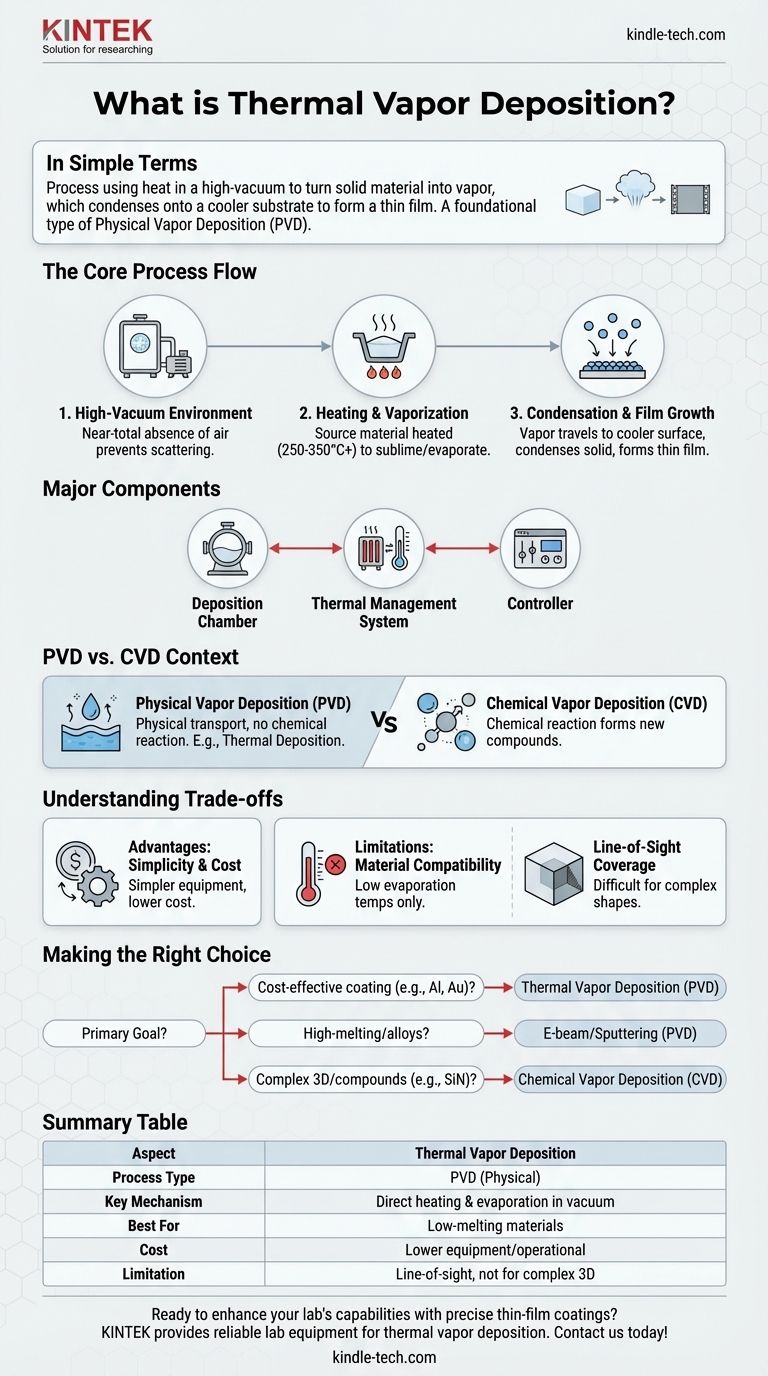
In simple terms, thermal vapor deposition is a process that uses heat inside a high-vacuum chamber to turn a solid material into a vapor. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming a very thin, uniform film. The entire process is fundamentally physical, relying on a simple change of state from solid to gas and back to solid.
Thermal vapor deposition is best understood as a foundational type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). Its defining characteristic is the use of direct heat for evaporation, distinguishing it from methods that use chemical reactions (CVD) or more complex energy sources.

