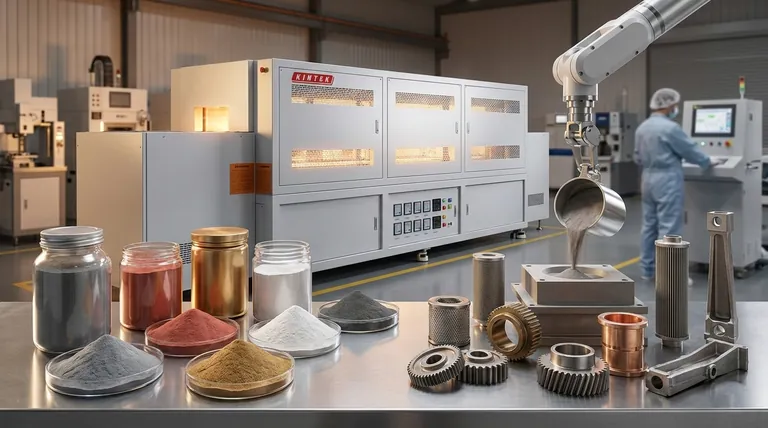
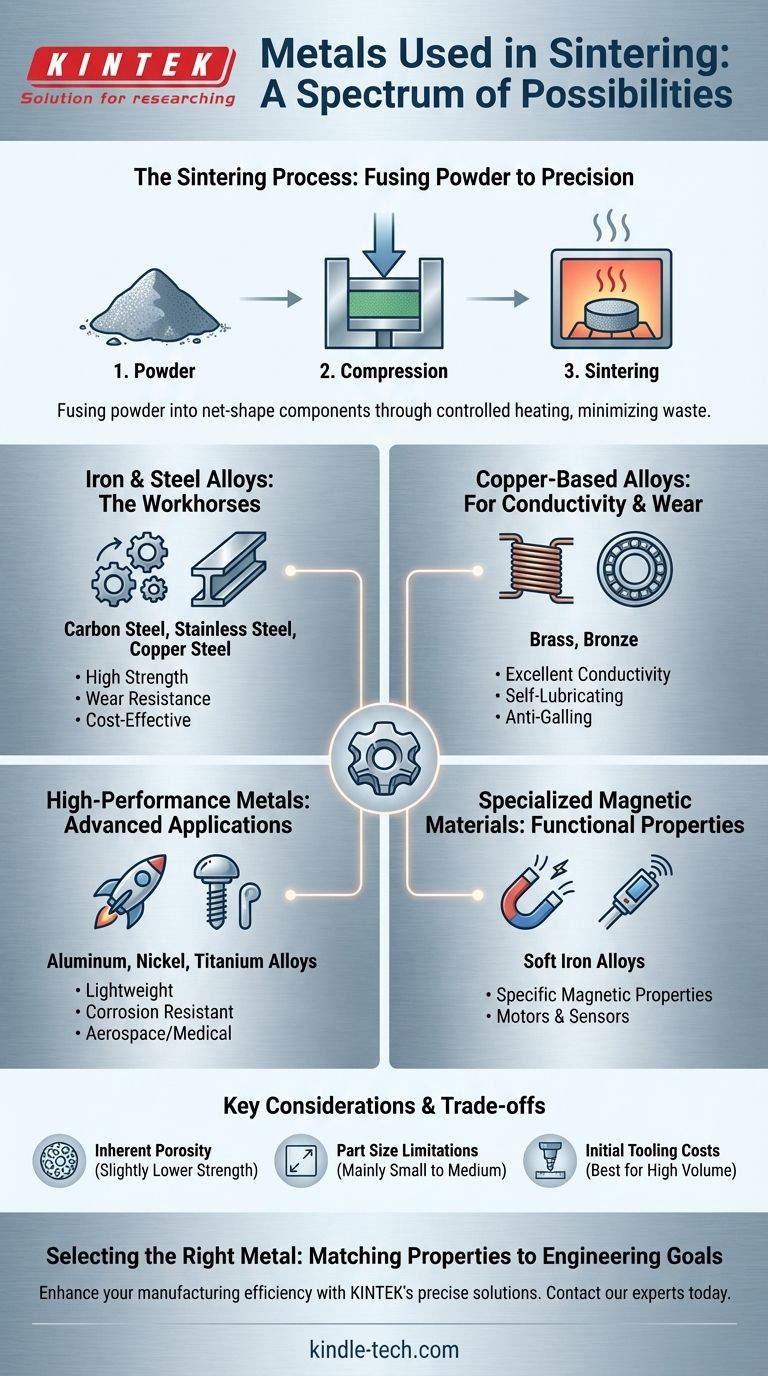
The range of metals used in sintering is exceptionally broad, extending far beyond a few niche materials. The most common metals include a wide variety of iron and steel alloys such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and copper-infused steels. Additionally, copper alloys like brass and bronze, as well as high-performance metals like aluminum, nickel, and titanium alloys, are frequently used.
