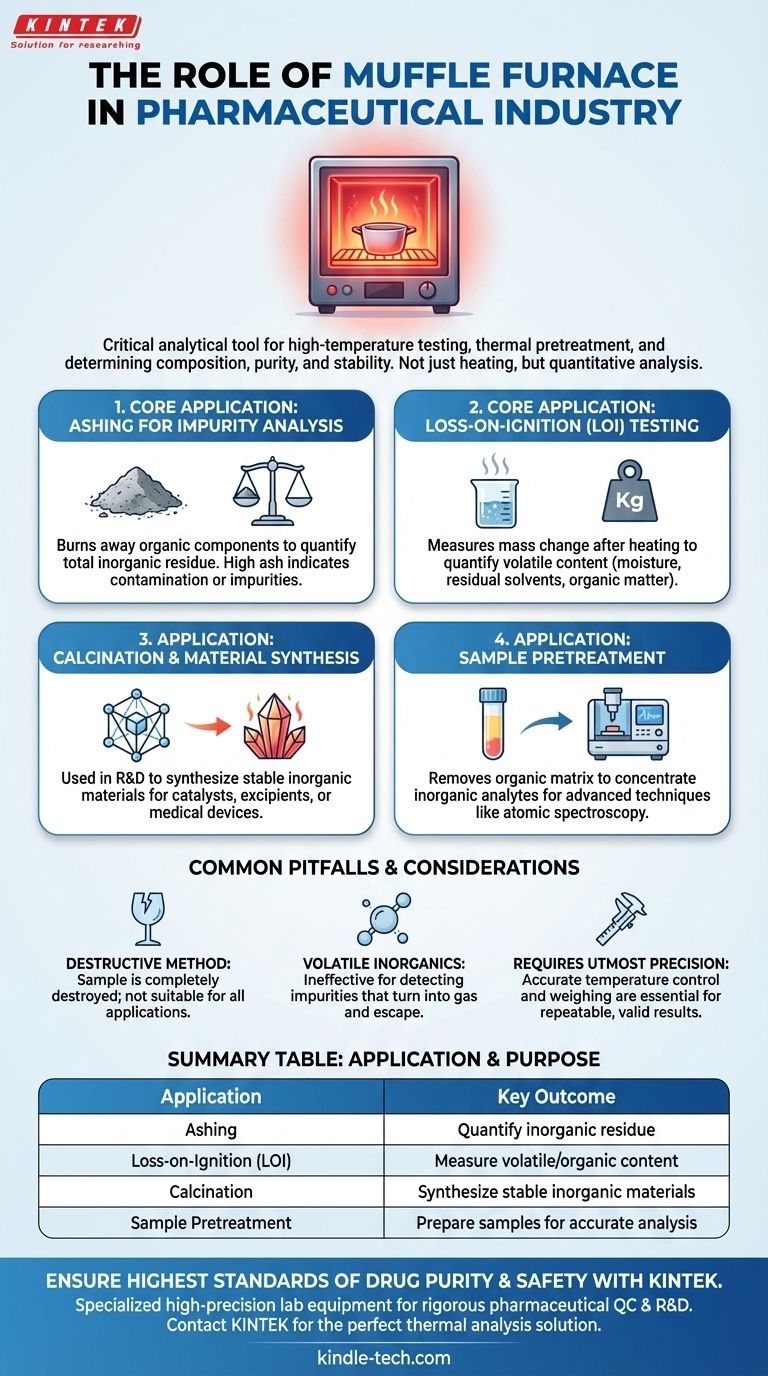
In the pharmaceutical industry, a muffle furnace is a critical analytical tool used for high-temperature testing and the thermal pretreatment of medical and drug samples. Its primary function is to subject a sample to a precise and controlled temperature environment, enabling the determination of its composition, purity, and stability.
The core purpose of a muffle furnace in a pharmaceutical context is not merely to heat things up. It is an instrument of quantitative analysis, used to burn away organic components in a controlled manner to isolate and measure the inorganic residue, which is essential for quality control and drug inspection.

Why High-Temperature Analysis is Critical in Pharma
The composition of a pharmaceutical product must be precise and consistent to ensure its safety and efficacy. Muffle furnaces provide the high-energy environment needed to break down samples and reveal their fundamental makeup.
