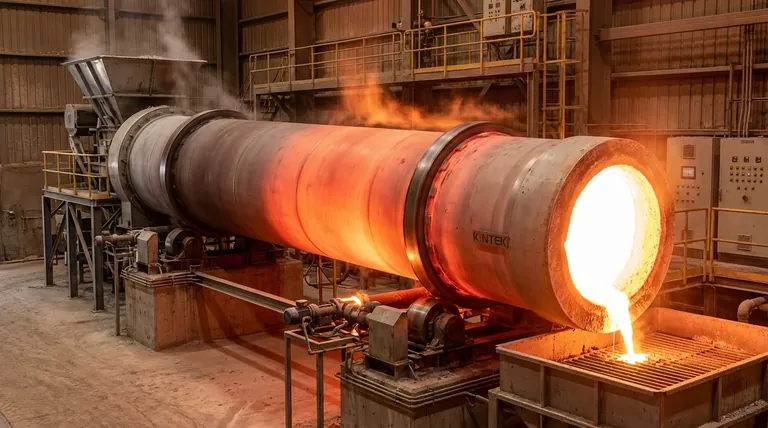
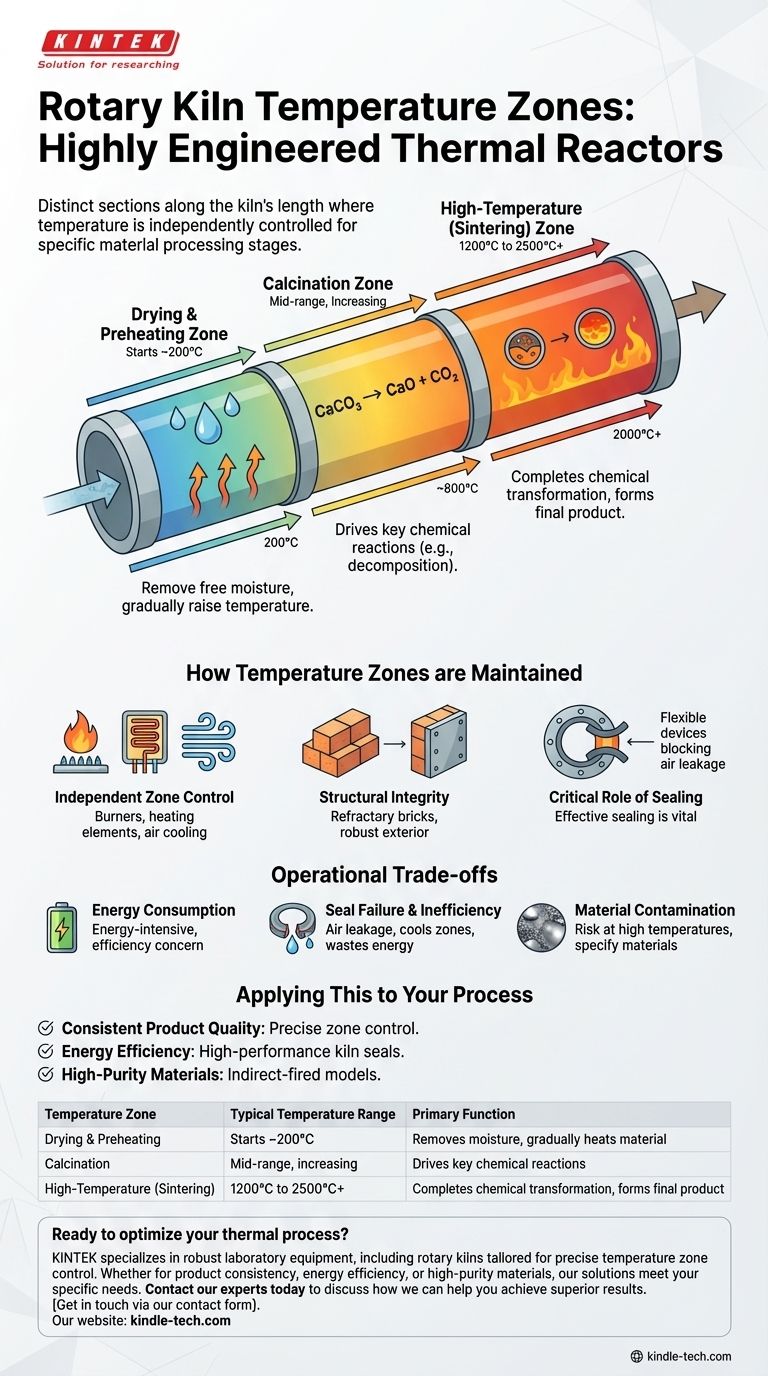
In a rotary kiln, a temperature zone is a distinct section along its cylindrical length where the temperature is independently controlled to perform a specific stage of material processing. Rather than having one uniform temperature, the kiln is divided into a series of zones—typically a preheating zone, a transition or calcination zone, and a high-temperature or sintering zone—each set to a precise temperature required for the process at hand.
