In short, a catalyst is used in pyrolysis to precisely control the chemical reactions. It acts as a chemical "guide," lowering the energy required for the process and steering the decomposition of raw materials toward producing a higher-quality, more valuable oil that is easier to refine.
The fundamental role of a catalyst is to transform pyrolysis from a brute-force thermal decomposition into a more targeted and efficient chemical conversion. This provides greater control over the final product, turning a complex process into a more predictable and valuable one.
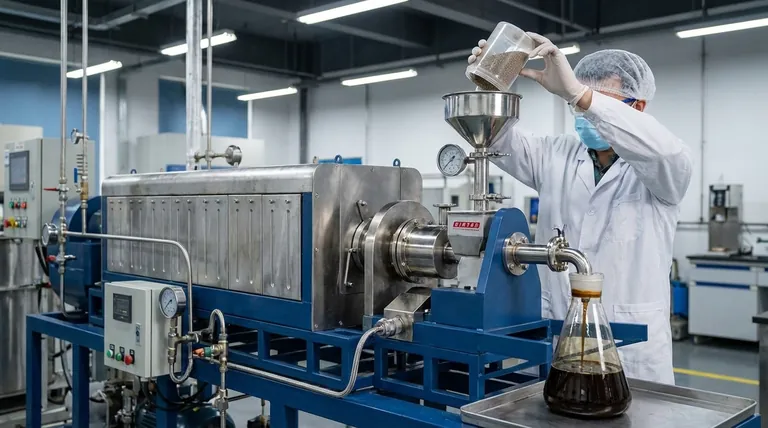

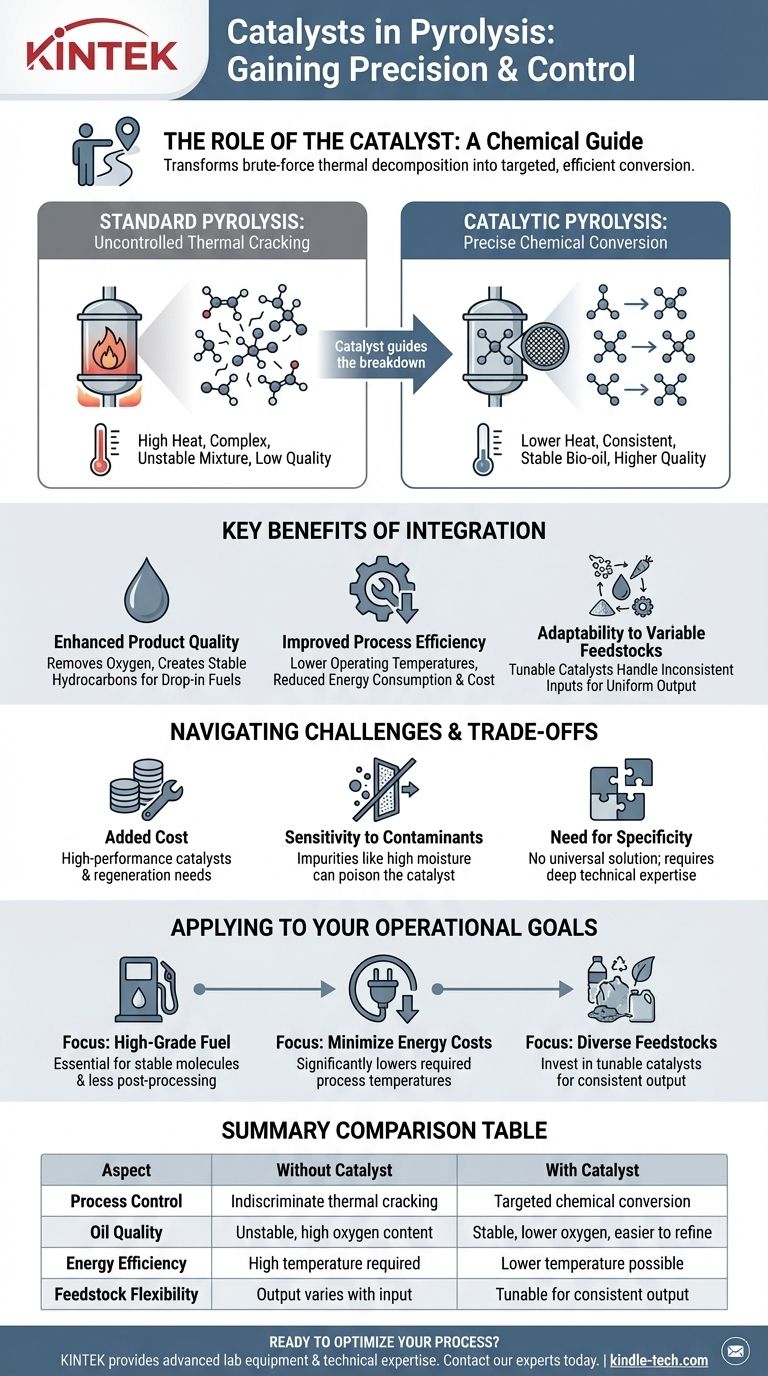
From Uncontrolled Cracking to Precise Conversion
To understand the catalyst's role, we must first understand the challenge it solves. The core issue with basic pyrolysis is a lack of control over the final output.
