In essence, thermal evaporation deposition is a process for applying an extremely thin layer of material onto a surface. It works by heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates, creating a vapor that travels and condenses onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, forming a uniform thin film.
Thermal evaporation is a fundamental vacuum deposition technique used to create functional coatings on a massive scale. Its importance lies in its relative simplicity and versatility, making it the foundational technology behind products ranging from reflective food packaging to the critical layers within advanced OLED displays and solar cells.
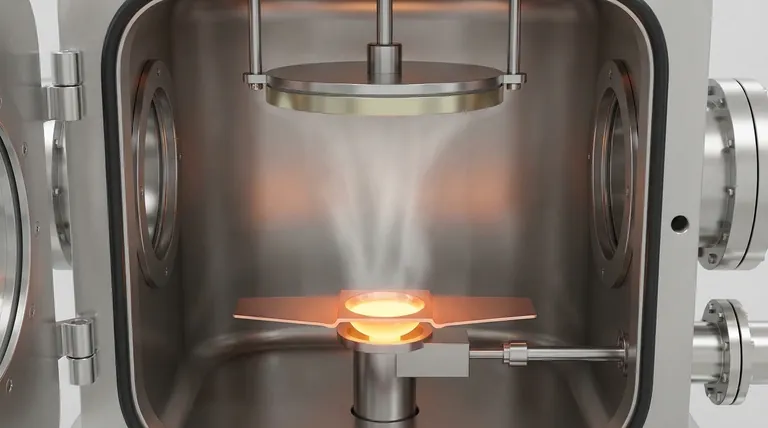
How Thermal Evaporation Works: A Foundational Process
To understand the role of thermal evaporation, it's best to break down the process into its core components. The entire operation occurs within a sealed vacuum chamber to ensure the purity and quality of the final film.
The Core Principle: From Solid to Vapor
The process begins with a source material, often a metal like aluminum or gold, placed in a small crucible or "boat." This boat is heated, typically by passing a strong electrical current through it (resistive heating). As the temperature rises, the source material melts and then evaporates, turning directly into a gas or vapor.
The Role of the Vacuum
The high-vacuum environment is critical for two reasons. First, it removes air and other gas molecules that could react with the hot vapor and contaminate the film. Second, it allows the evaporated atoms to travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate without colliding with other particles, ensuring a clean deposition path.
Condensation and Film Growth
The vaporized atoms travel through the vacuum chamber until they strike the cooler substrate—the object being coated. Upon impact, the atoms rapidly cool, condense back into a solid state, and adhere to the surface. This process builds up, atom by atom, to form a thin, uniform film.
Key Applications Across Industries
The films created by thermal evaporation are integral to countless modern technologies. Their function can be protective, decorative, or essential to the operation of a device.
In Advanced Electronics
This technique is a cornerstone of the electronics industry. It's used to deposit the ultra-thin metal layers that function as conductors and electrodes in OLEDs, solar cells, and thin-film transistors (TFTs). These components are vital for displays, renewable energy, and medical equipment.
In Optics and Protective Coatings
In the optics field, thermal evaporation is used to apply anti-reflective layers on lenses, mirror coatings, and UV-blocking films. Beyond optics, it's used to create the reflective, heat-insulating layers found in NASA spacesuits, firefighter uniforms, and emergency blankets.
In Everyday Consumer Goods
You interact with this technology daily. The metallic lining inside a bag of potato chips is often an aluminum film deposited on a polymer using thermal evaporation to protect the food from light and oxygen. It is also widely used for decorative coatings on jewelry and other accessories.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not the solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to appreciating why other deposition methods exist.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Purity
Thermal evaporation is generally a simpler, faster, and more cost-effective process compared to more complex methods like sputtering. It imparts less energy to the depositing atoms, which can be beneficial for delicate substrates like plastics or organic electronics (OLEDs).
Limitation: Film Adhesion and Density
The low energy of the process can be a drawback. Films produced by thermal evaporation may have lower density and weaker adhesion to the substrate compared to those from higher-energy processes. For applications requiring extremely durable or hard coatings, other methods are often preferred.
Limitation: Material Compatibility
This method works best for materials with relatively low boiling points, such as aluminum, gold, and silver. Materials with extremely high boiling points (refractory metals like tungsten) or complex alloys whose components evaporate at different rates are challenging to deposit with this technique.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the material, the substrate, and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metallic coatings on simple surfaces: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice, ideal for applications like packaging films and decorative coatings.
- If your primary focus is depositing pure, sensitive materials for organic electronics: This method's low-energy nature makes it a go-to for devices like OLEDs.
- If your primary focus is creating highly durable, dense, or complex alloy films: You will likely need to explore alternative high-energy methods like sputtering or electron-beam evaporation.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation is a foundational pillar of modern manufacturing, enabling the creation of precise, functional surfaces that define the world around us.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Heats a material in a vacuum until it evaporates and condenses on a substrate. |
| Best For | Cost-effective metallic coatings, OLEDs, and delicate substrates. |
| Limitations | Lower film adhesion/density; not ideal for high-melting-point materials. |
Need a reliable partner for your thin-film deposition?
Thermal evaporation is a cornerstone technique for creating essential coatings, and having the right equipment is critical for success. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems, to help you achieve precise and uniform thin films for your research or production needs.
Whether you're working on advanced electronics, optical coatings, or consumer goods, our expertise can help you select the right solution for your specific application. Let's discuss how we can support your project's success.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal evaporation system for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum evaporation? Purify Water or Create High-Purity Coatings
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage



















