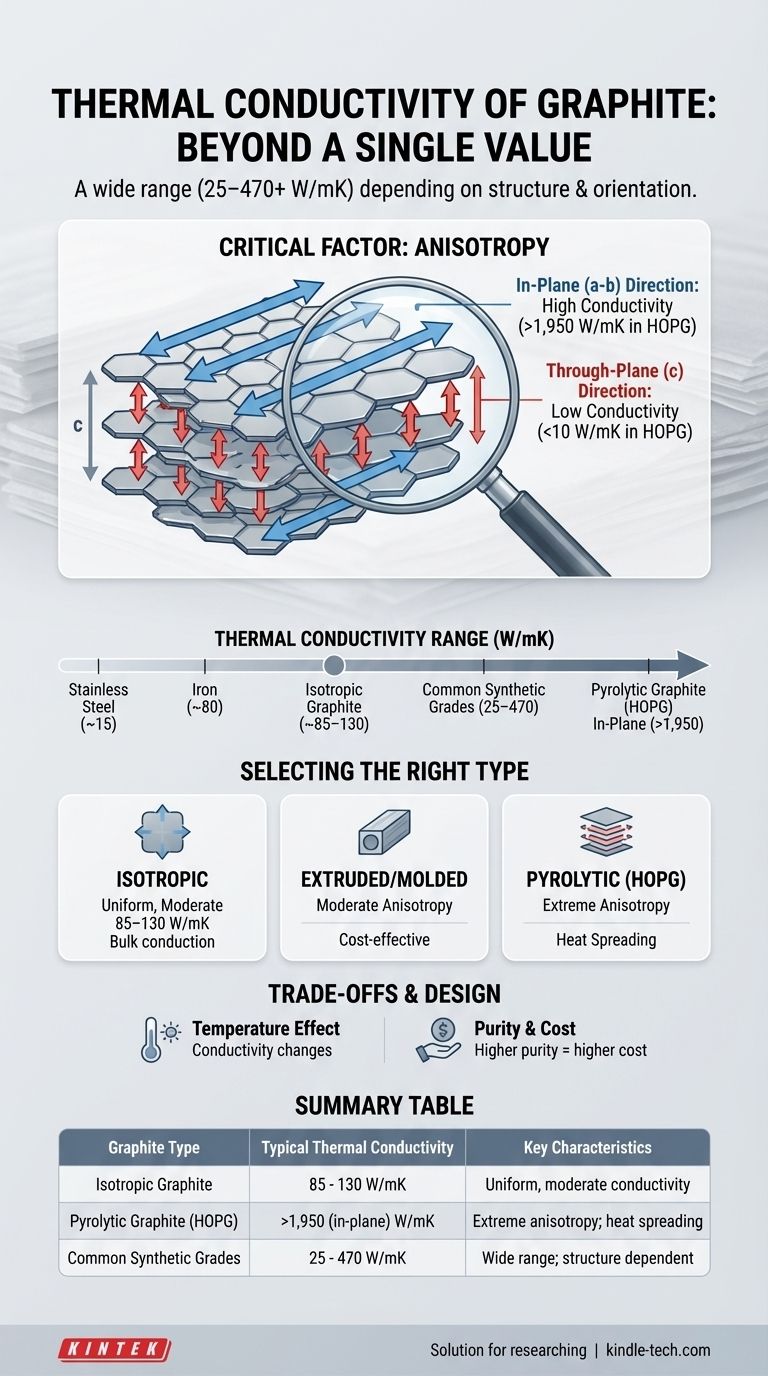
The thermal conductivity of graphite is not a single value but spans an extremely wide range, from 25 to 470 Watts per meter-Kelvin (W/mK) for common synthetic grades. This value is highly dependent on the material's specific structure, purity, and orientation, with specialized forms like pyrolytic graphite reaching over 1,950 W/mK in certain directions—far exceeding metals like iron or steel.
The core issue is that "graphite" is a category of materials, not a single substance. Its thermal performance is dictated by its internal crystalline structure and manufacturing process, meaning the right choice depends entirely on the specific engineering goal.

Why "Graphite" is Not a Single Answer
To select the right graphite, you must understand what causes its thermal conductivity to vary so dramatically. It comes down to its unique atomic structure and how that structure is arranged in the final product.
The Critical Role of Anisotropy
Graphite consists of stacked layers of graphene sheets. The bonds within these sheets are incredibly strong, allowing heat to travel very efficiently along the layer, known as the in-plane (a-b) direction.
