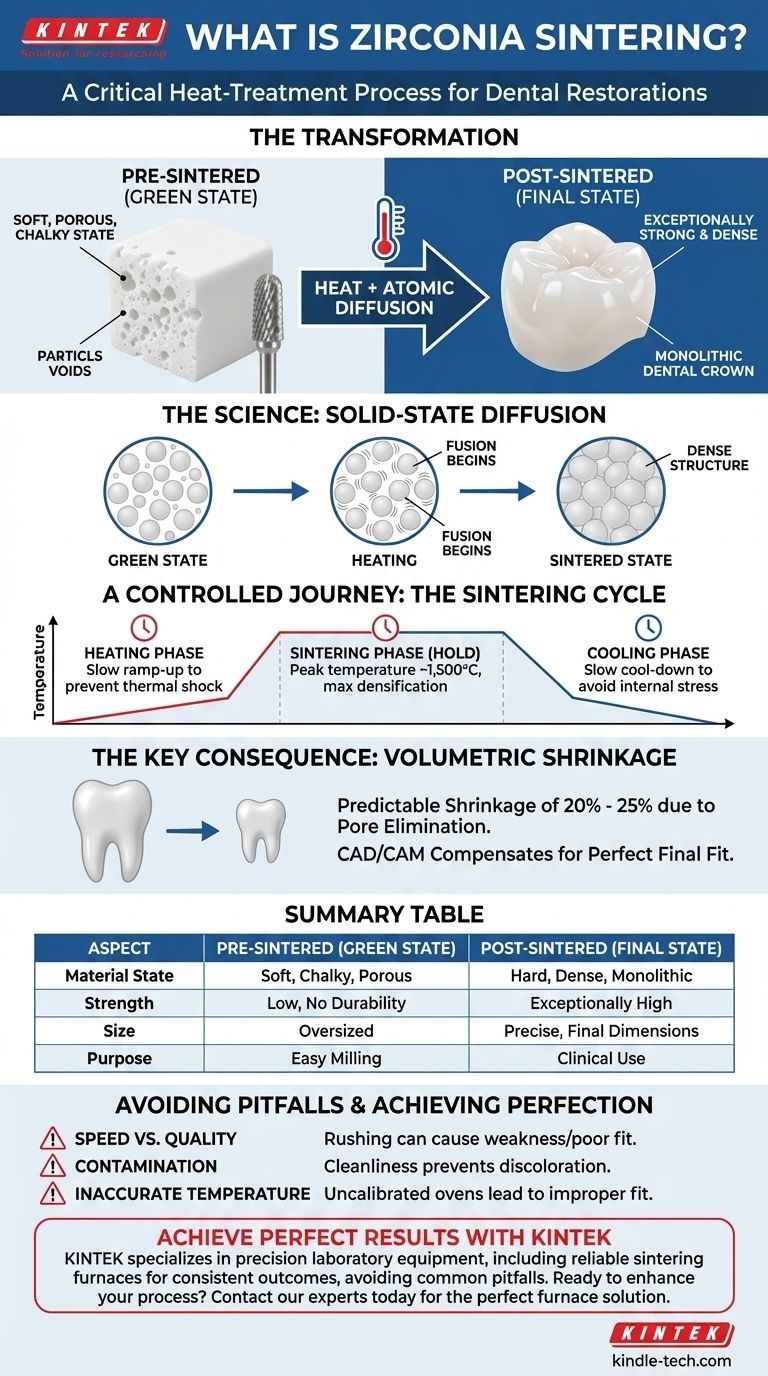
In simple terms, zirconia sintering is a critical heat-treatment process that transforms a soft, chalk-like, and oversized milled zirconia restoration into its final, dense, and exceptionally strong state. During this process, the material is heated to very high temperatures, causing its individual particles to fuse together, which eliminates internal porosity and results in significant, predictable shrinkage.
Sintering is not merely a heating step; it is a fundamental transformation that gives zirconia its final mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy. Understanding this process is essential for achieving a successful and durable final restoration.

The Science of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
To understand why sintering is necessary, you must first understand the state of zirconia before it enters the oven. The process is a carefully controlled journey from a fragile, porous state to a robust, monolithic structure.
The "Green State" Starting Point
Before sintering, zirconia exists in a pre-sintered or "green state." It has a soft, chalky consistency.
This state is ideal for milling because it reduces wear on milling burs and allows for rapid fabrication. However, in this form, the material has no clinical durability.
