To be precise, pyrolysis does not directly generate net energy in the way burning fuel does. Instead, it is a thermochemical conversion process that uses heat in an oxygen-free environment to break down a feedstock into three distinct, energy-dense products: a combustible gas (syngas), a liquid (bio-oil), and a solid (bio-char). These products store the chemical energy from the original material in more refined and useful forms.
The critical point to understand is that pyrolysis is an energy conversion technology, not an energy generation source. It transforms low-value materials like biomass or waste into valuable solid, liquid, and gaseous fuels, with the overall energy balance depending on how efficiently these fuels are then utilized.

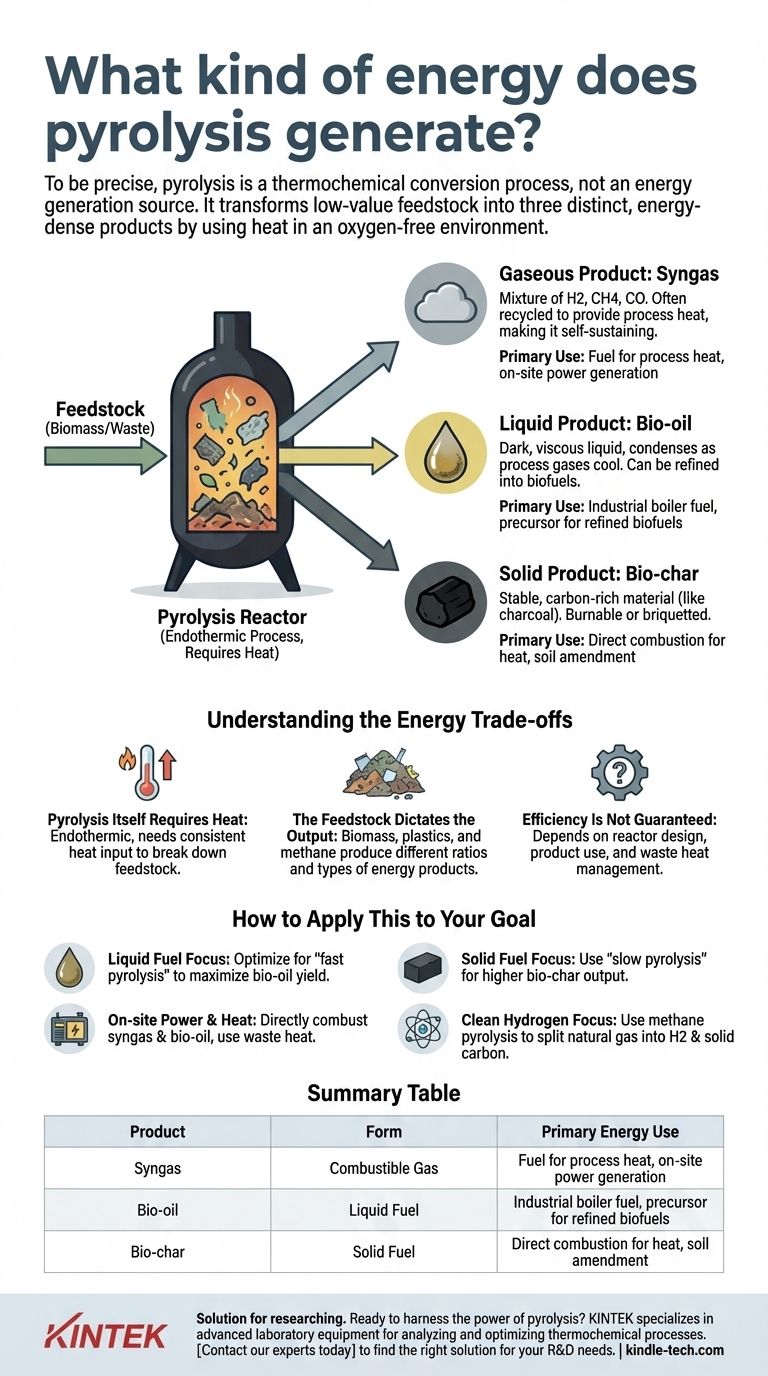
The Three Energy Pathways from Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis deconstructs complex organic materials by heating them without oxygen. This prevents combustion and instead breaks the material into simpler, energy-carrying components that are separated into gas, liquid, and solid streams.
The Solid Product: Bio-char
The primary solid output is a stable, carbon-rich material known as bio-char or coke.
This product is functionally similar to charcoal. It can be burned directly as a solid fuel or briquetted for easier transport and use in industrial boilers or heating applications.
The Liquid Product: Bio-oil
As the process gases cool, a complex liquid mixture known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil is condensed.
This dark, viscous liquid can be used as an industrial fuel oil in boilers and furnaces. With further refining, it can also be upgraded into more conventional liquid biofuels, such as biodiesel.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
The non-condensable portion of the output is a mixture of gases often called syngas (synthesis gas) or pyrolysis gas.
This gas contains combustible components like hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), and carbon monoxide (CO). Critically, this syngas is often recycled back into the system to provide the heat required to run the pyrolysis reactor, making the process partially or fully self-sustaining.
Understanding the Energy Trade-offs
Viewing pyrolysis as a simple energy source is a common misconception. The reality is a system with important inputs and variables that determine its net energy output.
Pyrolysis Itself Requires Heat
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a consistent input of heat energy to break down the feedstock.
The energy produced from its outputs must exceed this initial energy investment to be considered a net-positive process. This is why using the syngas product to fuel the reactor is a common and efficient design.
The Feedstock Dictates the Output
The specific type of material being processed has a massive impact on the energy products. Pyrolysis of biomass will yield different ratios of char, oil, and gas compared to the pyrolysis of plastics.
A specialized process like methane pyrolysis produces fundamentally different outputs: clean-burning hydrogen gas and solid carbon, representing a distinct pathway for producing a high-value energy carrier.
Efficiency Is Not Guaranteed
The overall energy efficiency depends heavily on the design of the pyrolysis unit and the subsequent use of its products. Energy can be lost as waste heat if the system is not well-engineered.
Furthermore, the collection and storage of the oil and char must be handled efficiently to preserve their energy content.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your primary objective determines which pyrolysis product you should prioritize and how the system should be optimized.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuel: You would optimize for a "fast pyrolysis" process, which uses higher temperatures and rapid cooling to maximize the yield of bio-oil for refining.
- If your primary focus is generating a stable solid fuel: You would use a "slow pyrolysis" process at lower temperatures, which increases the residence time and maximizes the output of bio-char.
- If your primary focus is on-site power and heat: You would design a system that directly combusts the syngas and bio-oil in a generator or boiler, often using the waste heat to dry incoming feedstock.
- If your primary focus is producing clean hydrogen: You would exclusively use methane pyrolysis, which is designed specifically to split natural gas into hydrogen gas and solid carbon.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is best understood as a flexible tool for converting a raw material into the most valuable and useful form of energy for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Product | Form | Primary Energy Use |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Combustible Gas | Fuel for process heat, on-site power generation |
| Bio-oil | Liquid Fuel | Industrial boiler fuel, precursor for refined biofuels |
| Bio-char | Solid Fuel | Direct combustion for heat, soil amendment |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your biomass or waste streams? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment for analyzing and optimizing thermochemical processes like pyrolysis. Whether you are developing new biofuels or optimizing reactor conditions, our precise tools help you maximize energy yields and efficiency. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your research and development needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















