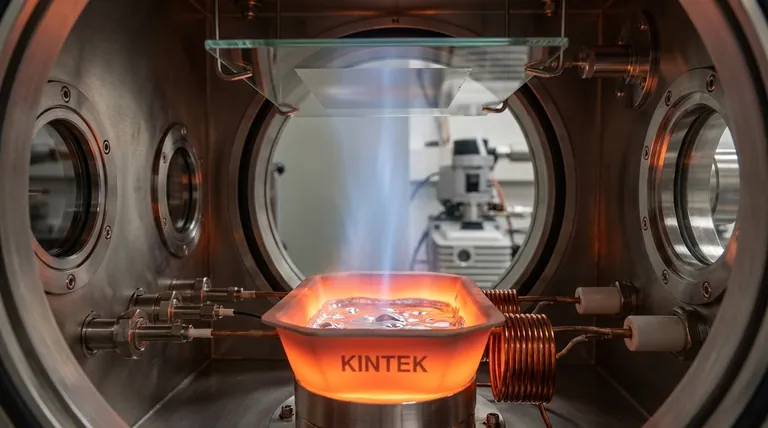
In essence, thermal evaporation is a vacuum deposition technique where a material is heated until it turns into a vapor, which then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface to form a very thin film. It is one of the simplest and oldest methods for creating coatings on a substrate, functionally similar to how steam from a boiling kettle condenses on a cold window.
Thermal evaporation is a foundational technology for depositing thin films of low-melting-point materials. Its primary advantage is simplicity, but this comes with significant trade-offs in film purity and quality compared to more advanced methods.

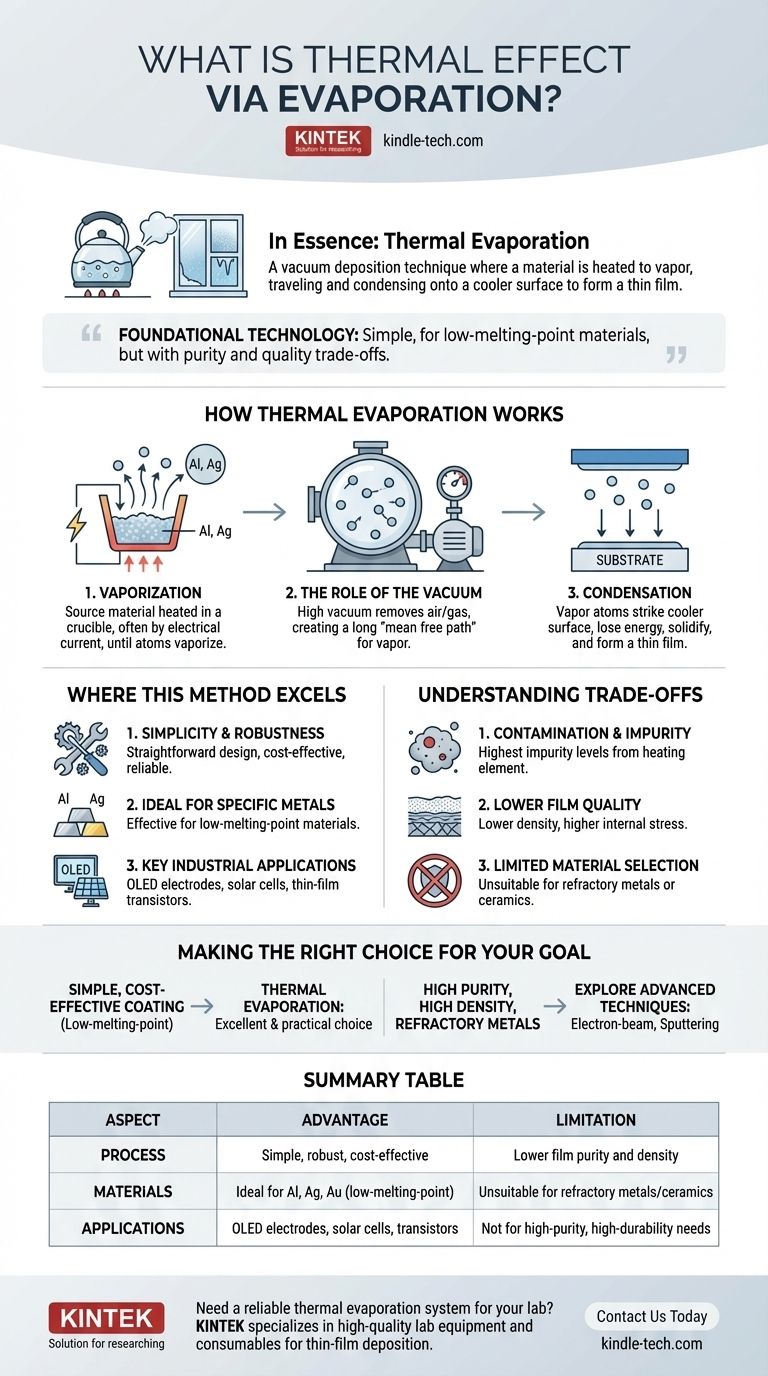
How Thermal Evaporation Works
The Core Principle: Vaporization
The process begins by placing the source material, often a metal like aluminum or silver, into a container called a crucible. This crucible is heated, typically by passing a large electrical current through it, causing its temperature to rise significantly.
As the source material heats up, its atoms gain enough energy to break free from the bulk material and enter a gaseous state, creating a vapor.
The Role of the Vacuum
This entire process is conducted inside a high-vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it removes air and other gas molecules that would otherwise interfere with the vaporized atoms.
This ensures the evaporated material can travel directly to the target substrate without colliding with or reacting to other particles, a concept known as a long "mean free path."
The Final Step: Condensation
The vaporized material travels through the vacuum and eventually strikes a cooler substrate (the object to be coated). Upon contact, the vapor atoms rapidly lose energy, cool down, and solidify, condensing into a thin, solid film on the substrate's surface.
Where This Method Excels
Simplicity and Robustness
As one of the oldest vacuum coating technologies, thermal evaporation is valued for its straightforward design and operation. The equipment is generally less complex and more cost-effective than other Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) systems.
Ideal for Specific Metals
This technique is highly effective for depositing materials with relatively low melting and boiling points. It is commonly used for metals such as aluminum, silver, and gold.
Key Industrial Applications
