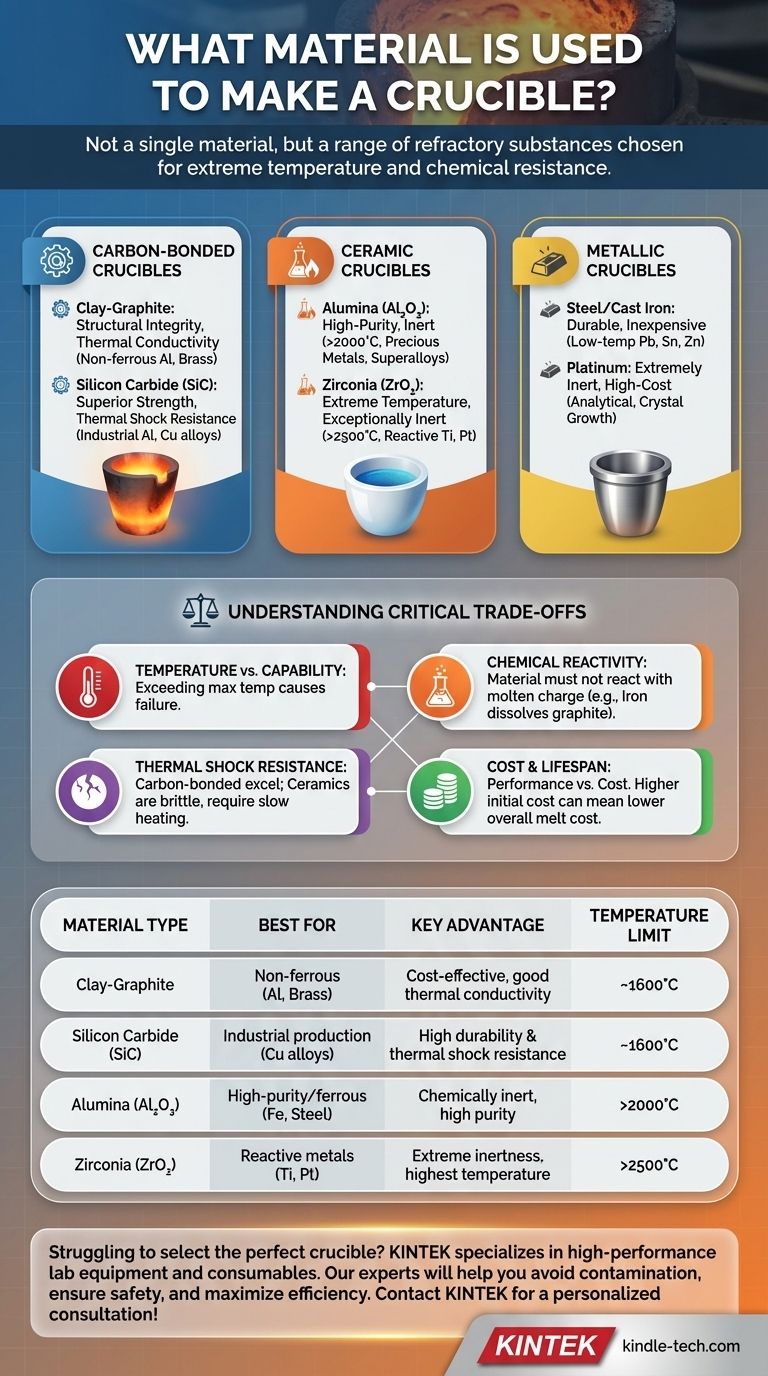
Crucibles are not made from a single material, but from a range of refractory substances specifically chosen for their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and chemical attack. The most common materials include clay-graphite composites, silicon carbide, and high-purity ceramics like alumina. The selection of a material is dictated entirely by the substance being melted and the temperatures required.
The choice of crucible material is a critical engineering decision, not a simple selection. The correct material prevents catastrophic failure and chemical contamination, and is determined by balancing the melting temperature of your charge, its chemical reactivity, and your operational budget.

The Primary Categories of Crucible Materials
To understand which crucible to use, you must first understand the fundamental properties of the main material families. Each has a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses.
Carbon-Bonded Crucibles
These are the workhorses of many foundries and labs. They blend graphite with other materials to achieve a balance of thermal performance and durability.