How Thermal Vapor Deposition Works: The Core Process
To truly grasp the technique, it's essential to understand the environment and the key stages involved. The process is a carefully controlled physical transformation.
The High-Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place within a sealed chamber where a high vacuum has been created. This near-total absence of air is critical.
A vacuum ensures that vaporized atoms from the source material can travel directly to the substrate without colliding with air molecules, which would otherwise scatter them and prevent a uniform coating.
Heating and Vaporization
A source material, often in the form of a small solid or powder, is heated. The heat source raises the material's temperature, typically in the range of 250 to 350 degrees Celsius, though this varies significantly by material.
This heating increases the material's vapor pressure to the point where it sublimates or evaporates, turning directly into a gaseous vapor.
Condensation and Film Growth
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum until they strike the cooler substrate.
Upon contact, the atoms rapidly lose their thermal energy, condense back into a solid state, and adhere to the surface. Over time, this atomic accumulation builds a thin, solid film layer by layer.
The Three Major Components
A typical thermal vapor deposition system is composed of three essential parts working in concert.
- The Deposition Chamber: This is the sealed, high-vacuum vessel where the process occurs, housing both the source material and the substrate.
- The Thermal Management System: This system includes the heating elements for the source and often a cooling mechanism for the substrate to regulate temperature and encourage condensation.
- The Controller: A control unit monitors and adjusts all critical factors, including vacuum pressure, temperature, and deposition time, to ensure a repeatable and high-quality outcome.
Placing Thermal Deposition in Context: PVD vs. CVD
The term "vapor deposition" is broad. Understanding where thermal deposition fits is crucial for making informed technical decisions. The primary distinction is between physical and chemical methods.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a family of processes where a material is physically transported from a source to a substrate without a chemical reaction. Think of it like water evaporating from a pot and condensing as dew on a cool window.
Thermal deposition is one of the simplest forms of PVD. Other PVD techniques include e-beam evaporation (using an electron beam to heat the source) and sputtering (bombarding a target with ions to eject atoms).
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is fundamentally different. In this process, precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber. These gases then react with each other or with the heated substrate surface to form a new solid material as the coating.
The key difference is that PVD is a physical process of evaporation and condensation, while CVD is a chemical process where new compounds are created directly on the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any manufacturing process, thermal vapor deposition has distinct advantages and limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
The equipment for thermal deposition is generally simpler and less expensive than that for other PVD methods like sputtering or CVD. This makes it a highly accessible technology for many applications.
Limitation: Material Compatibility
The process is best suited for materials with relatively low evaporation temperatures. Materials with extremely high melting points or compounds that break down (decompose) when heated are not good candidates for this technique.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Coverage
Because the vapor travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate, it is difficult to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition technique depends entirely on your material, substrate shape, and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective coating of simple materials (like aluminum or gold): Thermal vapor deposition is an excellent and highly efficient choice due to its simplicity.
- If your primary focus is coating high-melting-point materials or creating specific alloys: You should explore other PVD methods like e-beam evaporation or sputtering, which use more energetic sources.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform film on a complex 3D part or depositing a specific compound (like silicon nitride): Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the more appropriate technology due to its non-line-of-sight nature and reactive process.
By understanding its core principles and its place within the broader landscape of thin-film technologies, you can effectively leverage thermal vapor deposition for a wide range of applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Thermal Vapor Deposition |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Key Mechanism | Direct heating and evaporation in a vacuum |
| Best For | Low-melting-point materials (e.g., aluminum, gold) |
| Cost | Lower equipment and operational costs |
| Limitation | Line-of-sight coating; not for complex 3D shapes |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise thin-film coatings? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for thermal vapor deposition and other PVD processes. Our solutions help you achieve uniform, high-quality films efficiently and cost-effectively. Contact us today to discuss your specific application needs and discover how we can support your research and production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is the difference between oxidizing and reducing environments? Key Insights for Chemical Reactions
- How many types of vapor phase deposition techniques are present? PVD vs. CVD Explained
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings



















