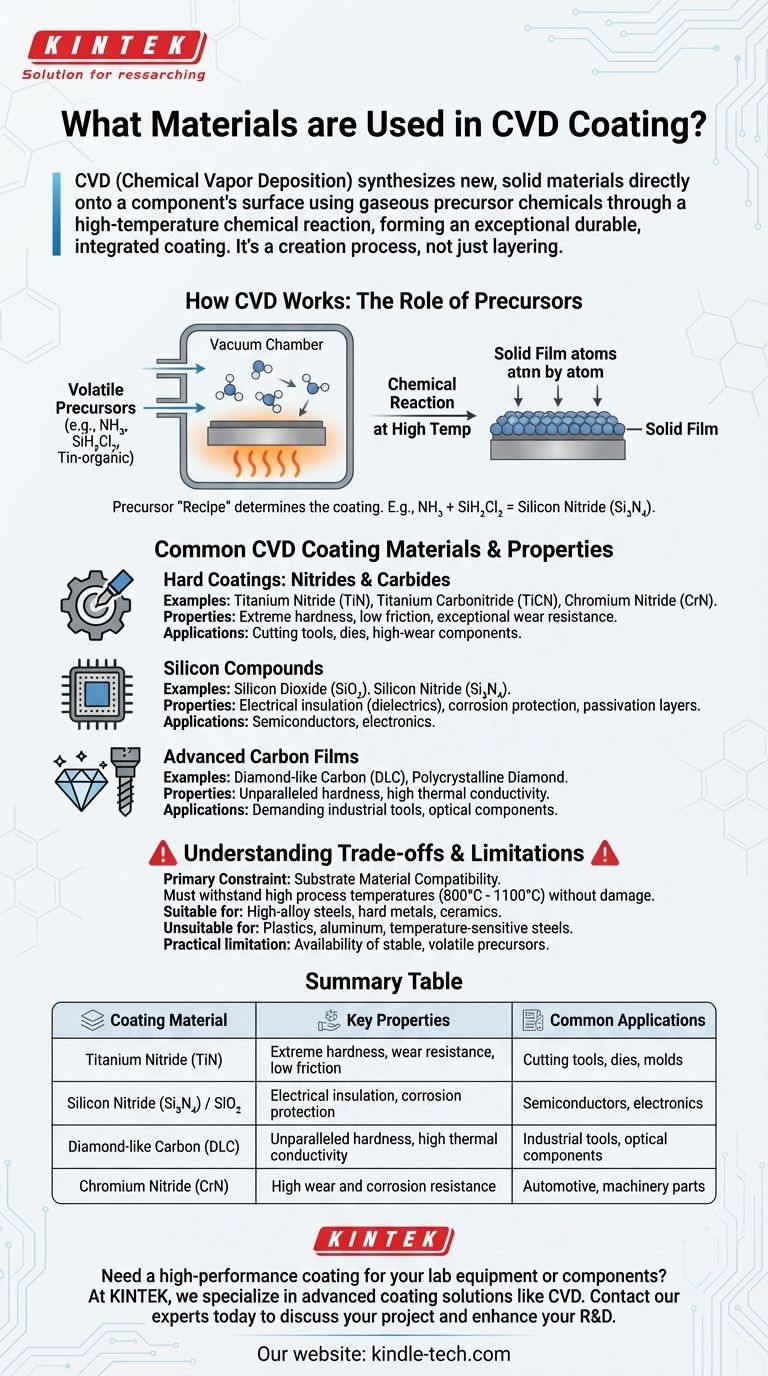
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses gaseous precursor chemicals to synthesize a new, solid material directly onto a component's surface. The most common materials created through this process include hard nitrides like titanium nitride, various silicon compounds, and advanced carbon-based films. This is not a simple layering process; it is a chemical reaction at high temperatures that forms an exceptionally durable and integrated coating.
The crucial takeaway is that CVD doesn't just apply a material; it creates it. The final coating material is synthesized on the substrate's surface from volatile chemical precursors, which is the defining principle of the process and its primary constraint.

