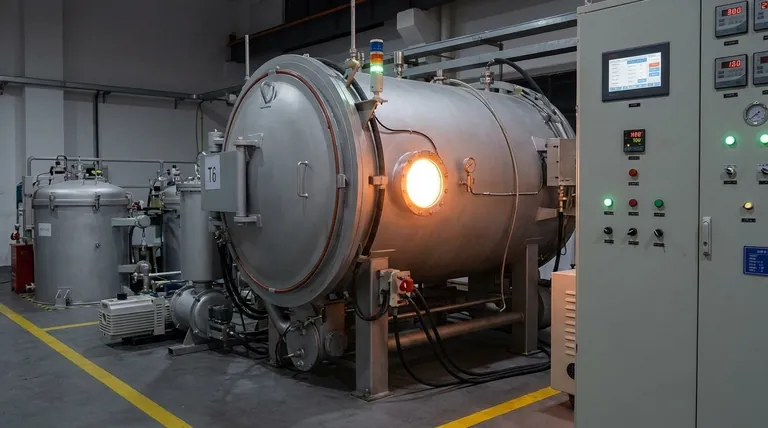
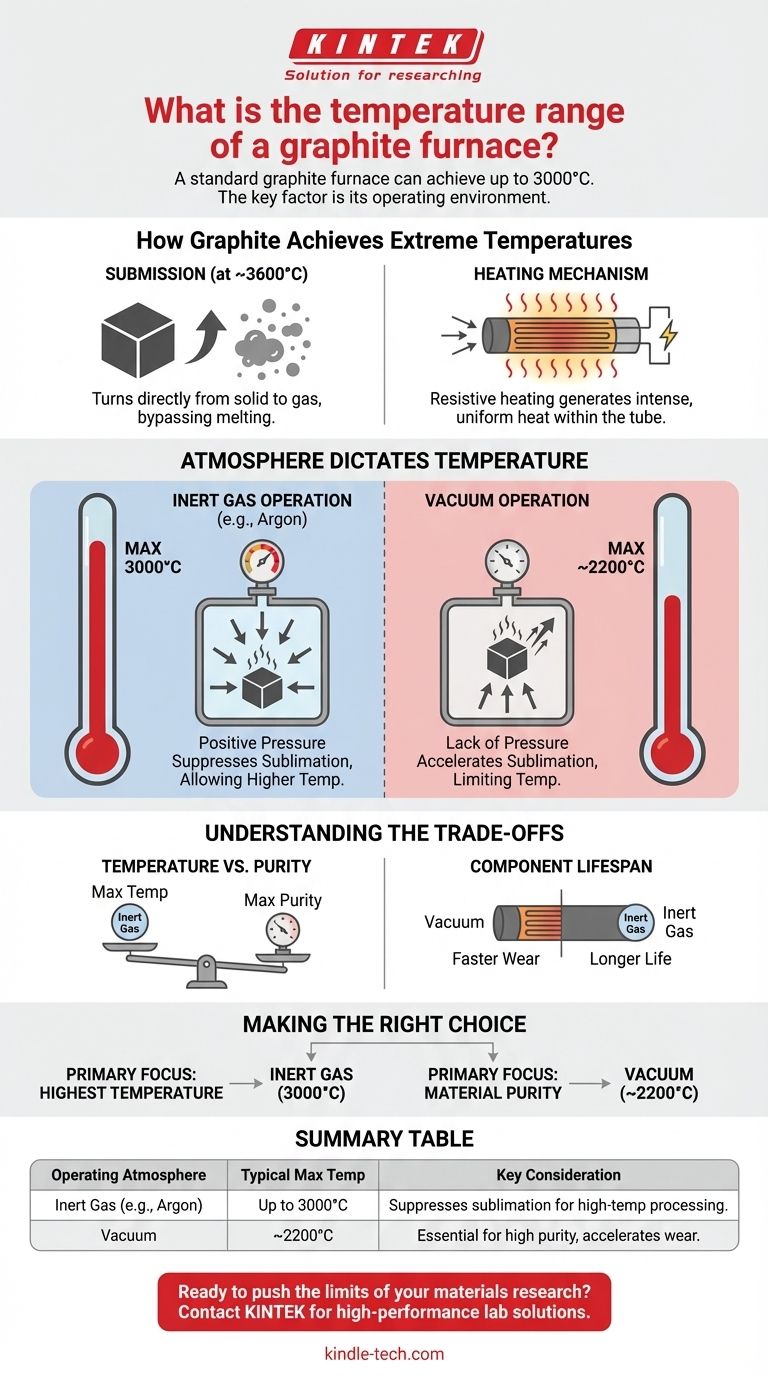
A standard graphite furnace can achieve an operating temperature as high as 3000°C. This capability makes it an essential tool for advanced materials science, high-purity processing, and specialized testing. However, the maximum achievable temperature is not a single number; it is fundamentally dependent on the furnace's design and, most critically, its internal atmosphere.
