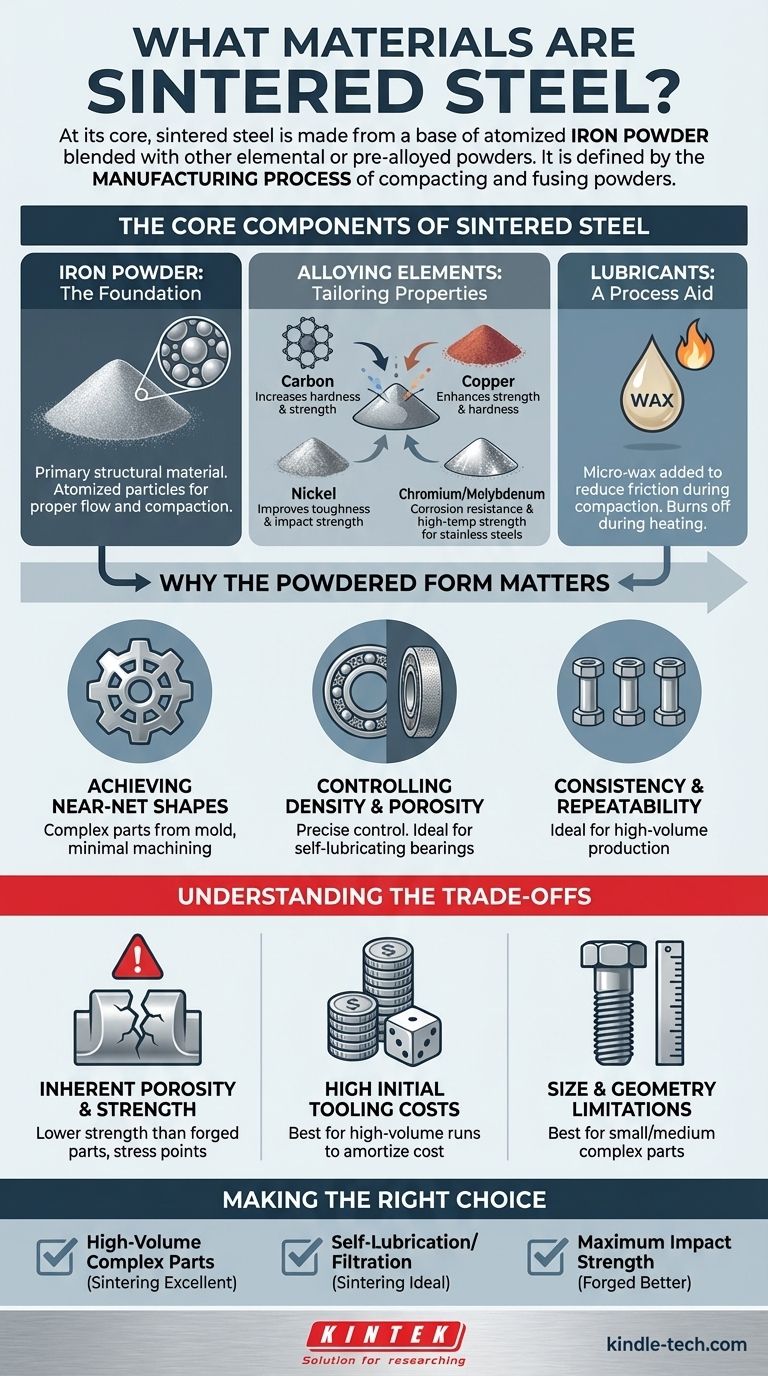
At its core, sintered steel is primarily made from a base of atomized iron powder. This iron powder is then blended with other elemental or pre-alloyed powders to achieve the desired properties of the final steel alloy. For example, to create sintered stainless steel, chromium and nickel powders are mixed with the base iron powder before the sintering process begins.
The key takeaway is that "sintered steel" is defined not by a unique set of materials but by the manufacturing process. It involves compacting metal powders—primarily iron mixed with specific alloying elements—and then heating them to fuse the particles together into a solid, functional part.

The Core Components of Sintered Steel
Understanding sintered steel requires looking at the individual powders that serve as its building blocks. Each component is selected to impart specific characteristics to the final product.
