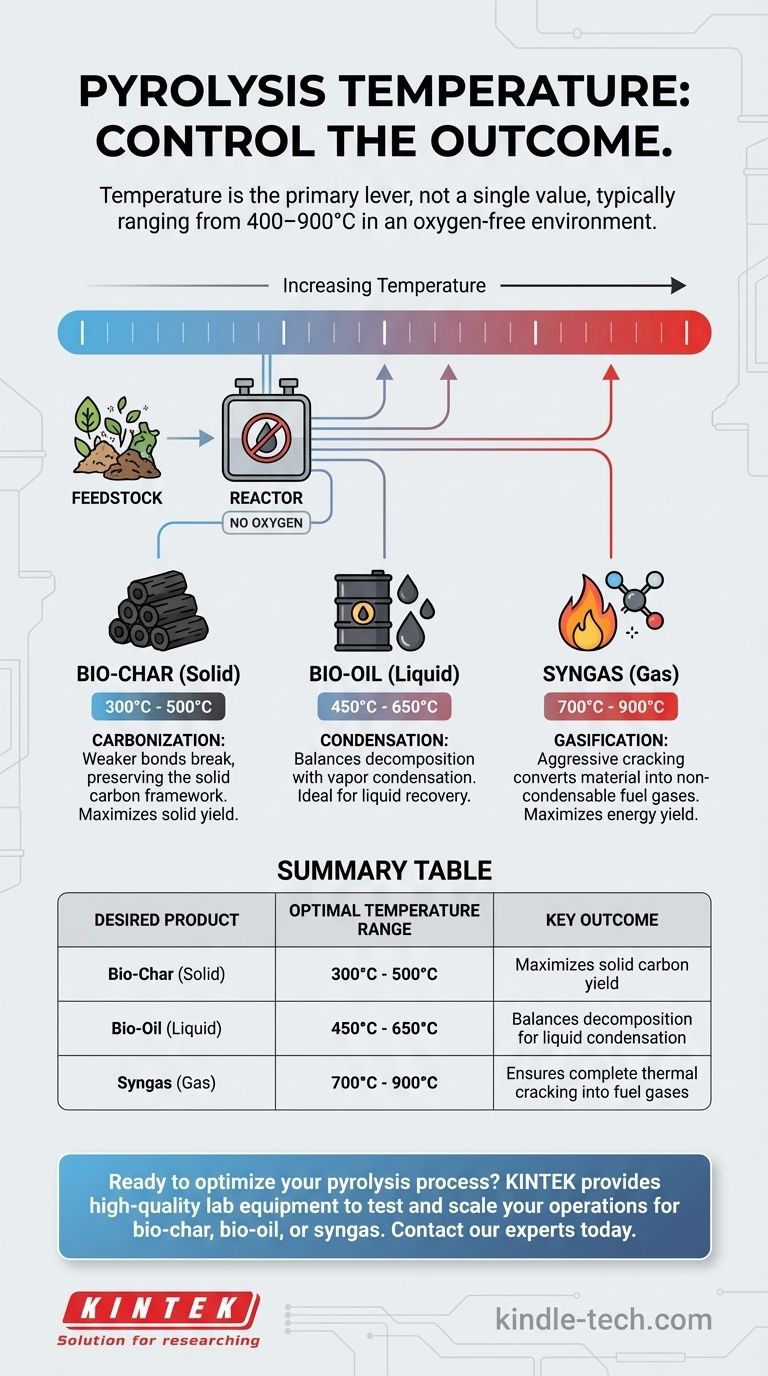
The temperature of pyrolysis is not a single value but a carefully controlled range that depends entirely on the feedstock and the desired final product. This thermochemical process, which decomposes material in an oxygen-free environment, typically operates between 400-900°C, though it can begin at temperatures as low as 200°C for materials like wood.
The core principle to understand is that temperature is the primary lever used to control the outcome of pyrolysis. Lower temperatures are used to maximize solid bio-char production, while higher temperatures are used to maximize the yield of energy-rich syngas.

How Temperature Dictates Pyrolysis Outcomes
Pyrolysis is fundamentally about using heat to break complex materials down into simpler, more valuable substances. The specific temperature applied directly determines which substances are produced and in what quantity.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
Pyrolysis involves heating a material, such as biomass or plastic, in a reactor without oxygen. The absence of oxygen is critical; it prevents combustion and instead forces the material's long molecular chains to fracture, or "crack," into smaller molecules.
The final outputs fall into three categories: a solid residue (bio-char), a condensable liquid (bio-oil), and non-condensable gases (syngas).
Low-Temperature Pyrolysis (Carbonization)
At lower temperatures, typically below 500°C, the decomposition process is less severe. The weaker chemical bonds break, but many of the more stable carbon structures remain intact.
This process favors the production of a high-quality, carbon-rich solid. This is the principle behind creating charcoal or bio-char, where the goal is to preserve as much of the solid carbon framework as possible.
High-Temperature Pyrolysis (Gasification)
As the temperature increases, generally above 700°C, the thermal energy becomes intense enough to break even the strongest molecular bonds.
This aggressive cracking process converts most of the material, including the liquids and solids formed at lower temperatures, into simple, non-condensable gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This is the ideal condition for maximizing syngas yield for fuel or energy generation.
Intermediate Temperatures for Bio-Oil
To maximize the production of liquid bio-oil, operators target a middle ground, often between 450-650°C.
At these temperatures, the process is hot enough to break down the initial feedstock but cool enough to allow the resulting vapors to be condensed into a liquid before they are further cracked into gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a temperature is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" temperature, only the optimal temperature for a specific goal.
Energy Consumption vs. Output
Higher temperatures require a significantly greater energy input. Running a reactor at 800°C is far more costly than running it at 450°C. This energy cost must be justified by the value of the final product, such as high-volume syngas for electricity generation.
It's More Than Just Temperature
While temperature is the dominant factor, it doesn't work in isolation. Other variables, including the feedstock type, the heating rate, pressure, and the residence time inside the reactor, all interact to influence the final product yields. Optimizing a process requires tuning all these factors in concert.
Choosing the Right Temperature for Your Goal
The correct approach is to define your desired output first and then select the temperature required to achieve it.
- If your primary focus is producing solid bio-char: Opt for lower-temperature pyrolysis, typically in the 300-500°C range, to maximize solid yield and carbon content.
- If your primary focus is generating liquid bio-oil: Target moderate temperatures, often between 450-650°C, which balances decomposition with the ability to condense valuable vapors.
- If your primary focus is creating syngas for energy: Use high-temperature pyrolysis, generally above 700°C, to ensure complete thermal cracking into non-condensable gases.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis means treating temperature not as a fixed setting, but as the primary control for transforming waste into value.
Summary Table:
| Desired Product | Optimal Temperature Range | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-Char (Solid) | 300°C - 500°C | Maximizes solid carbon yield |
| Bio-Oil (Liquid) | 450°C - 650°C | Balances decomposition for liquid condensation |
| Syngas (Gas) | 700°C - 900°C | Ensures complete thermal cracking into fuel gases |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? The precise temperature control required for maximum yield depends on high-quality lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in the reactors and consumables needed to accurately test and scale your pyrolysis operations, whether your goal is bio-char, bio-oil, or syngas production. Contact our experts today to discuss the right equipment for your specific feedstock and targets.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results



















