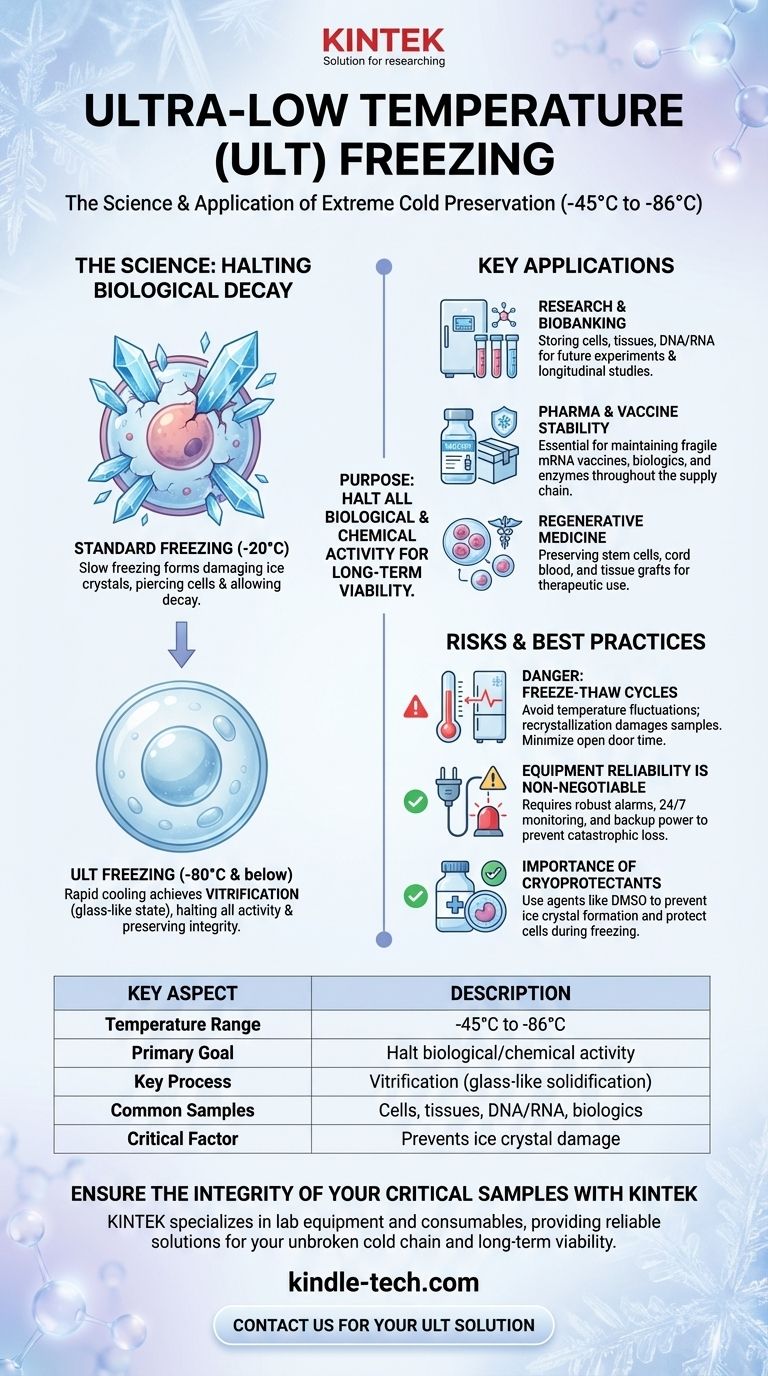
Ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezing is a specialized preservation method that uses extreme cold, typically between -45°C and -86°C, to store sensitive biological materials. Its primary purpose is to halt virtually all biological and chemical activity, thereby preserving the integrity, structure, and viability of samples like cells, tissues, and advanced pharmaceuticals for long-term use in research and medicine.
The core challenge in biological preservation is preventing degradation caused by molecular motion and ice crystal formation. Ultra-low temperatures solve this by effectively pausing time at a cellular level, ensuring that samples remain unchanged from the moment they are frozen.

The Science of Halting Biological Decay
Standard freezers, which operate around -20°C, are insufficient for the long-term preservation of complex biological materials. ULT freezing is necessary because of the specific physical and chemical changes that occur at much lower temperatures.
Why Standard Freezing Fails
When water freezes slowly, it forms large, sharp ice crystals. Inside a biological cell, these crystals act like microscopic knives, piercing cell membranes and destroying internal structures. This physical damage is often irreversible and renders the sample useless for most scientific applications.