However, the bonds between the layers are very weak. This makes it difficult for heat to transfer from one layer to the next, known as the through-plane (c) direction.
This property, anisotropy, is the single most important factor. Heat moves easily along the graphite planes but struggles to move across them.
The Impact of Form and Grade
Manufacturers can control the orientation of these graphite planes, leading to different grades with vastly different properties.
- Isotropic Graphite: The crystal grains are randomly oriented. This results in uniform, but moderate, thermal conductivity in all directions, typically in the 85-130 W/mK range.
- Extruded or Molded Graphite: The manufacturing process partially aligns the graphite planes, creating moderate anisotropy and conductivity that is higher in one direction than another.
- Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite (HOPG): This is a high-purity, synthetic form where the layers are almost perfectly aligned. It exhibits extreme anisotropy, with in-plane conductivity exceeding 1,950 W/mK (over 4x copper) while through-plane conductivity can be less than 10 W/mK (similar to stainless steel).
A Practical Range of Values
For context, let's compare these values to the metals mentioned in common references.
- Iron: ~80 W/mK
- Carbon Steel: ~50 W/mK
- Stainless Steel: ~15 W/mK
Even a standard block of isotropic graphite (~120 W/mK) is a significantly better conductor than steel. Specialized grades engineered for heat spreading are in a class of their own.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high thermal conductivity is attractive, it is not the only factor to consider. The unique properties of graphite introduce specific design challenges.
Anisotropy: A Double-Edged Sword
The exceptional in-plane conductivity of pyrolytic graphite makes it an ideal heat spreader. It can rapidly move thermal energy away from a hot spot across a surface.
However, its poor through-plane conductivity means it is a poor choice for moving heat through the material to an attached heat sink. This can create thermal bottlenecks if not accounted for in the design.
The Effect of Temperature
For highly crystalline forms of graphite, thermal conductivity typically peaks near or just below room temperature and then decreases as temperature rises.
For less crystalline or amorphous forms, the opposite can be true, where conductivity may increase with temperature in a specific range. It is critical to consult the manufacturer's data sheet for the specific grade and intended operating temperature of your application.
Purity, Density, and Cost
As a rule, higher thermal performance in graphite correlates with higher purity, density, and processing complexity. This means that high-performance grades like HOPG are significantly more expensive than common isotropic or molded graphite blocks.
Choosing the Right Graphite for Your Application
Your selection should be driven by a clear understanding of your primary thermal management goal.
- If your primary focus is spreading heat across a surface (e.g., for a CPU heat spreader or electronics thermal interface): You need a highly anisotropic material like pyrolytic graphite, oriented with its conductive planes parallel to the surface.
- If your primary focus is conducting heat in bulk (e.g., for a crucible or heating element): An isotropic graphite is a better choice, providing predictable and uniform thermal performance in all directions.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general thermal applications: A standard molded or extruded graphite block offers a significant performance uplift over metals like steel without the high cost of specialized grades.
Ultimately, treating graphite as a versatile but highly specialized material family is the key to leveraging its remarkable thermal properties.
Summary Table:
| Graphite Type | Typical Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Isotropic Graphite | 85 - 130 | Uniform, moderate conductivity in all directions |
| Pyrolytic Graphite (HOPG) | >1,950 (in-plane) | Extreme anisotropy; ideal for heat spreading |
| Common Synthetic Grades | 25 - 470 | Wide range; depends on structure and purity |
Struggling to select the right graphite for your thermal management needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of graphite materials tailored for laboratory and industrial applications. Our experts can help you choose the perfect grade—whether you need isotropic graphite for uniform heating or specialized pyrolytic graphite for superior heat spreading. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your project's efficiency with the right material solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of sputter coating? Achieve Atomic-Scale Precision and Uniformity
- What is the role of laboratory heating and stirring systems in alumina sol-gel? Achieve Superior Coating Homogeneity
- What is the most efficient way to remove excess low boiling point solvent from a high boiling point material? Use Rotary Evaporation for Fast, Safe Removal
- What is the difference between extruded and isostatic graphite? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the disadvantages of using graphite? Key Limitations in High-Tech Applications
- What is the source of bio-oil? Unlock Renewable Energy from Biomass
- What is the current of sputtering ion? Control Your Thin Film Deposition Rate and Quality
- What is the sputtering target for thin film? The Source Material Defining Your Coating's Performance



