The concept of temperature zones transforms the rotary kiln from a simple furnace into a highly engineered thermal reactor. The true purpose is not just to heat a material, but to guide it through a carefully choreographed temperature profile, ensuring specific chemical and physical changes occur at the right time and place.

The Purpose of the Thermal Profile
A rotary kiln uses its rotational and tilted design to move material from the feed end to the discharge end. The temperature zones are strategically arranged along this path to create a thermal journey that systematically transforms the raw feed into a finished product.
The Drying and Preheating Zone
This is the first section the material enters. Its primary role is to remove free moisture and gradually raise the material's temperature, preparing it for the high-temperature reactions to come. Temperatures here are the lowest in the kiln, often starting around 200°C.
The Calcination Zone
In the middle of the kiln, the temperature increases significantly. In processes like cement manufacturing, this is where calcination occurs—a chemical reaction driven by heat that, for example, decomposes calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and releases carbon dioxide. This zone is critical for the material's chemical conversion.
The High-Temperature (Sintering) Zone
This final, hottest zone is the heart of the process. Here, temperatures can reach extreme levels, often from 1200°C to over 2000°C, depending on the application. This intense heat causes the material to sinter or form clinker, completing its chemical transformation into the final desired product.
How Temperature Zones are Maintained
Achieving and maintaining these distinct, stable temperature zones requires sophisticated engineering. The control system is designed to manage a precise heat pattern that matches the specific firing needs of the product.
Independent Zone Control
Each temperature zone can be set and adjusted separately. This is achieved through a combination of strategically placed burners, 360° heater elements for uniform heat, and even air cooling mechanisms that provide stable, responsive temperature management.
Structural Integrity at High Temperatures
The kiln must be designed to withstand immense thermal stress. This involves using specialized refractory materials on the inside and robust external components. The overall temperature range of a kiln can span from 200°C to 2500°C, accommodating a vast array of industrial processes.
The Critical Role of Sealing
A key component for maintaining the thermal profile is the kiln seal. These flexible devices prevent cool ambient air from entering the kiln and hot gases from escaping at the junctions between the rotating cylinder and the stationary feed and discharge housings. Effective sealing is vital for maintaining the high temperatures required, particularly above 1000°C.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While powerful, operating a zoned rotary kiln involves balancing competing priorities and managing inherent challenges.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining a precise thermal profile, especially with zones exceeding 1200°C, is extremely energy-intensive. A significant portion of the operational cost is fuel or electricity, making efficiency a primary concern.
Seal Failure and Inefficiency
A compromised or failed seal is a major point of failure. It leads to air leakage, which can dramatically cool a zone, disrupt the thermal environment, and reduce the temperature of process gases, ultimately wasting energy and compromising product quality.
Material Contamination
At very high temperatures, there is a risk of metal contamination from the kiln components themselves. For high-purity applications, kilns must be customized with special materials or indirect heating designs where the flame does not directly contact the product.
Applying This to Your Process
Understanding the function of each zone allows you to optimize the kiln's operation for your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is consistent product quality: Prioritize precise and stable control over each individual temperature zone to ensure the material undergoes the correct transformation at each stage.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Invest in high-performance kiln seals to prevent heat loss and optimize the preheating zone to recover as much heat as possible from exhaust gases.
- If your primary focus is processing high-purity materials: Specify a kiln design, such as an indirect-fired model, that is engineered to suppress or eliminate sources of contamination.
Mastering the temperature zones is the key to unlocking the full potential of your rotary kiln process.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Zone | Typical Temperature Range | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Drying & Preheating | Starts ~200°C | Removes moisture, gradually heats material |
| Calcination | Mid-range, increasing | Drives key chemical reactions (e.g., decomposition) |
| High-Temperature (Sintering) | 1200°C to 2500°C+ | Completes chemical transformation, forms final product |
Ready to optimize your thermal process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in designing and supplying robust laboratory equipment, including rotary kilns tailored for precise temperature zone control. Whether your priority is product consistency, energy efficiency, or processing high-purity materials, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results with the right equipment and consumables. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What are the disadvantages of rotary kiln incinerator? High Costs and Operational Complexities
- What furnace is used for calcination? A Guide to Muffle, Rotary Kiln, and Shaft Furnaces
- How long is the calcination process? Optimize Your Process Time for Maximum Efficiency
- What is a fluidized bed chemical reaction? A Guide to Superior Heat Transfer & Continuous Processing
- How does a rotary kiln work? Unlock Continuous, High-Volume Thermal Processing
- What is biochar obtained from the pyrolysis? A Key Product of Biomass Conversion
- What is a carbon regeneration kiln? Reuse Spent Carbon to Cut Costs & Waste



















