In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), there are two sets of materials to consider: the material being coated (the substrate) and the material used for the coating itself (the target). A wide range of metals, metal alloys, and ceramics are used as coating materials, with common examples being Titanium Nitride, Chromium Nitride, and Gold. These are deposited onto substrates such as various steels, non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper, and even some plastics.
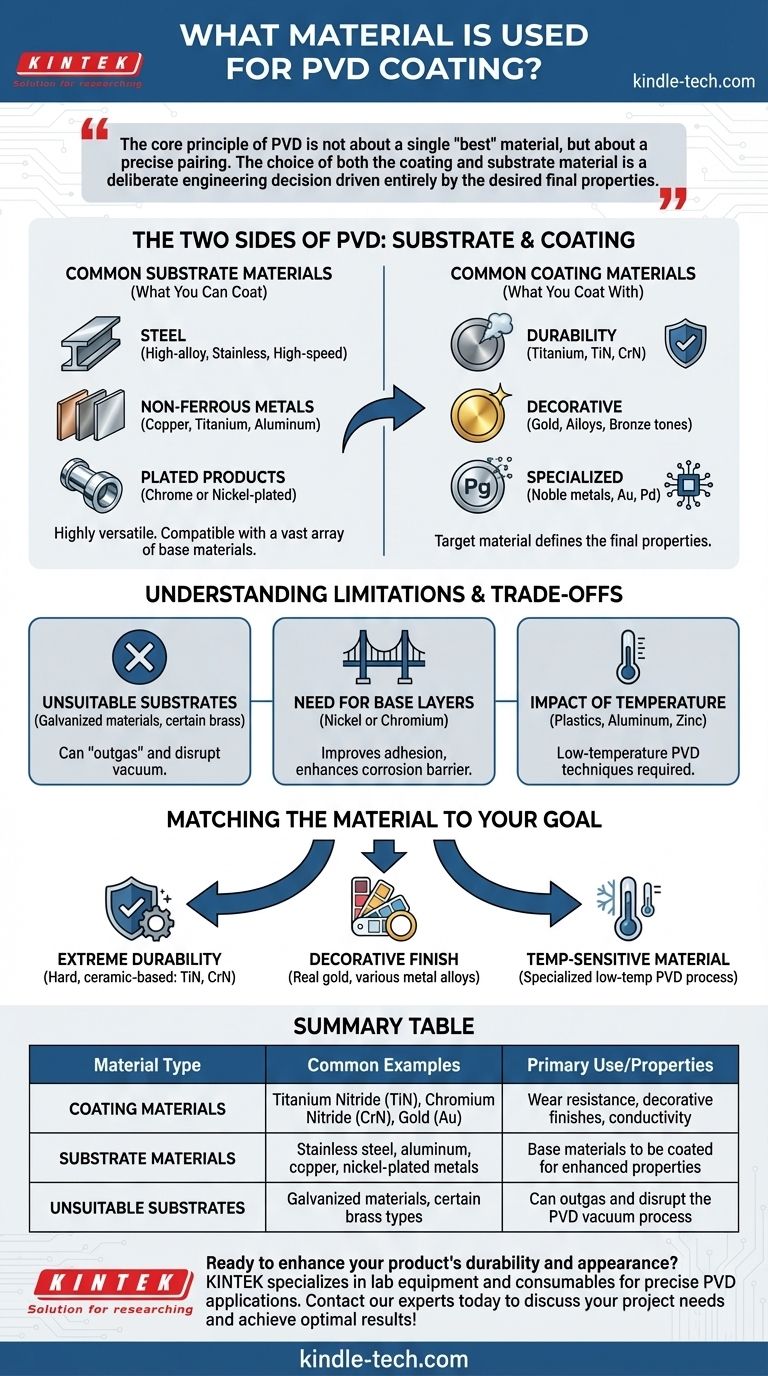
The core principle of PVD is not about a single "best" material, but about a precise pairing. The choice of both the coating and substrate material is a deliberate engineering decision driven entirely by the desired final properties, such as durability, color, or corrosion resistance.

The Two Sides of PVD: Substrate and Coating
To understand PVD materials, you must distinguish between the part being coated and the thin film being applied to it.
Common Substrate Materials (What You Can Coat)
The PVD process is highly versatile and compatible with a vast array of base materials.
Suitable substrates include all families of steel, especially high-alloy types like stainless steel and high-speed steels. Non-ferrous metals such as copper, titanium, and aluminum are also commonly coated.
Even materials that are already plated, such as chrome or nickel-plated metal products, can serve as a substrate for a subsequent PVD coating. This is often done to add a final layer for color or enhanced wear resistance.
Common Coating Materials (What You Coat With)
The "target" material is what is vaporized and deposited onto the substrate. The choice of target material directly defines the properties of the final coating.
For durability and wear resistance, titanium is a popular choice due to its strength and corrosion resistance. It often forms metal-ceramic compounds like Titanium Nitride (TiN), which create an extremely hard surface layer.
For decorative purposes, the options are broad. Real gold (in various karats) can be used for luxury applications. However, other metals and alloys are frequently used to achieve specific colors, such as gold or bronze tones, at a lower cost.
For specialized applications like electronics, noble metals like gold (Au), gold-palladium blends, and other platinum-group metals are used. Their primary benefit is high conductivity and resistance to oxidation.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While PVD is a powerful technology, it is governed by strict material and process constraints. Ignoring these rules is a common source of failure.
Unsuitable Substrate Materials
Certain materials are incompatible with the high-vacuum environment required for PVD.
Galvanized materials and brass that has not been galvanized are generally not suitable for PVD. These materials can "outgas" during the process, disrupting the vacuum and preventing a high-quality, bonded coating from forming.
The Need for Base Layers
A PVD coating does not always adhere directly to the primary substrate.
For some applications, an intermediate base layer of nickel or chromium is required. This layer acts as a bridge, improving the PVD coating's adhesion and providing a more robust barrier against corrosion.
The Impact of Temperature
The PVD process generates heat, which can damage sensitive materials.
Substrates with low melting points, such as plastics, aluminum, and zinc castings, require specialized low-temperature PVD techniques. This constraint limits the types of coatings that can be applied and must be considered from the outset.
Matching the Material to Your Goal
Your choice of PVD material should be a direct reflection of your project's most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Specify a hard, ceramic-based coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Chromium Nitride (CrN).
- If your primary focus is a specific decorative finish: Your choice can range from real gold to various metal alloys selected for their inherent color and luster.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: You must use a low-temperature PVD process, which will dictate the available coating materials compatible with that technique.
Ultimately, selecting the right PVD material is about precisely defining your goal and understanding the interplay between the substrate, the coating, and the process itself.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Primary Use/Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Materials | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), Gold (Au) | Wear resistance, decorative finishes, conductivity |
| Substrate Materials | Stainless steel, aluminum, copper, nickel-plated metals | Base materials to be coated for enhanced properties |
| Unsuitable Substrates | Galvanized materials, certain brass types | Can outgas and disrupt the PVD vacuum process |
Ready to enhance your product's durability and appearance with the right PVD coating? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD applications, helping you select the ideal coating and substrate pairing for superior wear resistance, corrosion protection, or decorative finishes. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs and achieve optimal results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