Thermal evaporation is a workhorse process for specific applications where its limitations are not critical. This includes creating the metallic electrodes in OLEDs, solar cells, and thin-film transistors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Contamination and Impurity
A significant drawback of thermal evaporation is the potential for contamination. The hot crucible or heating element can also release particles that mix with the source material's vapor, leading to the highest impurity levels among common PVD methods.
Lower Film Quality
Films produced by thermal evaporation tend to have a lower density and higher internal stress compared to those from more energetic processes like sputtering. While this can sometimes be improved with secondary techniques, the baseline quality is often lower.
Limited Material Selection
The reliance on simple heating makes this method unsuitable for materials that require extremely high temperatures to vaporize. Refractory metals (like tungsten or molybdenum) and many ceramics cannot be effectively deposited using this technique.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a deposition method, the decision hinges on the required film properties and the material being used.
- If your primary focus is a simple, cost-effective coating of a low-melting-point metal: Thermal evaporation is an excellent and highly practical choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving high purity, high density, or superior film durability: You must explore more advanced techniques like electron-beam evaporation or sputtering.
- If you need to deposit refractory metals or complex compounds: Thermal evaporation is not a suitable method, and other PVD processes are required.
Understanding the fundamental trade-offs between simplicity and performance is the key to leveraging this technology effectively.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Simple, robust, cost-effective | Lower film purity and density |
| Materials | Ideal for Al, Ag, Au (low-melting-point) | Unsuitable for refractory metals/ceramics |
| Applications | OLED electrodes, solar cells, thin-film transistors | Not for high-purity, high-durability needs |
Need a reliable thermal evaporation system for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for thin-film deposition. Whether you're coating electrodes for OLEDs or developing solar cells, our solutions ensure cost-effective performance. Contact us today to find the perfect equipment for your research or production needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications



