Sintering's core value lies in its versatility. It is not a process limited to specific materials but a powerful manufacturing technique that can transform a wide array of powdered metals into complex, precise, and cost-effective components.

What is Sintering and Why Does It Matter?
To understand which metals are used, it's crucial to first understand the fundamental process. Sintering is about consolidation and fusion, not melting.
The Core Principle: Fusing Powder
The sintering process starts with a fine metal powder. This powder is compressed into a desired shape, often called a "green compact," and then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature just below its melting point.
At this high temperature, the individual metal particles bond and fuse, a process driven by atomic diffusion. This consolidates the loose powder into a solid, unified mass with low porosity.
The Key Advantage: Net-Shape Manufacturing
The primary benefit of sintering is its ability to produce parts at or very near their final dimensions, often referred to as net-shape manufacturing.
This precision minimizes or eliminates the need for secondary machining operations. The result is less material waste, reduced labor, and more consistent product quality, making it ideal for high-volume production of complex parts like gears, bearings, and pulleys.
The Spectrum of Sinterable Metals
The list of compatible metals is extensive and continues to grow with advances in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing. They can be grouped into several key families.
Iron and Steel Alloys: The Workhorses
This is the largest and most common category of sintered materials. The balance of strength, wear resistance, and low cost makes them the default choice for many mechanical and structural applications.
Common examples include:
- Iron and Carbon Steels
- Stainless Steels (both 300 and 400 series)
- Copper Steels (iron-copper blends)
- Nickel Steels
- High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels
Copper-Based Alloys: For Conductivity and Wear
Copper and its alloys are chosen for their unique combination of electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and natural lubricity, making them ideal for bearings and electrical components.
This group includes brass and bronze, which are valued for their excellent wear resistance and anti-galling properties.
High-Performance and Specialty Metals
For more demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries, sintering is used with advanced metals.
These materials include aluminum, nickel, and titanium alloys. Their use in sintering is critical for creating lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant components through methods like additive manufacturing.
Specialized Magnetic Materials
Sintering is also used to create components with specific magnetic properties. Soft iron magnetic alloys are processed this way to produce parts for use in electrical motors, sensors, and solenoids.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Challenge of Inherent Porosity
Sintered parts almost always retain a small amount of porosity compared to parts made from fully molten metal (casting) or solid billet (machining). This can impact the ultimate tensile strength and ductility of the final component.
Limitations on Part Size
The need to uniformly compress the initial powder places practical limits on the size of components that can be produced. Very large or bulky parts are typically not well-suited for traditional press-and-sinter processes.
Initial Tooling Costs
The dies used to compress the metal powder must be made from hardened tool steel and are precision-machined. This represents a significant upfront investment, making sintering most cost-effective for medium to high-volume production runs where the cost can be amortized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right metal is a matter of matching material properties to your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of structural parts: Iron and steel alloys offer the best combination of strength, durability, and economy.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance or performance in extreme environments: Stainless steel, nickel, or titanium alloys are the ideal candidates for your application.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity or self-lubricating bearing properties: Copper-based alloys like bronze and brass deliver superior performance for these specific needs.
By understanding the wide range of available materials, you can leverage sintering to create precise and economical components for nearly any engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Metal Family | Common Examples | Key Properties & Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Iron & Steel Alloys | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Copper Steel | Strength, wear resistance, cost-effective for structural parts |
| Copper-Based Alloys | Brass, Bronze | Excellent electrical/thermal conductivity, self-lubricating for bearings |
| High-Performance Metals | Aluminum, Nickel, Titanium Alloys | Lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance for aerospace/medical |
| Magnetic Materials | Soft Iron Alloys | Specific magnetic properties for motors and sensors |
Need the perfect sintered metal for your component?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced sintering processes. Whether you're working with common steel alloys or high-performance titanium, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to explore how our solutions can enhance your manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace with a H2-N2 atmosphere used for NiO pre-treatment? Key to Catalyst Activation
- What advantages does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace offer for UO2? Precision Fuel Densification
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes



















