At its core, thermal evaporation under a vacuum is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique used to apply an extremely thin and uniform coating of material onto a surface. The process works by heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it vaporizes. These vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler target object, known as a substrate, forming the desired film.
The central principle to understand is that the vacuum is not merely a container; it is the critical enabling factor. It creates an ultra-clean, collision-free environment that allows vaporized atoms to travel directly from the source to the substrate, which is essential for forming a high-quality, uniform film.

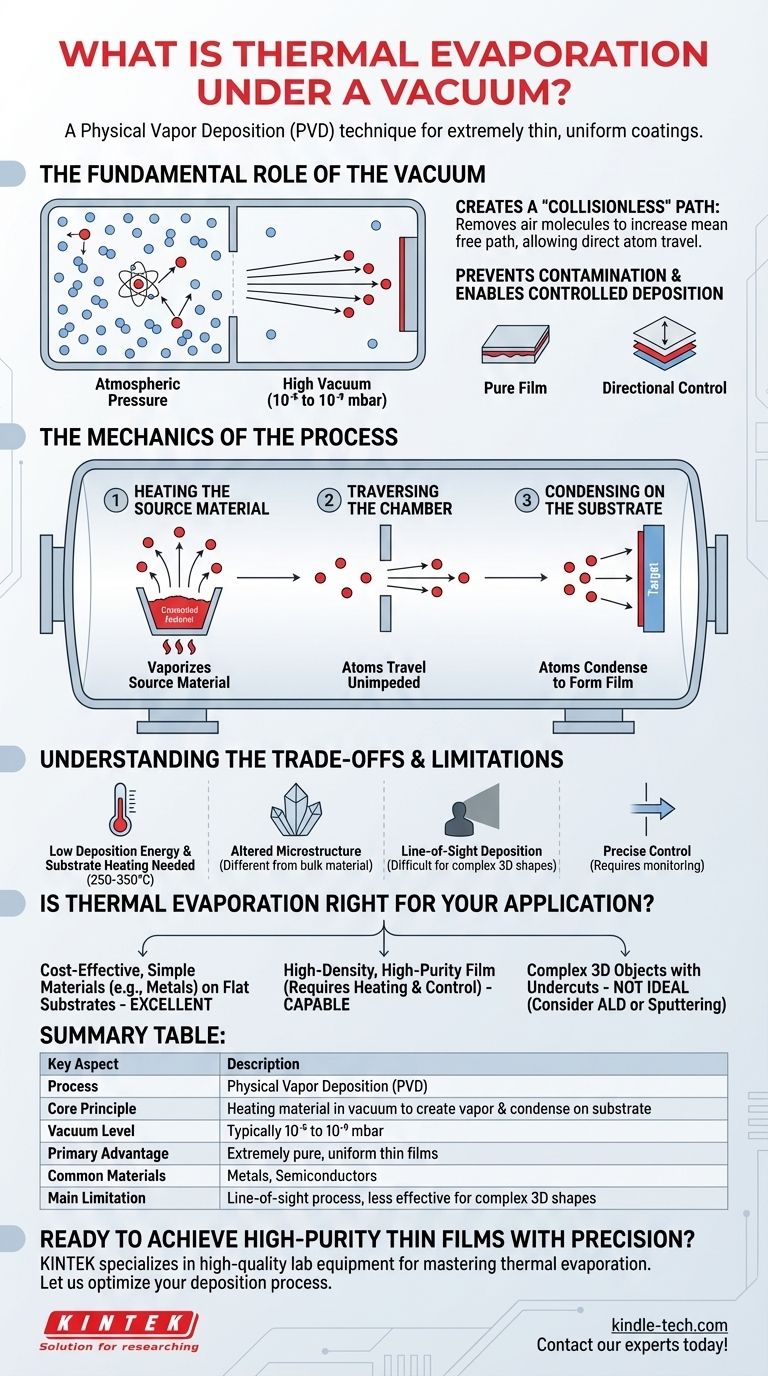
The Fundamental Role of the Vacuum
The success of thermal evaporation hinges entirely on the quality of the vacuum environment. Without it, the process would fail to produce a usable thin film.
Creating a "Collisionless" Path
The primary purpose of the high vacuum is to remove virtually all air and gas molecules from the chamber. This dramatically increases the mean free path—the average distance a vaporized atom can travel before colliding with another particle.