The Role of Heat and Atomic Diffusion
The core of sintering is a process called solid-state diffusion. As the furnace temperature rises, the individual zirconia particles gain enough energy to move and bond with their neighbors.
This atomic-level fusion closes the microscopic gaps (pores) between the particles. As these voids are eliminated, the material becomes dramatically denser and stronger.
The Three Critical Phases of a Sintering Cycle
A typical sintering cycle is not just about reaching a peak temperature; it involves a precise and controlled progression through three stages.
- Heating Phase: The temperature is increased gradually. A slow ramp-rate is crucial to prevent thermal shock, where a rapid temperature change between the surface and the core of the zirconia can cause fractures.
- Sintering Phase (Hold): The restoration is held at a peak temperature (often around 1,500°C) for a specific duration. The majority of densification and shrinkage occurs during this hold time as particles fully fuse.
- Cooling Phase: Like the heating phase, cooling must be slow and controlled. Cooling too quickly can introduce internal stresses, weakening the final restoration and making it prone to premature failure.
The Key Consequence: Volumetric Shrinkage
The most notable outcome of sintering is a significant and uniform reduction in the restoration's size.
Why Shrinkage Occurs
Shrinkage is a direct and unavoidable result of densification. As the millions of tiny pores between the zirconia particles are eliminated, the overall volume of the material decreases.
This volumetric shrinkage is typically between 20% and 25%.
How Shrinkage Is Managed
This shrinkage is not a defect; it is a known, quantifiable property of the material.
CAD/CAM design software automatically compensates for it. The software enlarges the digital design of the restoration by the specific shrinkage factor of the zirconia block being used, ensuring the pre-sintered part is milled in an oversized state.
The Impact on Final Fit
When the sintering process is executed correctly, the oversized "green state" restoration shrinks down to the precise dimensions specified in the original digital design. This predictable outcome is what ensures the final restoration fits the patient perfectly.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Variables
While the process is reliable, improper execution can lead to compromised results. Understanding the variables is key to troubleshooting and ensuring consistency.
Speed vs. Quality
Different sintering cycles exist. Conventional cycles are longer (several hours) and are proven to achieve maximum strength and esthetics.
High-speed sintering cycles can drastically reduce furnace time, but it's critical to use zirconia specifically validated for these cycles. Rushing an incompatible material can result in lower translucency, reduced strength, and an inadequate fit.
The Risk of Contamination
The sintering oven must be impeccably clean. Any debris or contaminants from other materials (like coloring liquids or dust) can be baked into the zirconia's surface during sintering.
This contamination can cause discoloration, white spots, or weak points in the final restoration.
Inaccurate Temperature
The final properties and accuracy of zirconia are directly tied to the furnace reaching and holding the correct temperature. An uncalibrated oven that runs too hot or too cool will result in an improper fit.
An under-fired restoration may not shrink enough and will be weaker, while an over-fired one may shrink too much.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your clinical or business needs will influence which sintering protocol you choose. A well-managed process is fundamental to a successful outcome, regardless of the path taken.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and esthetics: Use a conventional, longer sintering cycle as recommended by the zirconia manufacturer to ensure complete densification and optimal material properties.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround for a same-day restoration: Use a validated high-speed cycle with a zirconia material specifically designed for this purpose, and ensure your oven is calibrated for that exact cycle.
- If you are troubleshooting a poor fit or weak restoration: Systematically review your entire process, from ensuring the correct shrinkage factor is used in the software to verifying the accuracy and cleanliness of your sintering oven.
Mastering the principles of sintering transforms it from a simple heating step into a predictable and powerful tool for creating exceptional restorations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pre-Sintered (Green State) | Post-Sintered (Final State) |
|---|---|---|
| Material State | Soft, chalky, porous | Hard, dense, monolithic |
| Strength | Low, no clinical durability | Exceptionally high strength |
| Size | Oversized by 20-25% | Precise, shrunken to final dimensions |
| Purpose | Ideal for easy milling | Ready for clinical use |
Achieve Perfect Results with Every Sintering Cycle
Mastering zirconia sintering is critical for producing strong, accurately fitting dental restorations. The right equipment ensures consistent outcomes, whether you're using conventional or high-speed protocols.
KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory equipment and consumables, including reliable sintering furnaces designed for dental labs. Our solutions help you avoid common pitfalls like thermal shock, contamination, and inaccurate shrinkage, ensuring your restorations meet the highest standards of quality and fit.
Ready to enhance your sintering process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your lab's needs and ensure predictable, high-quality results for every case.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results



