The Goal: Quantifying Inorganic Content
Many quality control tests revolve around measuring the amount of inorganic material in a sample. This could be intentional (as in a mineral-based supplement) or unintentional (as in impurities or contaminants).
A muffle furnace operates at temperatures high enough to combust all organic and volatile compounds, such as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and organic excipients.
The Method: Thermal Decomposition
What remains after this high-temperature process, known as ashing, is a small amount of non-combustible residue. By carefully weighing the sample before and after heating, analysts can calculate the exact percentage of inorganic material.
Core Pharmaceutical Applications of a Muffle Furnace
The general principle of thermal decomposition is applied in several specific, standardized tests within the pharmaceutical industry.
Ashing for Impurity Analysis
Ashing is the most common application. The process determines the total amount of inorganic residue in a drug substance or finished product after incineration.
This residue represents the sum of all non-volatile inorganic impurities. A high ash content can indicate contamination from the manufacturing process or impurities in the raw materials, making it a critical quality-control parameter.
Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) Testing
Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) is a related technique that measures the change in mass of a sample after it has been heated to a high temperature.
This test is used to quantify the content of volatile substances, such as moisture or residual solvents, or the total organic content. It provides a clear measure of what was "lost" during heating, complementing the data gained from ashing.
Calcination and Material Synthesis
In pharmaceutical research and development, a muffle furnace may be used for calcination. This process involves heating a solid material to drive off specific compounds and induce a phase transition.
This is useful for synthesizing stable, inorganic materials that might be used as catalysts, excipients, or in specialized medical devices.
Sample Pretreatment for Further Analysis
Sometimes, a sample must be prepared for more advanced analytical techniques, such as atomic spectroscopy.
Using a muffle furnace removes the organic matrix, which can interfere with these sensitive measurements. This pretreatment concentrates the inorganic analytes of interest, allowing for more accurate and reliable analysis.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a destructive tool with specific limitations that must be understood for proper use.
It Is a Destructive Method
The sample being tested is completely destroyed during the ashing or LOI process. This means it is only suitable for applications where the sample can be sacrificed for analysis.
Not for Volatile Inorganic Compounds
This method is ineffective for detecting inorganic impurities that are volatile at the testing temperatures. If a contaminant (like a mercury or arsenic compound) can turn into a gas and escape, it will not be measured in the final ash.
Requires Utmost Precision
Accurate and repeatable results depend entirely on precise temperature control and precise weighing before and after the process. Any errors in temperature ramps, duration, or measurement will lead to invalid conclusions, which is unacceptable in a regulated pharmaceutical environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application determines which furnace process is most relevant.
- If your primary focus is routine Quality Control (QC): Your work will center on standardized ashing and Loss-on-Ignition tests to verify that products meet predefined purity specifications.
- If your primary focus is Research & Development (R&D): You will use the furnace more broadly for sample pretreatment, calcination to synthesize new materials, or to characterize novel formulations.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is an indispensable tool for ensuring the purity, safety, and consistency of pharmaceutical products from development to final inspection.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Burn off organic material | Quantify inorganic residue/impurities |
| Loss-on-Ignition (LOI) | Measure volatile content | Determine moisture or organic content lost |
| Calcination | Synthesize or transform materials | Create stable inorganic compounds for R&D |
| Sample Pretreatment | Prepare samples for advanced analysis | Remove organic matrix for accurate spectroscopy |
Ensure the highest standards of drug purity and safety in your laboratory.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-precision lab equipment, including reliable muffle furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of the pharmaceutical industry. Our furnaces offer the exact temperature control and consistency required for critical quality control tests like ashing and loss-on-ignition.
Let us help you enhance your analytical capabilities and maintain compliance. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect thermal analysis solution for your pharmaceutical QC or R&D needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a natural sintering? Uncover the Geological Process That Forms Ore Deposits
- What is the difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Thermal Needs
- What is muffle furnace principle and procedure? Master Safe, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a crucible and a furnace? Understanding the Heat Source and Container Partnership
- What are the safety precautions for muffle furnace? A Complete Guide to Safe High-Temperature Operation



