Iron Powder: The Foundation
The vast majority of any sintered steel part is atomized iron powder. This serves as the primary structural material. The size and shape of these iron particles are carefully controlled to ensure proper flow and compaction in the die.
Alloying Elements: Tailoring Properties
This is where the material is truly defined. By adding specific powders to the iron base, manufacturers can create a wide range of steel alloys with different mechanical properties.
Common alloying elements include:
- Carbon (as graphite powder): The most critical element for turning iron into steel, increasing hardness and strength.
- Copper: Enhances strength and hardness through precipitation strengthening during the sintering process.
- Nickel: Improves toughness, impact strength, and hardenability.
- Chromium & Molybdenum: Key for creating sintered stainless steels, providing corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength.
Lubricants: A Process Aid
A non-metallic component, such as a micro-wax, is almost always added to the powder mix. This lubricant reduces friction between the powder and the die walls during the compaction stage, ensuring uniform density and preventing damage to the tooling. It is designed to burn off completely during the initial phase of the heating cycle.
Why the Powdered Form Matters
The use of powdered metals is the defining characteristic of sintering and unlocks its primary advantages over traditional casting or forging.
Achieving Near-Net Shapes
Sintering allows for the creation of complex and intricate parts directly from the mold. This "near-net shape" capability dramatically reduces or eliminates the need for post-process machining, saving both time and material waste.
Controlling Density and Porosity
The process gives engineers precise control over the final part's density. While high-density parts can be made to rival the strength of wrought steel, the process can also be used to create parts with controlled porosity. This is ideal for self-lubricating bearings, which are impregnated with oil, or for filters.
Consistency and Repeatability
As noted in manufacturing analysis, the die-compaction process is exceptionally consistent. This makes sintering ideal for high-volume production runs where every part must be a near-perfect replica of the last, such as in the automotive or appliance industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has specific limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Inherent Porosity and Strength
Unless secondary operations like sizing or infiltration are performed, a sintered part will typically have some residual porosity. This can make it less strong than a fully dense part made from forging. The tiny internal voids can act as stress concentration points under extreme loads.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The dies and tooling required for the compaction process are made from hardened tool steel and are expensive to produce. This high initial investment means that sintering is most cost-effective for high-volume production runs that can amortize the cost of the tooling over thousands or millions of parts.
Size and Geometry Limitations
The process is generally best suited for small to medium-sized components. Extremely large parts can be difficult to produce due to the immense pressures required for uniform compaction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintered steel is an engineering decision driven by the specific demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice for creating intricate components like gears and cams with minimal machining and waste.
- If your primary focus is self-lubrication or filtration: The ability to control porosity makes sintering the ideal method for producing oil-impregnated bearings and specialized filters.
- If your primary focus is maximum impact strength or fatigue resistance: A forged or machined component from a solid billet may be a more suitable choice for applications facing extreme and unpredictable loads.
Ultimately, sintered steel provides a precise and repeatable manufacturing path for creating complex steel parts when its unique balance of properties aligns with your engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sintered Steel | Key Properties/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Powder | Primary structural base | Atomized particles for compaction |
| Alloying Elements | Tailor mechanical properties | Carbon (hardness), Copper (strength), Nickel (toughness) |
| Lubricants | Aid in compaction process | Micro-wax (burns off during heating) |
| Porosity Control | Define part functionality | High density for strength, controlled voids for self-lubrication |
Need precision-engineered sintered steel parts for your high-volume production? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for creating complex, near-net-shape components with controlled porosity and exceptional consistency. Let our expertise in sintering materials help you achieve efficiency and reduce waste. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What types of sensitive medical articles can be stored in ULT freezers? Preserve Critical Samples at -80°C
- What role does the right ULT freezer play in a lab's success? Securing Your Most Valuable Samples
- What is regeneration carbon? A Sustainable Way to Reuse Activated Carbon
- What roles do the heating unit and jacketed system play in solar collector simulation? Optimize Your Thermal Research
- Which reactor configuration is preferred in biochar production? Slow Pyrolysis for Maximum Biochar Yield
- Is pyrolysis of plastic harmful to the environment? It Depends on How You Manage the Outputs
- What happens during sintering? Transform Powder into Dense, Strong Components
- What can XRF be used on? Analyze Solids, Liquids, Powders & More



