The most common type is clay-graphite. The clay provides structural integrity and high-temperature resistance, while the graphite provides excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid and even heating of the contents.
A step up is silicon carbide (SiC). These crucibles offer superior strength, better resistance to thermal shock, and a higher temperature tolerance than clay-graphite. They are extremely durable and provide a long service life for melting metals like aluminum and copper alloys.
Ceramic Crucibles
Ceramic crucibles are prized for their extreme temperature resistance and chemical inertness, making them essential for high-purity applications.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃) is a high-purity ceramic with a very high melting point (over 2000°C / 3600°F). It is chemically stable and ideal for melting precious metals, superalloys, or materials where contamination must be avoided.
For the most demanding applications, Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide, ZrO₂) is used. It has an even higher melting point than alumina and is exceptionally inert, making it suitable for highly reactive metals like titanium and platinum group metals.
Metallic Crucibles
In some cases, a metal crucible is the most practical choice, provided its melting point is significantly higher than the material it holds.
Steel or cast iron crucibles are commonly used for melting low-temperature, non-ferrous metals like lead, tin, and zinc. They are durable, inexpensive, and readily available.
At the other extreme, platinum crucibles are used in analytical chemistry and for growing specific types of crystals. Platinum is extremely inert and has a high melting point, but its cost makes it prohibitive for all but the most specialized applications.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible involves balancing four key factors: temperature, reactivity, thermal shock, and cost. Ignoring any one of these can lead to failed melts, contaminated products, or dangerous equipment failure.
Temperature vs. Material Capability
Each material has a clear operational ceiling. Using a crucible above its maximum recommended temperature will cause it to soften, crack, or melt. A clay-graphite crucible suitable for aluminum (melting at 660°C) is completely inadequate for melting steel (melting around 1500°C).
Chemical Reactivity: The Hidden Danger
Temperature is not the only concern. The crucible material must not react with the molten charge. For example, you should never melt iron or steel in a graphite-based crucible. The molten iron will dissolve the carbon directly from the crucible walls, contaminating your metal and destroying the crucible. For ferrous metals, a ceramic like alumina is required.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when heated or cooled too quickly. Carbon-bonded crucibles (graphite, SiC) excel here due to their high thermal conductivity. They can be heated rapidly without cracking.
Ceramic crucibles (alumina, zirconia) are brittle and have poor thermal shock resistance. They must be heated and cooled slowly and carefully according to a precise schedule to prevent them from shattering.
Cost and Lifespan
There is a direct relationship between performance and cost. Clay-graphite is the most affordable option, while Zirconia and Platinum represent a massive financial investment. While a silicon carbide crucible costs more than a clay-graphite one, its longer lifespan in a high-production environment can lead to a lower overall cost per melt.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the correct material choice. Let this guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist or small-scale casting of non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass): A clay-graphite crucible offers the best balance of performance and affordability.
- If your primary focus is industrial production with high-wear metals like copper alloys: A silicon carbide crucible will provide a longer service life and better durability, justifying the higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is melting ferrous metals (iron, steel): You must use a ceramic crucible, such as alumina or magnesia, to prevent carbon contamination and crucible degradation.
- If your primary focus is laboratory analysis or melting high-purity, reactive metals (titanium, superalloys): An alumina or zirconia crucible is non-negotiable to ensure material purity and withstand the extreme conditions.
Matching the crucible material to the specific demands of your work is the foundation of a safe, efficient, and successful high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Temperature Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay-Graphite | Non-ferrous metals (Al, Brass) | Cost-effective, good thermal conductivity | ~1600°C |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Industrial production (Cu alloys) | High durability & thermal shock resistance | ~1600°C |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | High-purity/ferrous metals (Fe, Steel) | Chemically inert, high purity | >2000°C |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | Reactive metals (Ti, Pt) | Extreme inertness, highest temperature | >2500°C |
Struggling to select the perfect crucible for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles tailored for your specific application—from cost-effective clay-graphite for hobbyists to ultra-pure ceramics for research. Our experts will help you avoid contamination, ensure safety, and maximize efficiency. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and get the right crucible for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using alumina crucibles for the TGA of modified alkyd resins? Ensure Accurate Results
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data



