How CVD Fundamentally Works: The Role of Precursors
The choice of materials in CVD is dictated entirely by the chemistry of the process. You cannot simply place a block of solid material in the machine and have it deposited.
From Gas to Solid Film
The CVD process involves injecting specific volatile gases, known as precursors, into a vacuum chamber containing the part to be coated (the substrate).
When the chamber is heated to a high reaction temperature, these precursor gases decompose and react with each other. This chemical reaction forms a new, solid material that deposits atom by atom onto the substrate, creating a thin, dense, and highly adherent film.
The "Recipe": Precursors Determine the Coating
The final coating is a direct result of the precursor "recipe" used. Each desired coating material requires a specific set of precursor gases that contain the necessary chemical elements.
For example, to create a silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) coating, the process chamber is supplied with precursors like ammonia (NH₃) and dichlorosilane (SiH₂Cl₂). To deposit a tin oxide (SnO₂) film, the precursors might be a tin-organic compound and water vapor (H₂O).
Common CVD Coating Materials and Their Properties
The range of CVD materials is vast, but they generally fall into a few key categories valued for their high-performance characteristics.
Hard Coatings: Nitrides and Carbides
Materials like Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), and Chromium Nitride (CrN) are among the most common CVD coatings. They are prized for their extreme hardness, low friction, and exceptional wear resistance, making them ideal for cutting tools, dies, and other high-wear components.
Silicon Compounds
Coatings like silicon dioxide (SiO₂) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) are fundamental to the electronics industry. They serve as excellent electrical insulators (dielectrics), protective barriers against corrosion, and passivation layers on semiconductors. Silicon-based films can also be "doped" with other elements to precisely functionalize their electronic properties.
Advanced Carbon Films
CVD is used to create some of the hardest known materials. This includes depositing films of diamond-like carbon (DLC) or even pure polycrystalline diamond. These coatings provide unparalleled hardness and thermal conductivity for the most demanding industrial and optical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the CVD process has specific requirements that limit its application. The primary constraint is not the coating material itself, but the substrate being coated.
The High-Temperature Requirement
CVD is an inherently high-temperature process, often operating between 800°C and 1100°C (1475°F to 2012°F), though lower temperature variants exist. This heat is necessary to provide the energy needed to drive the chemical reactions.
Substrate Material Compatibility
The most critical limitation of CVD is that the substrate must be able to withstand the high process temperatures without melting, warping, or losing its essential properties. This makes CVD ideal for materials like high-alloy steels, hard metals (cermets), and ceramics. However, it is generally unsuitable for plastics, aluminum, or temperature-sensitive alloyed steels that would be compromised by the heat.
Precursor Availability
A final practical limitation is the need for a suitable precursor. A stable, sufficiently volatile, and reasonably safe precursor gas must exist for the desired coating material. If a precursor cannot be found or handled, the material cannot be deposited via CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right coating technology depends entirely on the material you are coating and your performance goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance on a temperature-stable part: CVD is an excellent choice for applying hard nitride or carbide coatings onto steel tools or dies.
- If your primary focus is fabricating electronic or optical components: CVD is the industry standard for depositing the highly pure silicon compounds and other functional films required for semiconductors.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like plastic or aluminum: CVD is likely unsuitable due to the high heat, and you should investigate a lower-temperature alternative like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Understanding this fundamental relationship between the precursor chemistry, process temperature, and substrate material is the key to successfully leveraging CVD technology.
Summary Table:
| Coating Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, low friction | Cutting tools, dies, molds |
| Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) / Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | Electrical insulation, corrosion protection | Semiconductors, electronics |
| Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) / Diamond | Unparalleled hardness, high thermal conductivity | Industrial tools, optical components |
| Chromium Nitride (CrN) | High wear and corrosion resistance | Automotive components, machinery parts |
Need a high-performance coating for your lab equipment or components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced coating solutions using technologies like CVD. Whether you require extreme wear resistance for tools, protective barriers for electronic components, or specialized functional films, our expertise ensures optimal performance and durability for your laboratory needs.
Let us help you select the right coating material and process for your specific application. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition



















