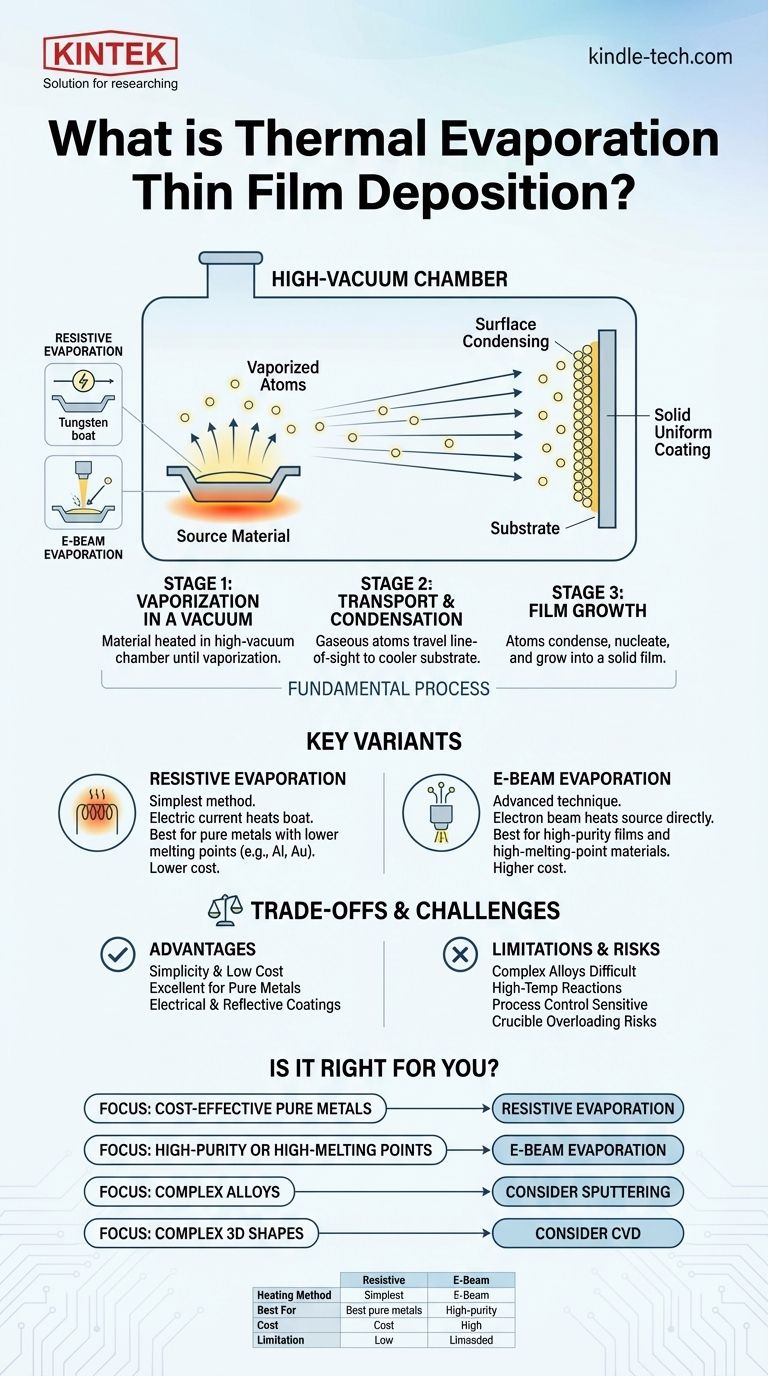
At its core, thermal evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique used to create ultra-thin films of material. The process works by heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it vaporizes. These gaseous atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, forming a solid, uniform coating.
Thermal evaporation is best understood as a highly controlled method of "boiling" a material in a vacuum so that its vapor deposits onto a surface. It is a foundational, relatively simple, and widely used technique for applying thin films of pure materials, especially metals.