The key takeaway is that a graphite furnace's temperature range is a function of its operating environment. Furnaces pressurized with an inert gas can reach 3000°C, while vacuum furnaces are typically limited to around 2200°C to prevent the rapid degradation of the graphite heating element itself.

How Graphite Achieves Extreme Temperatures
Graphite is uniquely suited for high-temperature applications due to its fundamental physical properties. Understanding these properties is key to understanding the furnace's capabilities.
The Role of Sublimation
Unlike most materials, graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimates—turning directly from a solid to a gas—at approximately 3600°C. This exceptionally high sublimation point is what allows the material to remain structurally stable at extreme temperatures.
The Heating Mechanism
In a graphite furnace, the graphite tube itself is the heating element. A high electrical current is passed through the tube, and its natural electrical resistance generates intense, uniform heat through resistive heating.
How Operating Atmosphere Dictates Temperature
The environment inside the furnace is the single most important factor determining its maximum safe operating temperature. The choice is almost always between an inert gas or a vacuum.
Inert Gas Operation (Up to 3000°C)
To reach the highest possible temperatures, the furnace is backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, such as argon. This gas creates positive pressure inside the furnace chamber.
This pressure physically suppresses the sublimation of the graphite heating element, allowing it to be pushed to its upper limit of 3000°C without rapidly degrading.
Vacuum Operation (Typically ~2200°C)
Operating the furnace under a vacuum is essential for applications requiring extreme purity or preventing any reaction between the sample and a gas atmosphere.
However, the vacuum environment has the opposite effect of inert gas. The lack of pressure accelerates the sublimation of the graphite, causing the heating element to degrade at a much lower temperature. For this reason, vacuum graphite furnaces are often limited to a maximum of 2200°C to ensure a reasonable lifespan for the components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision between using an inert gas or a vacuum is a critical trade-off between achieving maximum temperature and ensuring maximum purity.
Temperature vs. Purity
If your process requires the absolute highest temperature for melting, sintering, or graphitization, an inert gas environment is necessary.
If your process cannot tolerate any atmospheric contamination and requires the cleanest possible environment, a vacuum is the only option, but you must accept a lower temperature ceiling.
Lifespan of Components
Consistently operating any furnace at its absolute maximum temperature will shorten the life of its heating elements and insulation. This effect is significantly more pronounced in a vacuum, where the graphite heating tube will wear out faster due to increased sublimation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct operating parameters, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperature: Utilize an inert gas atmosphere to suppress graphite sublimation and safely operate up to 3000°C.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing atmospheric reactions: A vacuum furnace is the correct choice, but you must work within its lower maximum temperature of approximately 2200°C.
Ultimately, understanding this direct relationship between internal pressure and sublimation is the key to leveraging the full potential of a graphite furnace for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Operating Atmosphere | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas (e.g., Argon) | Up to 3000°C | Suppresses graphite sublimation for high-temperature processing. |
| Vacuum | ~2200°C | Essential for high-purity applications but accelerates component wear. |
Ready to push the limits of your materials research?
Choosing the right furnace configuration is critical for your success. Whether your priority is achieving extreme temperatures up to 3000°C or ensuring an ultra-pure vacuum environment, KINTEK's expertise in high-performance lab equipment can guide you to the perfect solution.
We specialize in providing reliable graphite furnaces and consumables tailored to the demanding needs of advanced laboratories.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure you get the performance and purity your research demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial uses of graphite? Leverage Its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- What are the interferences of graphite furnace? Overcome Matrix & Spectral Issues for Accurate GFAAS
- What is carbonization process? A Complete Guide to Converting Biomass to Charcoal
- What is special about graphite? Unlocking Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications
- Does graphite conduct electricity when melted? Discover the Secrets of Liquid Carbon Conductivity
- Why is graphite the best conductor of heat? Understanding Its Directional Thermal Superiority



