The Goal of Standard Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the process of breaking down complex organic materials—like waste plastic or biomass—at high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. The goal is to thermally crack large, complex molecules into smaller, more useful ones, primarily a liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
The Problem: A Low-Quality, Complex Mixture
Without a catalyst, this process is largely indiscriminate. The intense heat breaks chemical bonds almost at random, resulting in a complex, often unstable mixture of hundreds of different organic compounds. This oil is typically acidic, contains too much oxygen, and requires significant, costly upgrading before it can be used as a conventional fuel.
The Catalyst as a "Chemical Guide"
A catalyst introduces a level of precision. It provides an active surface where specific chemical reactions can occur more easily and at a lower energy level. Instead of random thermal cracking, the catalyst favors certain reaction pathways, guiding the breakdown of feedstock into a more desirable and consistent set of molecules.
The Key Benefits of Catalytic Pyrolysis
Introducing a catalyst is a strategic decision to overcome the inherent limitations of thermal-only pyrolysis. It delivers clear advantages in product quality, process efficiency, and adaptability.
Enhancing Final Product Quality
The primary benefit is a superior end product. A catalyst can promote reactions that remove oxygen and create more stable hydrocarbon molecules, similar to those found in conventional crude oil. This results in a higher-quality pyrolysis oil that is more easily upgraded into drop-in fuels.
Improving Process Efficiency
Catalysts allow reactions to occur at lower temperatures. This principle is seen in other high-temperature industrial processes, such as the synthesis of diamonds where a metal catalyst reduces the extreme temperature and pressure required. In pyrolysis, this translates directly to lower energy consumption, reducing operational costs and technological complexity.
Adapting to Variable Feedstocks
Raw materials like biomass or mixed plastics are notoriously inconsistent. Their chemical makeup and properties can vary significantly. Tunable catalysts can be designed to handle this variability, favoring specific reactions to produce a consistent output even when the input material changes.
Understanding the Challenges and Trade-offs
While powerful, catalysts are not a universal solution and introduce their own set of operational complexities. An objective assessment must acknowledge these factors.
Added System Cost
High-performance catalysts can be expensive, representing a significant capital and operational cost. Their eventual need for replacement or regeneration must be factored into the economic model of the plant.
Sensitivity to Contaminants
The performance of a catalyst is highly sensitive to the quality of the feedstock. Impurities can "poison" the catalyst, blocking its active sites and rendering it ineffective. For example, high moisture content (above 10%) in biomass can hinder the process, and other contaminants must be removed through pre-treatment, adding another layer of complexity.
The Need for Specificity
There is no "one-size-fits-all" catalyst. The ideal choice depends entirely on the specific type of feedstock being processed and the desired chemical composition of the final oil. Selecting and managing the right catalyst requires deep technical expertise.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your decision to use a catalyst should be based on your specific operational and economic objectives.
- If your primary focus is producing high-grade, easily refined fuel: A catalyst is essential for creating stable, desirable hydrocarbon molecules and reducing the need for extensive post-processing.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy costs: A well-chosen catalyst can significantly lower the required process temperature, leading to substantial savings in energy consumption.
- If you are processing diverse or inconsistent feedstocks: You must invest in tunable or specialized catalysts designed to handle the specific chemical makeup of your input materials to ensure a consistent output.
Ultimately, integrating a catalyst is the key strategic decision for gaining precision, efficiency, and control over the pyrolysis process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Without Catalyst | With Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Process Control | Indiscriminate thermal cracking | Targeted chemical conversion |
| Oil Quality | Unstable, high oxygen content | Stable, lower oxygen, easier to refine |
| Energy Efficiency | High temperature required | Lower temperature possible |
| Feedstock Flexibility | Output varies with input | Tunable for consistent output |
Ready to transform your pyrolysis process?
Catalytic pyrolysis is the key to unlocking higher efficiency and a more valuable end product. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and technical expertise needed to develop and optimize your catalytic processes. Whether you're working with biomass, plastics, or other feedstocks, our solutions are designed to help you achieve precise control and superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific pyrolysis goals and drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