Halting All Enzymatic Activity
Even in a frozen state, many enzymatic and chemical reactions can continue at a very slow rate, leading to the gradual degradation of DNA, RNA, proteins, and other critical molecules. Dropping the temperature to -80°C or below effectively stops this molecular activity, preventing this slow decay and ensuring true long-term stability.
Achieving a "Glass-Like" State
The goal of rapid, ultra-low temperature freezing is vitrification. This process cools the water within and around cells so quickly that it doesn't have time to form damaging crystals. Instead, it solidifies into a stable, glass-like amorphous state, locking all cellular components in place without causing structural harm.
Key Applications of ULT Freezing
The ability to perfectly preserve biological function is critical across numerous scientific and medical fields. ULT freezers are fundamental tools for this work.
Research and Biobanking
Laboratories use ULT freezers to create biobanks, which are organized collections of biological samples. This includes storing cell lines, bacteria, viral cultures, tissue samples, and extracted DNA or RNA for future experiments, ensuring that researchers have access to consistent and viable materials over many years.
Pharmaceutical and Vaccine Stability
Many modern biologic drugs, enzymes, and vaccines—especially mRNA-based vaccines—are incredibly fragile. ULT storage is essential for maintaining their molecular structure and efficacy throughout the manufacturing process and supply chain, a practice known as the "cold chain."
Regenerative Medicine
The storage of stem cells, cord blood, and tissue grafts for future therapeutic use relies entirely on ULT cryopreservation. This technology makes it possible to keep these living materials viable for years until they are needed for patient treatment.
Understanding the Risks and Best Practices
While powerful, ULT freezing is an unforgiving process. Failure to adhere to strict protocols can result in the complete loss of invaluable samples.
The Danger of Freeze-Thaw Cycles
Even minor temperature fluctuations can be destructive. Each time a sample warms slightly and refreezes, small ice crystals can grow larger in a process called recrystallization, causing progressive damage. Samples should be handled quickly, and freezer doors should not be left open.
Equipment Reliability is Non-Negotiable
A ULT freezer is a single point of failure for potentially irreplaceable work. A mechanical breakdown or power outage can be catastrophic. For this reason, these systems require robust alarm systems, 24/7 temperature monitoring, and access to backup power generators or secondary freezer units.
The Importance of Cryoprotectants
For many cell types, simply freezing them is not enough. Samples are often prepared in a special solution containing cryoprotectant agents (like DMSO or glycerol). These chemicals help prevent ice crystal formation and protect cells from the stresses of extreme cold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Proper implementation of ULT storage depends entirely on your specific objective. A clear understanding of your priorities will dictate your procedural and equipment needs.
- If your primary focus is long-term research viability: Prioritize meticulous sample inventory and minimize freeze-thaw cycles by organizing freezer contents for quick access.
- If your primary focus is clinical or pharmaceutical manufacturing: Adherence to validated protocols (SOPs), flawless equipment monitoring, and maintaining an unbroken cold chain are your most critical tasks.
- If you are new to ULT storage: Your first step is to invest in a high-quality freezer with reliable alarms and backup systems before developing a detailed sample management plan.
By mastering these principles, you can ensure your critical biological materials are perfectly preserved and ready for future discovery.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -45°C to -86°C |
| Primary Goal | Halt biological/chemical activity for long-term preservation |
| Key Process | Vitrification (glass-like solidification) |
| Common Samples | Cells, tissues, DNA/RNA, vaccines, biologics |
| Critical Factor | Prevents ice crystal damage and molecular degradation |
Ensure the Integrity of Your Critical Samples
Mastering ultra-low temperature storage is essential for protecting your invaluable research, biobanking, and pharmaceutical materials. The right equipment and protocols are the foundation of reliable preservation.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the reliable solutions you need to maintain an unbroken cold chain and protect your samples from degradation. Our expertise helps you implement best practices for long-term viability.
Let's discuss your ULT freezing requirements. Contact us today to find the perfect preservation solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
- 938L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Advanced Laboratory Storage
- 808L Precision Laboratory Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of ultra-low temperature freezers available? Choose the Right ULT Freezer for Your Lab
- Why are ULT freezers considered vital equipment in labs? Ensuring Uncompromised Sample Integrity for Critical Research
- How should frost be removed from Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers? Protect Your Samples and Equipment
- What is convection-based cooling in ultra-low temperature freezers? Achieve Superior Temperature Stability for Your Samples
- How are advancements in compressor technology and refrigerant fluids improving ULT freezers? Boost Efficiency & Cut Costs



