The Fundamental Process: From Solid to Thin Film
To truly grasp thermal evaporation, it's essential to understand the three distinct stages that transform a solid source material into a functional thin film. The entire process relies on the physics of phase transition in a controlled environment.
Stage 1: Vaporization in a Vacuum
The process begins by placing the source material, often in a small container called a "boat" or crucible, into a high-vacuum chamber.
A high-vacuum environment is critical. It removes atmospheric gases that could react with the vaporized material or impede its path to the substrate, ensuring the purity of the final film.
Once the vacuum is established, the source material is heated using one of two primary methods until it evaporates or sublimes into a gaseous state.
Stage 2: Transport and Condensation
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the source toward the substrate. This is often referred to as a "line-of-sight" deposition process.
When the gaseous atoms reach the cooler substrate (such as a silicon wafer, glass, or plastic), they rapidly lose energy and condense back into a solid state.
Stage 3: Film Growth
As more atoms arrive and condense, they nucleate and grow into a continuous, solid thin film on the substrate's surface.
The thickness of this film is carefully controlled by monitoring the deposition rate and time.
Key Variants of Thermal Evaporation
While the principle remains the same, the method of heating the source material defines the two major variants of the technique.
Resistive Evaporation
This is the simplest and most common form. It uses a refractory metal boat or filament (often made of tungsten) that holds the source material.
An electric current is passed through this boat, causing it to heat up due to its electrical resistance. This heat is transferred to the source material, causing it to evaporate.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
E-beam evaporation is a more advanced technique used for materials with very high melting points or for applications requiring higher film purity.
A high-energy beam of electrons is generated and magnetically guided to strike the source material directly. The intense, focused energy causes localized boiling and vaporization of the material from the crucible.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Like any engineering process, thermal evaporation has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
The primary advantage of thermal evaporation, especially the resistive method, is its relative simplicity and lower equipment cost compared to more complex PVD techniques like sputtering.
This makes it an excellent choice for depositing pure metals like aluminum, gold, or chromium for applications such as electrical contacts or reflective coatings.
Limitation: Material Constraints
The technique is less suitable for depositing complex alloys or compounds. Different elements in an alloy have different vapor pressures, meaning they will evaporate at different rates, altering the composition of the final film.
Materials can also undergo reductions or decompositions at high temperatures, which can compromise the integrity and desired properties of the coating.
Challenge: Process Control and Risks
Achieving precise control over the film's structure (its morphology) can be difficult. The process is also sensitive to the amount of material loaded into the source.
Overloading a crucible can lead to particle fracturing or even explosions within the vacuum chamber, creating defects in the film and potentially damaging the equipment.
Is Thermal Evaporation Right for Your Application?
Choosing a deposition technique requires aligning the method's capabilities with your end goal. Thermal evaporation excels in specific scenarios but is less ideal for others.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of pure metals: Resistive thermal evaporation is an excellent, industry-standard choice for creating conductive or reflective layers.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys with precise stoichiometry: You should consider alternative PVD methods like magnetron sputtering, which offers superior compositional control.
- If your primary focus is achieving high-purity films or depositing high-melting-point materials: E-beam evaporation is the superior choice as the energy source does not directly contact the source material.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, three-dimensional shapes: The line-of-sight nature of thermal evaporation is a significant limitation; a non-line-of-sight technique like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) may be required.
Understanding these fundamentals empowers you to select the most effective deposition strategy for your specific engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Resistive Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electrical current heats a metal boat/filament | High-energy electron beam strikes source directly |
| Best For | Pure metals with lower melting points (e.g., Al, Au) | High-purity films; high-melting-point materials |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler setup | Higher cost, more complex |
| Key Limitation | Potential for material reaction with boat | Higher equipment cost and complexity |
Ready to integrate thermal evaporation into your lab workflow?
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for all your thin film deposition needs. Whether you are exploring resistive or e-beam evaporation for your research or production, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for depositing pure metals effectively.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements and enhance your capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition



