In a high vacuum, the mean free path is much longer than the distance from the source to the substrate. This ensures the evaporated material travels in a straight, unimpeded line, a condition known as collisionless transport.
Preventing Contamination and Reactions
Atmospheric air contains reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor. If these were present during deposition, they would immediately react with the hot source material and the newly forming film.
The vacuum removes these contaminants, ensuring the deposited layer is pure and sticks well to the clean substrate surface. Deposition in a poor vacuum results in a non-uniform, "fuzzy," and often non-functional coating.
Enabling Controlled Deposition
By eliminating random collisions and contamination, the vacuum allows for a highly directional and controlled deposition process. This control is what makes it possible to create films with precise thicknesses, often measured in nanometers.
The Mechanics of the Process
The process can be broken down into a few key steps, all occurring within a high-vacuum chamber typically operating between 10⁻⁵ and 10⁻⁹ mbar.
Heating the Source Material
The coating material, such as a metal or semiconductor, is placed in a container called a crucible. This crucible is then heated, usually by passing a strong electrical current through it, until the source material reaches a temperature where its vapor pressure becomes significant. At this point, atoms begin to evaporate from its surface.
Traversing the Chamber
Once evaporated, the atoms travel away from the source with thermal energy. Thanks to the vacuum, they move in a straight line-of-sight path toward the substrate without scattering off residual gas molecules. A mechanical shutter is often used to block this path until the evaporation rate is stable and to stop it once the desired thickness is reached.
Condensing on the Substrate
When the vaporized atoms strike the cooler substrate, they lose their energy and condense back into a solid state. This slow, atom-by-atom buildup is how the thin film is formed. The thickness is precisely monitored in real-time using tools like a thin film monitor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not without its challenges. Understanding its inherent limitations is crucial for successful application.
Low Deposition Energy
The atoms arrive at the substrate with relatively low thermal energy. This can sometimes result in a film that is less dense or has weaker adhesion compared to films created by higher-energy processes like sputtering.
The Need for Substrate Heating
To overcome the low deposition energy, the substrate is often heated to temperatures around 250 °C to 350 °C. This additional energy allows the arriving atoms to move around on the surface, find ideal positions, and form a denser, more stable film structure.
Altered Microstructure
The combination of low-energy deposition and substrate heating means the resulting film's microstructure—its internal crystal or grain structure—can be significantly different from that of the original bulk material. This must be accounted for when the film's mechanical or electrical properties are critical.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the atoms travel in straight lines, thermal evaporation is a line-of-sight process. It cannot easily coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces, as those areas are shadowed from the source.
Is Thermal Evaporation Right for Your Application?
Choosing a deposition technique requires matching the process capabilities to your end goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple materials: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for common metals like aluminum, gold, or chromium on flat substrates, offering a balance of simplicity and speed.
- If your primary focus is a high-density, high-purity film: The process is fully capable, but you must factor in the need for substrate heating and process control to achieve the desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D objects: A non-line-of-sight method like atomic layer deposition (ALD) or certain sputtering configurations would be a more suitable choice.
Ultimately, understanding that the vacuum enables a clean, direct path for atoms is the key to mastering thermal evaporation and achieving a high-quality, functional thin film.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technique |
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum to create a vapor that condenses on a substrate |
| Vacuum Level | Typically 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁹ mbar |
| Primary Advantage | Creates extremely pure, uniform thin films |
| Common Materials | Metals (e.g., Gold, Aluminum), Semiconductors |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight process, less effective for complex 3D shapes |
Ready to achieve high-purity thin films with precision?
The principles of thermal evaporation are key to successful coating applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed to master this process. Whether you are working in semiconductor research, optics, or materials science, our expertise and reliable products ensure you get the consistent results your work demands.
Let us help you optimize your deposition process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation of thin film? A Guide to High-Purity PVD Coating
- What is the difference between thermal evaporator and e-beam evaporator? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Films
- What are the advantages of ion beam assisted evaporation over thermal evaporation technique? Discover Superior Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between evaporation and deposition? A Guide to Thin-Film Manufacturing
- What is thermal evaporation method? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin-Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation of organic materials? The Gentle Method for OLED & Electronics
- What are the problems with physical Vapour deposition? High Cost, Slow Speed, and Line-of-Sight Limitations



















